Renesas SH7641 User Manual
Page 487
Section 13 Direct Memory Access Controller (DMAC)
Rev. 4.00 Sep. 14, 2005 Page 437 of 982
REJ09B0023-0400
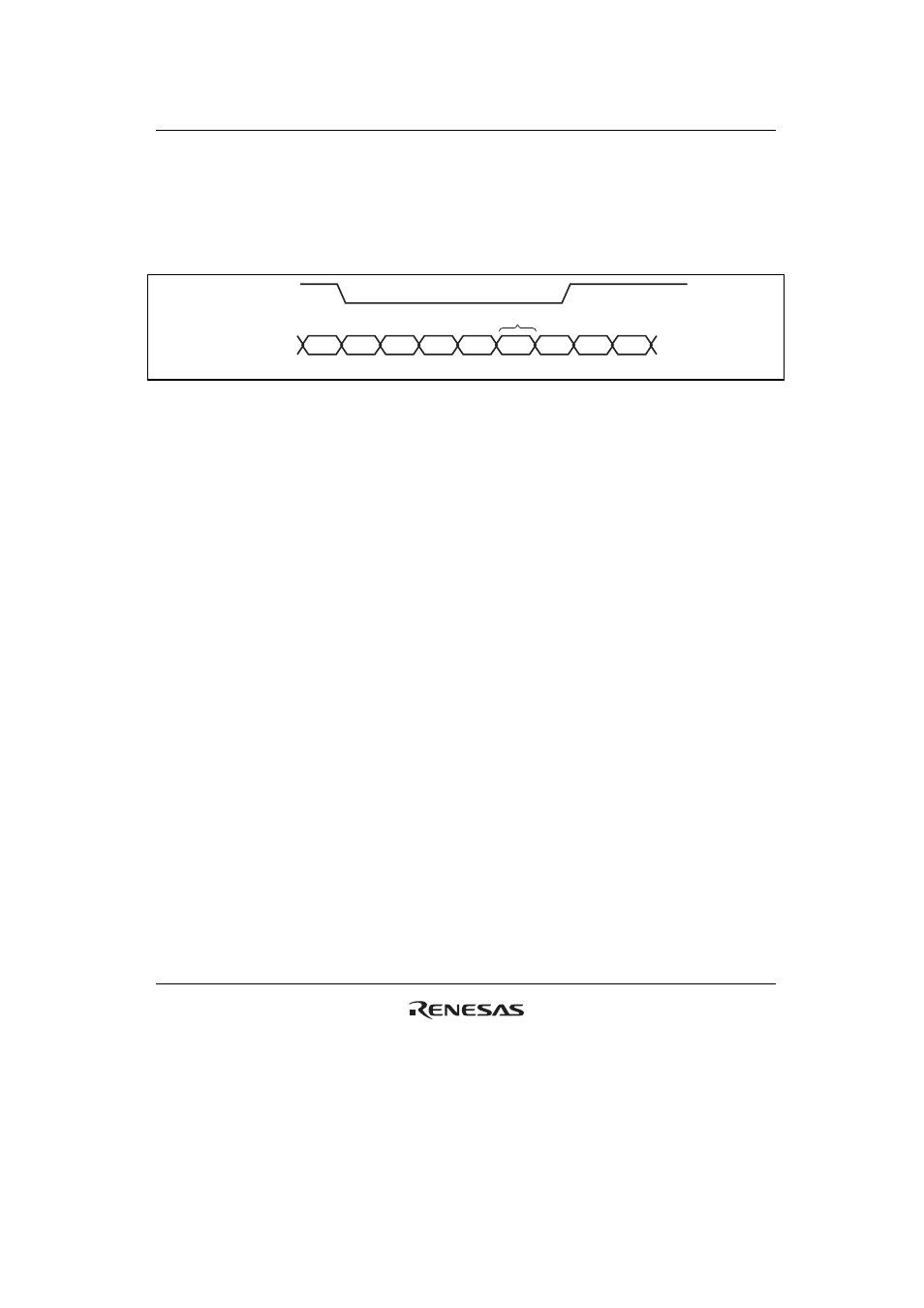
Figure 13.9 shows an example of DMA transfer timing in the cycle steal mode. Transfer
conditions shown in the figure are:
1. Dual address mode
2.
DREQ low level detection
CPU
CPU
CPU
DMAC DMAC
CPU
DMAC DMAC
CPU
DREQ
Bus cycle
Bus mastership returned to CPU once
Read/Write
Read/Write
Figure 13.9 DMA Transfer Example in the Cycle-Steal Normal Mode
(Dual Address,
DREQ Low Level Detection)
• Intermittent Mode 16 and Intermittent Mode 64
In the intermittent mode of cycle steal, DMAC returns the bus mastership to other bus master
whenever a unit of transfer (byte, word, longword, or 16 bytes) is complete. If the next transfer
request occurs after that, DMAC gets the bus mastership from other bus master after waiting
for 16 or 64 clocks in B
φ count. DMAC then transfers data of one unit and returns the bus
mastership to other bus master. These operations are repeated until the transfer end condition is
satisfied. It is thus possible to make lower the ratio of bus occupation by DMA transfer than
the normal mode of cycle steal.
When DMAC gets again the bus mastership, DMA transfer can be postponed in case of entry
updating due to cache miss.
This intermittent mode can be used for all transfer section; transfer requester, source, and
destination. The bus modes, however, must be cycle steal mode in all channels.
Figure 13.10 shows an example of DMA transfer timing in cycle steal intermittent mode. Transfer
conditions shown in the figure are:
1. Dual address mode
2.
DREQ low level detection
