2 control modes, 1 overview of control modes, 2 speed control mode – Yaskawa MP940 User Manual
Page 409
11.2 Control Modes
11-7
11
11.2 Control Modes
This section describes the motion control modes that can be used by the MP940.
11.2.1 Overview of Control Modes
Five control modes are available for MP940 Motion Modules. These modes can be switched
in real time, according to the purpose.
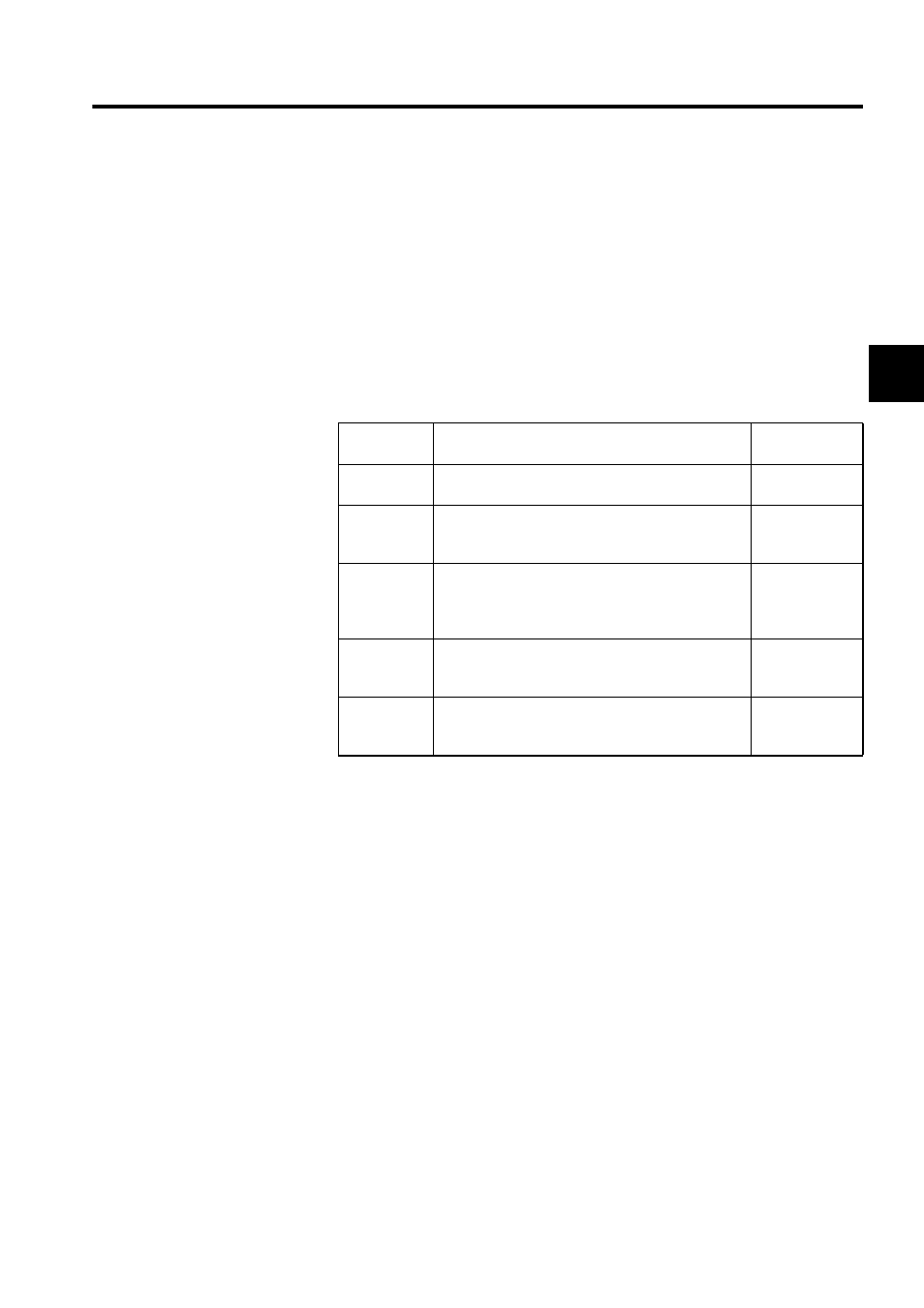
The following table shows the control mode that can be used by MP940 Motion Modules,
and gives an overview and some examples of their uses.
∗
There are two methods for returning to the zero point:
• Using ZERO POINT RETURN command for position control
• Using Zero Point Return Mode
11.2.2 Speed Control Mode
Overview
This mode is used to rotate the motor at the desired speed.
A speed reference is output to the servodrive according to the specified speed reference, lin-
ear acceleration/deceleration time constant, and filter time constant.
The acceleration/deceleration time can be set as desired.
S-curve acceleration/deceleration can be easily performed by the user program (one com-
mand).
The Speed Control Mode can also be used for a general-purpose D/A converter. In this case,
set the linear acceleration/deceleration time constant and the filter time constant to “0.”
Control Mode
Overview
Typical
Applications
Speed
Control Mode
Rotates the motor at the specified speed.
Conveyors or
main axes
Torque
Control Mode
Outputs the specified torque.
Injection mold-
ing machines or
presses
Position
Control
Mode*
Specifies the target position and speed. Executes a
position loop, identifies the difference to the target
position from the encoder, converts the difference to
the speed reference, and performs position control.
Conveyors or XY
tables
Phase
Control Mode
While executing speed control using a standard speed
reference, generates the target position from the speed
reference, and performs phase control.
Electronic cams
or electronic
shafts
Zero Point
Return
Mode*
Performs zero point positioning when an incremental
encoder is used.
