Bridge – Brocade Mobility Access Point System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 5.5.0.0 and later) User Manual
Page 808
798
Brocade Mobility Access Point System Reference Guide
53-1003100-01
13
4. Select Route Entries.
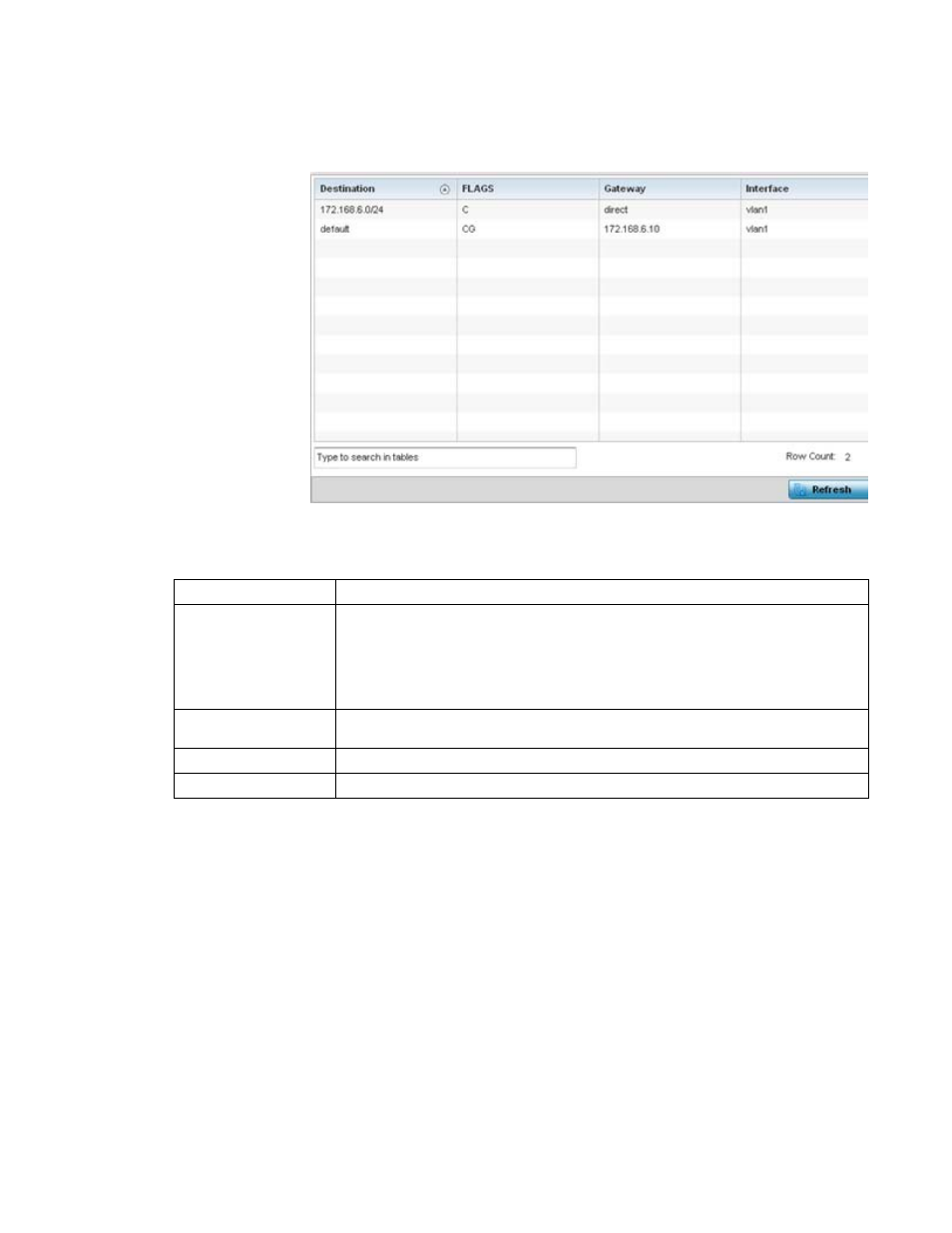
FIGURE 65
Access Point - Network Route Entries screen
The Route Entries screen supports the following:
Bridge
Bridging is a forwarding technique used in networks. Bridging makes no assumption about where a
particular address is located. It relies on the flooding and examination of source addresses in
received packet headers to locate unknown devices. Once a device is located, its location is stored
in a table to avoid broadcasting to that device again. Bridging is limited by its dependency on
flooding, and is used in local area networks only. A bridge and an access point are very much alike,
as an access point can be viewed as a bridge with a number of ports.
The Bridge screen provides details about the Integrate Gateway Server (IGS), which is a router
connected to an access point. The IGS performs the following:
•
Issues IP addresses
•
Throttles bandwidth
Destination
Displays the IP address of the destination route address.
FLAGS
The flag signifies the condition of the direct or indirect route. A direct route is where the
destination is directly connected to the forwarding host. With an indirect route, the destination
host is not directly connected to the forwarding host. Possible flags include U (route is up), H
(target is a host), G (use gateway), R (reinstate route for dynamic routing), D (dynamically
installed by daemon or redirect), M (modified from routing daemon or redirect), A (installed by
addrconf), C (cache entry) or! (reject route).
Gateway
Displays the IP address of the gateway used to route packets to the specified destination
subnet.
Interface
Displays the interface name of the destination subnet.
Refresh
Select the Refresh button to update the screen’s statistics counters to their latest values.
