Brocade Mobility Access Point System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 5.5.0.0 and later) User Manual
Page 360
350
Brocade Mobility Access Point System Reference Guide
53-1003100-01
5
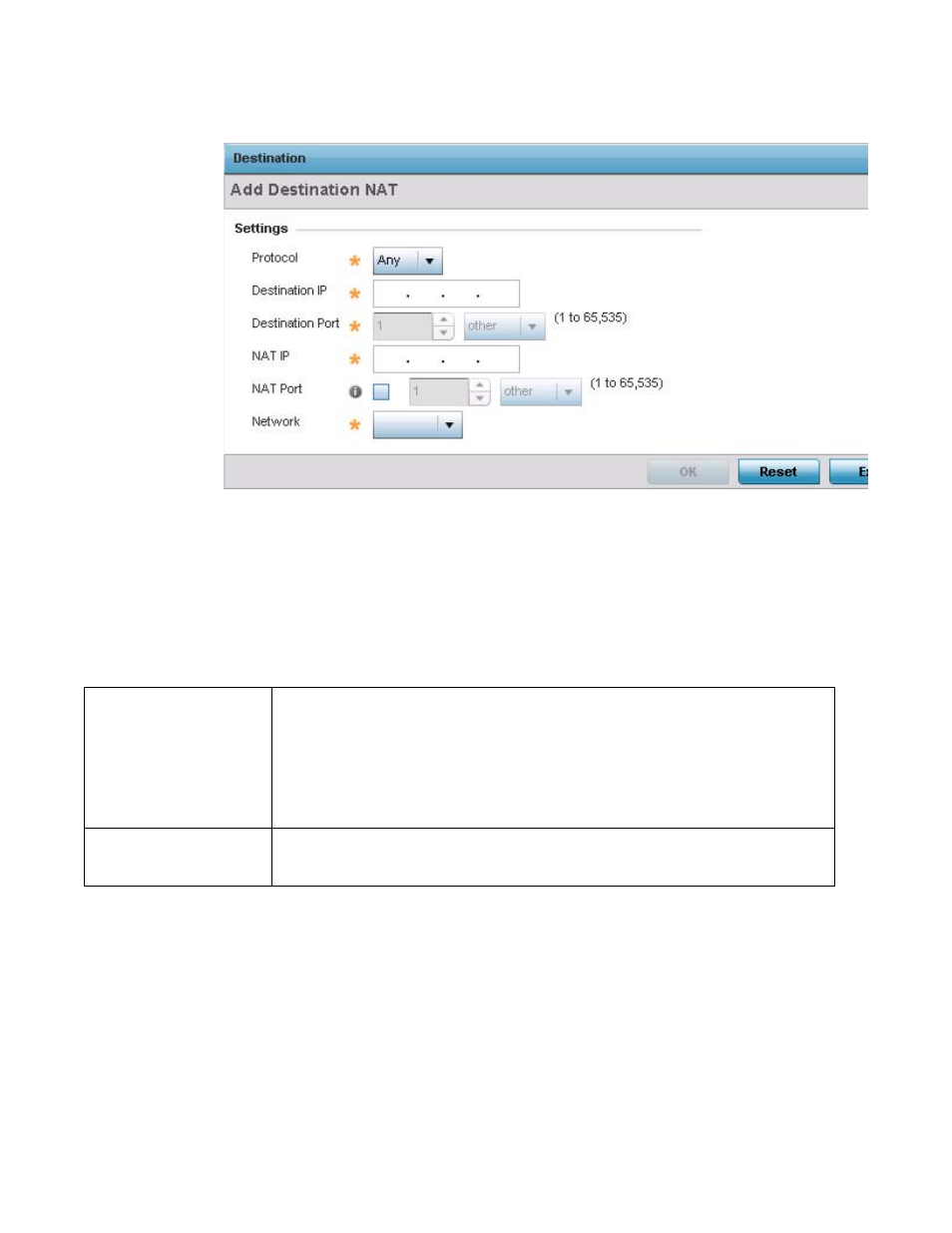
FIGURE 190
Device Overrides - Add Destination NAT screen
Set or override the following Destination configuration parameters:
Static NAT creates a permanent, one-to-one mapping between an address on an internal network
and a perimeter or external network. To share a Web server on a perimeter interface with the
Internet, use static address translation to map the actual address to a registered IP address. Static
address translation hides the actual address of the server from users on insecure interfaces.
Casual access by unauthorized users becomes much more difficult. Static NAT requires a
dedicated address on the outside network for each host.
Protocol
Select the protocol for use with static translation. TCP, UDP and Any are available options. TCP is a
transport layer protocol used by applications requiring guaranteed delivery. It’s a sliding window
protocol handling both timeouts and retransmissions. TCP establishes a full duplex virtual
connection between two endpoints. Each endpoint is defined by an IP address and a TCP port
number. The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) offers only a minimal transport service, non-guaranteed
datagram delivery, and provides applications direct access to the datagram service of the IP layer.
UDP is used by applications not requiring the level of service of TCP or are using communications
services (multicast or broadcast delivery) not available from TCP. The default setting is Any.
Destination IP
Enter the local address used at the (source) end of the static NAT configuration. This address (once
translated) will not be exposed to the outside world when the translation address is used to interact
with the remote destination.
