2 index register [e], [f, 2 functions of devices in dvp-plc – Delta Electronics Programmable Logic Controller DVP-PLC User Manual
Page 57
2 Functions of Devices in DVP-PLC
DVP-PLC Application Manual
2-29
2. Latched register: When the power of PLC is switched off, the data in the register will not be cleared but will retain
at the value before the power is off. You can use RST or ZRST instruction to clear the data in the latched register.
3. Special purpose register: Every register of this kind has its special definition and purpose, mainly for storing the
system status, error messages and monitored status. See 2.10 and 2.11 for more details.
4. Index register E, F: The index register is a 16-bit register. There are 2 points of E, F in ES/EX/SS series MPU; 8
points (E0 ~ E3, F0 ~ F3) in SA/SX/SC series MPU; 16 points (E0 ~ E7, F0 ~ F7) in EH/EH2/SV series MPU. If the
index register is to be used as a 32-bit register, please designate E. When E is already designated in a 32-bit
instruction, using also F will not be allowed.
5. File register: There are 1,600 file registers (K0 ~ K1,599) in SA/SX/SC series MPU and 10,000 file registers (K0
~ K9,999) in EH/EH2/SV series MPU. The file register does not have an exact device No.; therefore the read/write
function of file registers has to be executed by instruction API 148 MEMR, API 149 MEMW or through peripheral
devices HPP and WPLSoft.
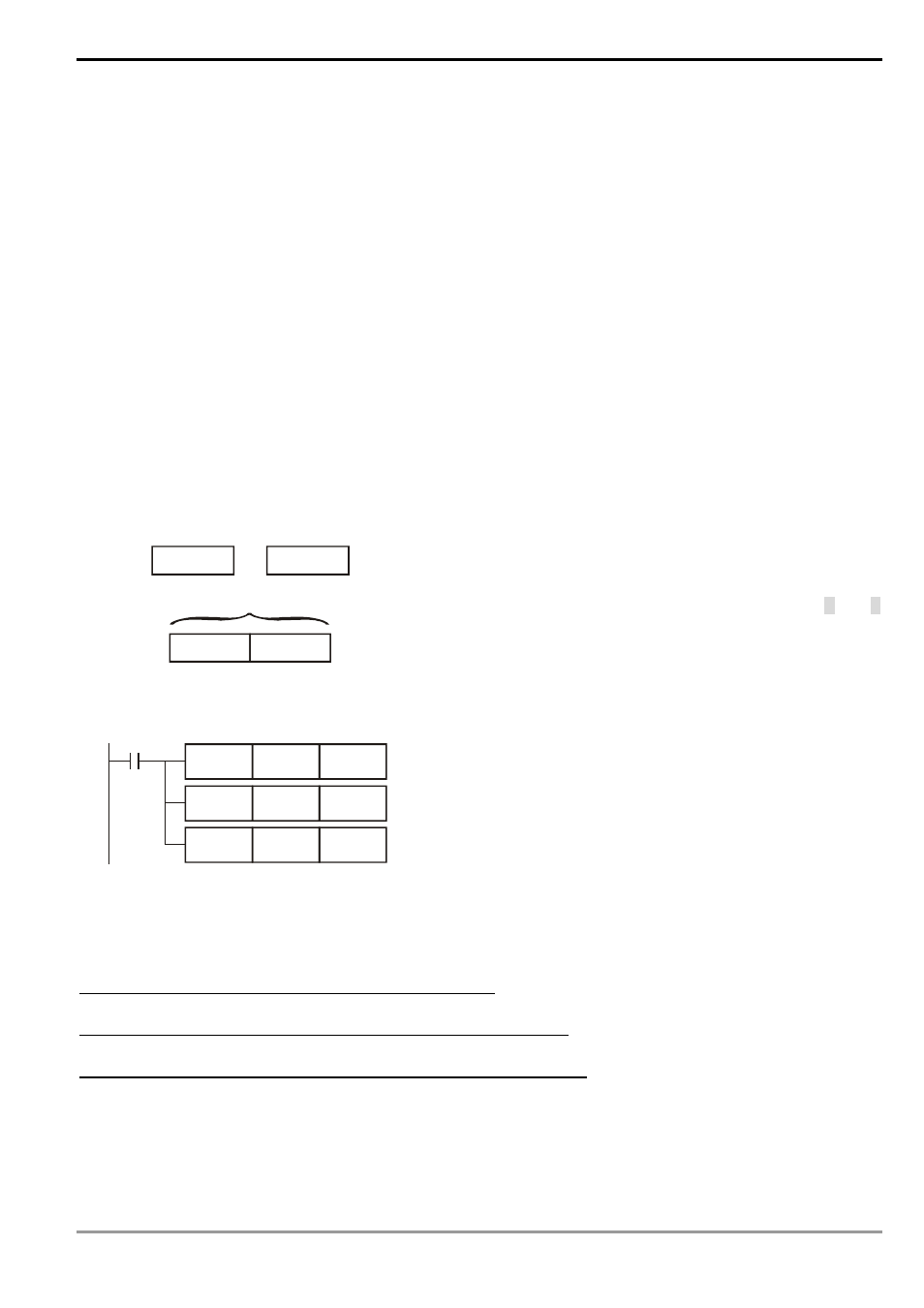
2.8.2 Index Register [E], [F]
F0
E0
E0
F0
16 bits
16 bits
32 bits
Higher 16 bits Lower 16 bits
Index registers E, F are 16-bit data registers and can be written and
read.
If you need to use a 32-bit register, you have to designate E. In this
case, F will be covered by E and cannot be used anymore; otherwise,
the content in E (32-bit) will be incorrect. We suggest you use DMOVP
K0 E instruction, the content in E (including F) will be cleared to “0”
when the power of PLC is switched on.
The combination of E, F when you use a 32-bit index register:
(F0, E0), (F1, E1), (F2, E2), …(F7, E7)
K14
F0
X0
K8
E0
MOV
D5E0
D10F0
MOV
MOV
When X0 = On, E0 = 8, F0 = 14, D5E0 = D (5 + 8) = D13, D10F0 = D
(10 + 14) = D24. At this moment, the content in D13 will be moved to
D24.
The index register is the same as normal operands, can be used for moving or comparison on word devicies (KnX,
KnY, KnM, KnS, T, C, D) and bit devices (X, Y, M, S). ES/SA series MPU does not support constant (K, H) index
register, but EH/EH2/SV series MPU supports constant (K, H) index register.
ES/EX/SS series MPU has 2 points of index registers E0, F0
SA/SX/SC series MPU has 8 points of index registers E0 ~ E3, F0 ~ F3
EH/EH2/SV series MPU has 16 points of index registers E0 ~ E7, F0 ~ F7
Some instructions do not support index registers. For how to use index register E, F to modify the operands, see
Chapter 5.4 for more details.
When you use the instruction mode in WPLSoft to generate constant (K, H) index register function, please use
symbol “@”. For example, “MOV K10@E0 D0F0”
