Brocade Mobility Access Point System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 5.5.0.0 and later) User Manual
Page 122
112
Brocade Mobility Access Point System Reference Guide
53-1003100-01
5
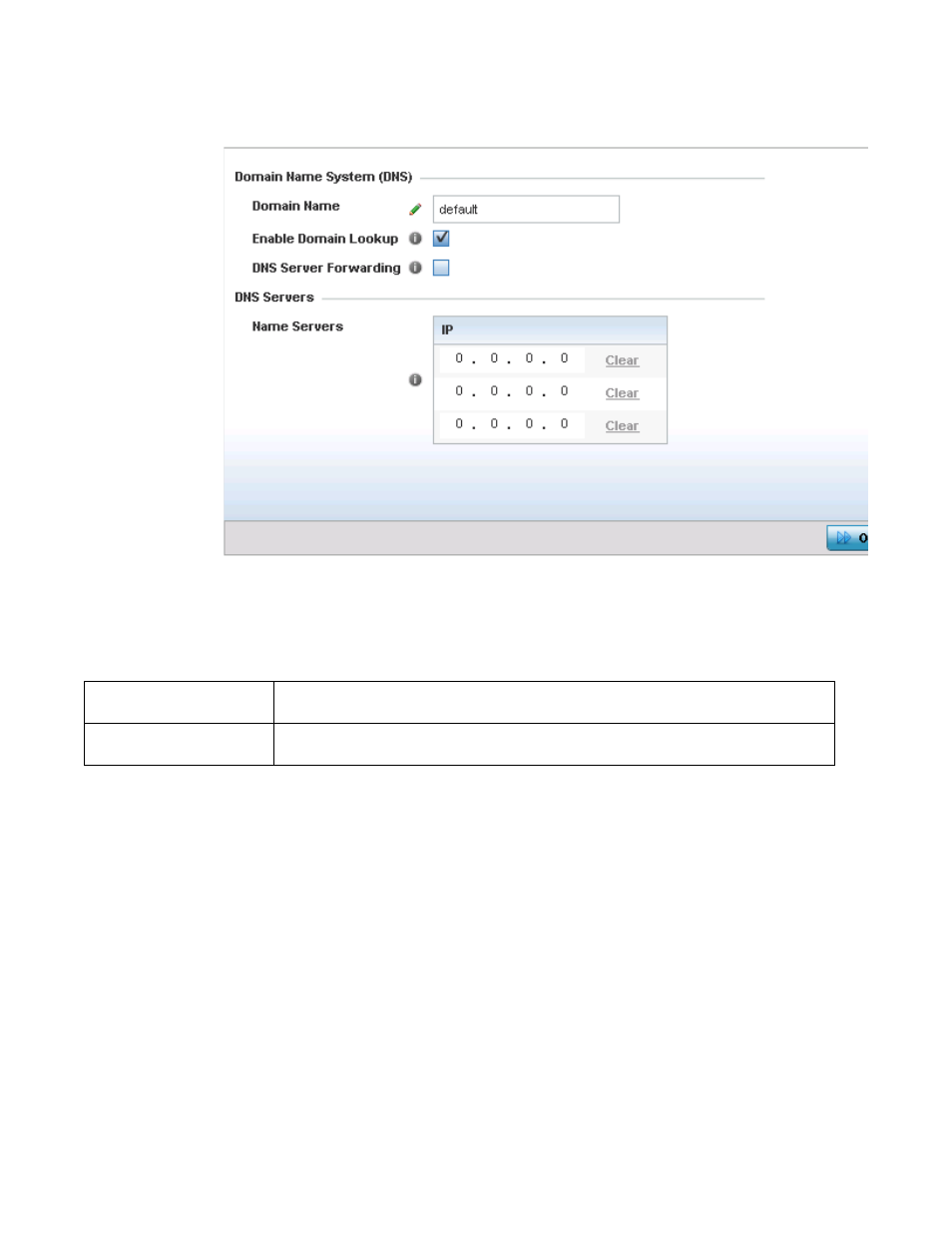
FIGURE 30
Network - DNS screen
5. Provide a default Domain Name used when resolving DNS names. The name cannot exceed
64 characters.
6. Set the following DNS configuration data:
7. In the Name Servers field, provide the IP addresses of up to three DNS server resources
available to the access point.
8. Select OK to save the changes made to the DNS configuration. Select Reset to revert to the
last saved configuration.
ARP
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an IP address to a hardware MAC
address recognized on the network. ARP provides protocol rules for making this correlation and
providing address conversion in both directions.
When an incoming packet destined for a host arrives, the gateway uses ARP to find a physical host
or MAC address that matches the IP address. ARP looks in its ARP cache and, if it finds the
address, provides it so the packet can be converted to the right packet length and format and sent
to the destination. If no entry is found for the IP address, ARP broadcasts a request packet in a
Enable Domain Lookup
Select this option to enable DNS. When enabled, human friendly domain names can be converted
into numerical IP destination addresses. This feature is enabled by default.
DNS Server Forwarding
Select to enable the forwarding DNS queries to external DNS servers if a DNS query cannot be
processed by the access point’s own DNS resources. This feature is disabled by default.
