Audio editing basics, About audio waveforms, 157 audio editing basics 157 – Apple Final Cut Pro X (10.1.2) User Manual
Page 157
Chapter 8
Edit audio
157
You use the same tools used for video editing when you edit audio clips in Final Cut Pro. The
following editing features are covered elsewhere in Final Cut Pro Help:
•
Change edit mode: Set the edit mode for a clip to video only or audio only. See
on page 114.
•
Add markers to clips: Add markers to mark specific reference points within an audio clip. See
on page 148.
•
Trim audio: Make precision edits to the audio waveform—for example, to take out an
unwanted sound in the recording. See
on page 122.
•
Add audio crossfades: Create a smooth transition when connecting two separate audio
waveforms. See
Add transitions to your project
on page 214.
•
Use compound clips: Compound clips let you combine any video or audio clips into a single
compound clip. From an audio standpoint, compound clips let you apply the same audio
effect or enhancement to a group of clips, similar to applying an effect or adjustment to the
overall mix. See
on page 269.
•
Export audio: You can export your project as an audio file in either mono, stereo, or surround
sound. You can also export media by role. See
on page 399.
Audio editing basics
About audio waveforms
Audio waveforms are visual representations of the actual sound. Audio waveforms appear in clips
in the following ways:
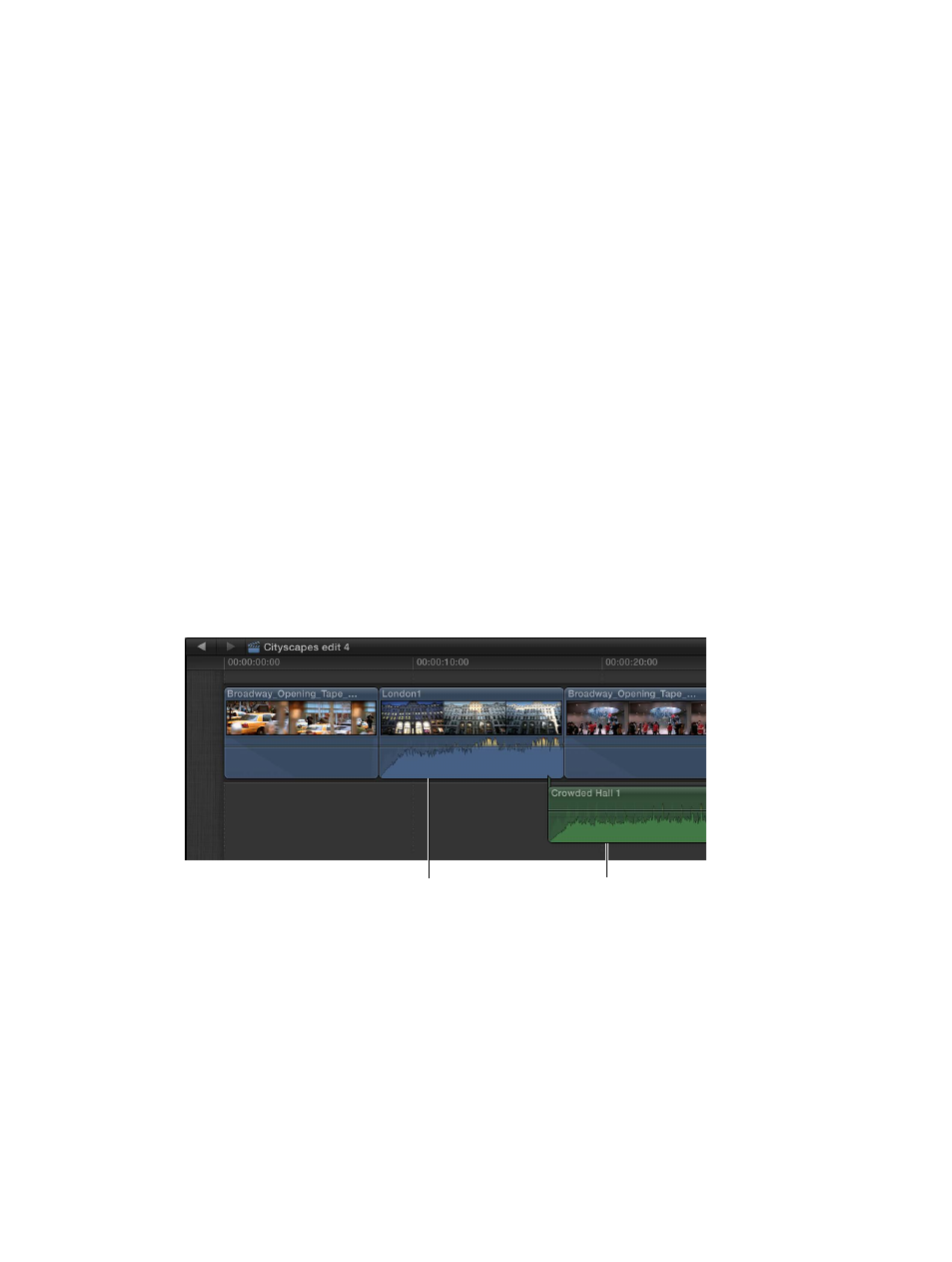
•
As the bottom portion of a video clip, colored blue
•
As a detached or an audio-only clip, colored green
Audio-only clip
Audio portion of a video clip
An audio waveform’s amplitude and length change according to the underlying sound’s volume
and duration. A short, loud sound such as a drum beat has a sharp, peaked waveform, whereas
low-level crowd noise has a lower, more uniform waveform. These properties make it easier to
find specific edit points when trimming clips or keyframing effects.
In Final Cut Pro, audio waveforms change according to a clip’s volume level or applied effects.
The waveform appears larger when the volume is high and smaller when the volume is low.
You edit audio clips in the Timeline by first listening to a clip’s audio through playback and
skimming, and then applying changes to the clip, using the waveform as a reference.
67% resize factor
