Media files and clips, 22 media files and clips – Apple Final Cut Pro X (10.1.2) User Manual
Page 22
Chapter 2
Final Cut Pro basics
22
A Final Cut Pro project holds all of the information for your final movie, including your editing
decisions and links to all the source clips and events. For more information about editing your
project, see
on page 99 and
on page 117.
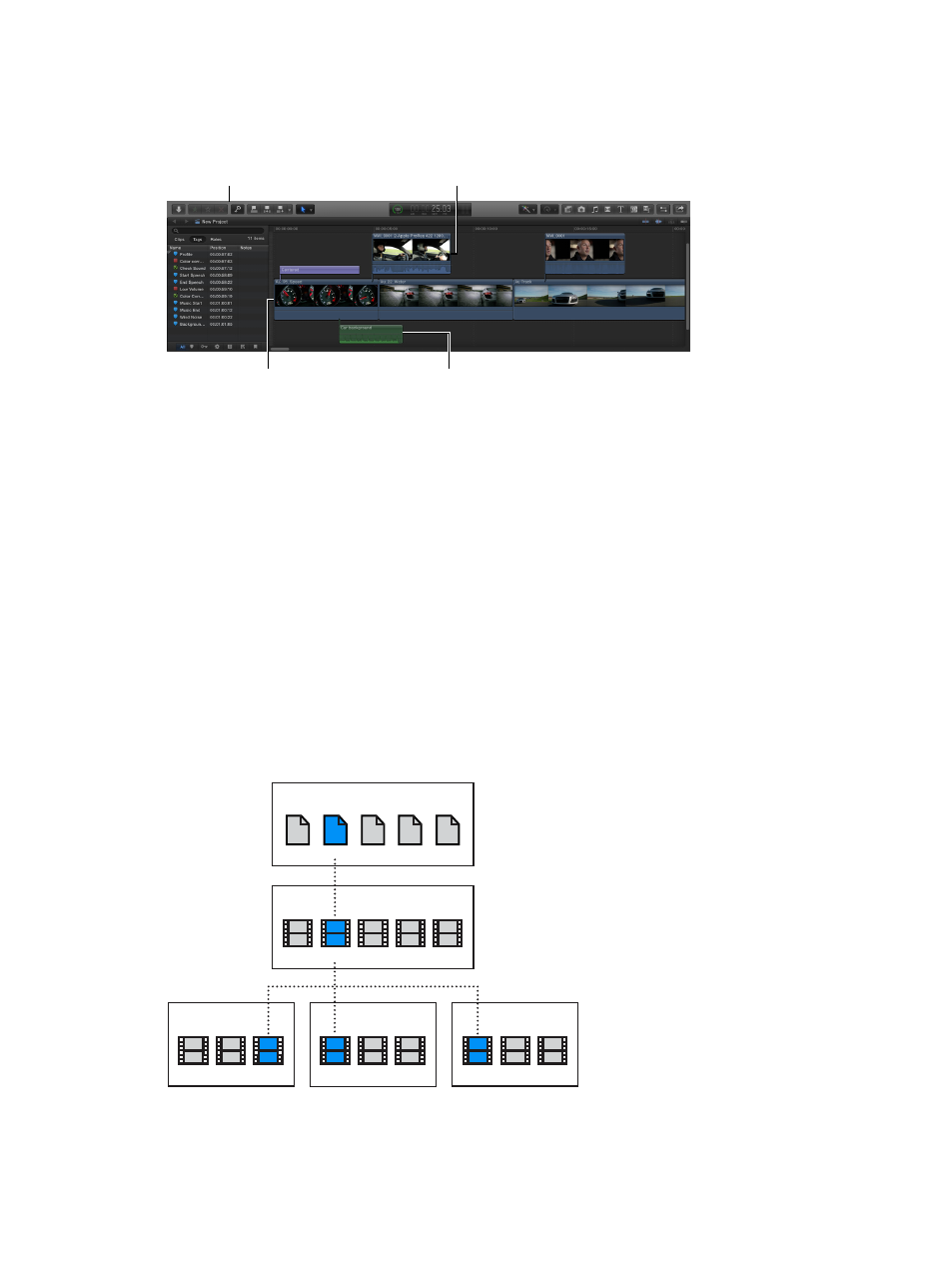
Toolbar:
Perform
common tasks by
clicking a button.
Connected clips:
Add titles and
cutaway shots. In the Magnetic
Timeline, everything stays in sync.
Audio clips:
Add music
and sound effects as
connected clips.
Primary storyline:
Add and
arrange clips to construct
your movie.
Media files and clips
After you import media into your Final Cut Pro library, clips representing the source media files
appear in the Browser. A large event may hold many clips.
Media files are the raw materials you use to create your project. A media file is a video, audio,
still-image, or graphics file on your hard disk that contains footage transferred from a camcorder
or recording device or originally created on your computer. Media files can contain multiple
video and audio components. Because media files—especially video files—tend to be quite
large, projects that use a lot of footage require one or more high-capacity hard disks.
Clips represent your media, but they are not the media files themselves. The clips in a project
simply point to (link to) the source media files on your hard disk. When you modify a clip, you
are not modifying the media file, just the clip’s information in the project. This is known as
nondestructive editing, because all of the changes and effects you apply to clips in Final Cut Pro
never affect the media itself. Trimmed or deleted pieces of clips are removed from your project
only, not from the source clips in your library or from the source media files on your hard disk.
Project 2
Toy1
Browser clips
Media files on your hard disk
Project 3
Project 1
Toy1.mov
Toy1
Toy1
Toy1
67% resize factor
