Feedback 1 or feedback 2 noise fault, Ground short fault, Drive hardware fault – Rockwell Automation 1784-PM16SE SoftLogix Motion Card Setup and Configuration Manual User Manual
Page 371: Overspeed fault, Overload fault
Publication 1784-UM003A-EN-P – June 2003
Motion Object Attributes 363
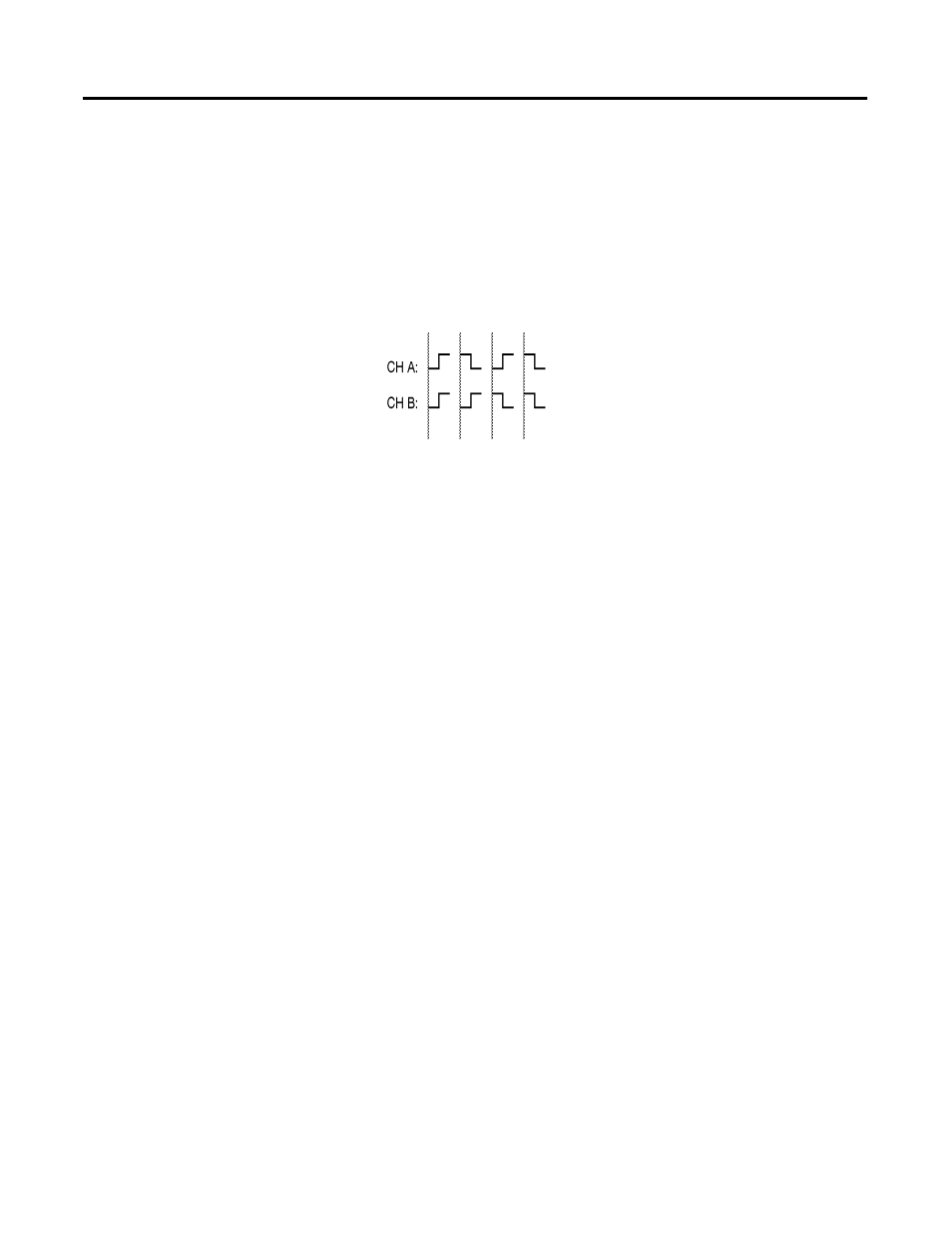
Feedback 1 or Feedback 2 Noise Fault
If the Feedback Noise Fault bit attribute is set for a specific feedback source, it
indicates that simultaneous transitions of the feedback A and B channels has
been detected by the servo module which is referred to generally as feedback
noise. When the feedback device is an encoder, feedback noise (shown below)
is most often caused by loss of quadrature in the feedback device itself or
radiated common-mode noise signals being picked up by the feedback device
wiring, both of which may be able to be seen on an oscilloscope.
Figure 13.17 Channel Quadrature
For example, loss of channel quadrature for an encoder can be caused by
physical misalignment of the feedback transducer components, or excessive
capacitance (or other delays) on the encoder signals. Proper grounding and
shielding techniques can usually cure radiated noise problems. This fault
condition is latched and requires execution of an explicit MAFR (Motion Axis
Fault Reset) or MASR (Motion Axis Shutdown Reset) instruction to clear.
Ground Short Fault
When the drive detects a imbalance in the D.C bus supply current, the Ground
Short Fault bit is set, indicating that current is flowing through an improper
ground connection.
Drive Hardware Fault
The Drive Hardware Fault bit is set when the drive detects a serious hardware
fault.
Overspeed Fault
The Overspeed Fault bit is set when the speed of the axis as determined from
the feedback has exceeded the overspeed limit which is typically set to 150% of
configured velocity limit for the motor.
Overload Fault
When the load limit of the motor/drive is first exceeded, the Overload
warning bit is set. If, however, the condition persists, the Overload fault is set.
Often this bit is tied into the IT limit of the drive.
