Adding data loading and validation, Using error handling and debugging – Adobe Flash Professional CC 2014 v.13.0 User Manual
Page 865
You must typically process information before you send it to the server, so it’s formatted in a way that the server understands. When the server
receives the data, it can be manipulated in any number of ways and sent back to the SWF file in a format that it can accept, which can range from
name-value pairs to complex objects.
Note: Your application server must have the MIME type of its output set to application/x-www-urlform-encoded. If that MIME type is missing, the
result is usually unusable when it reaches Flash Professional.
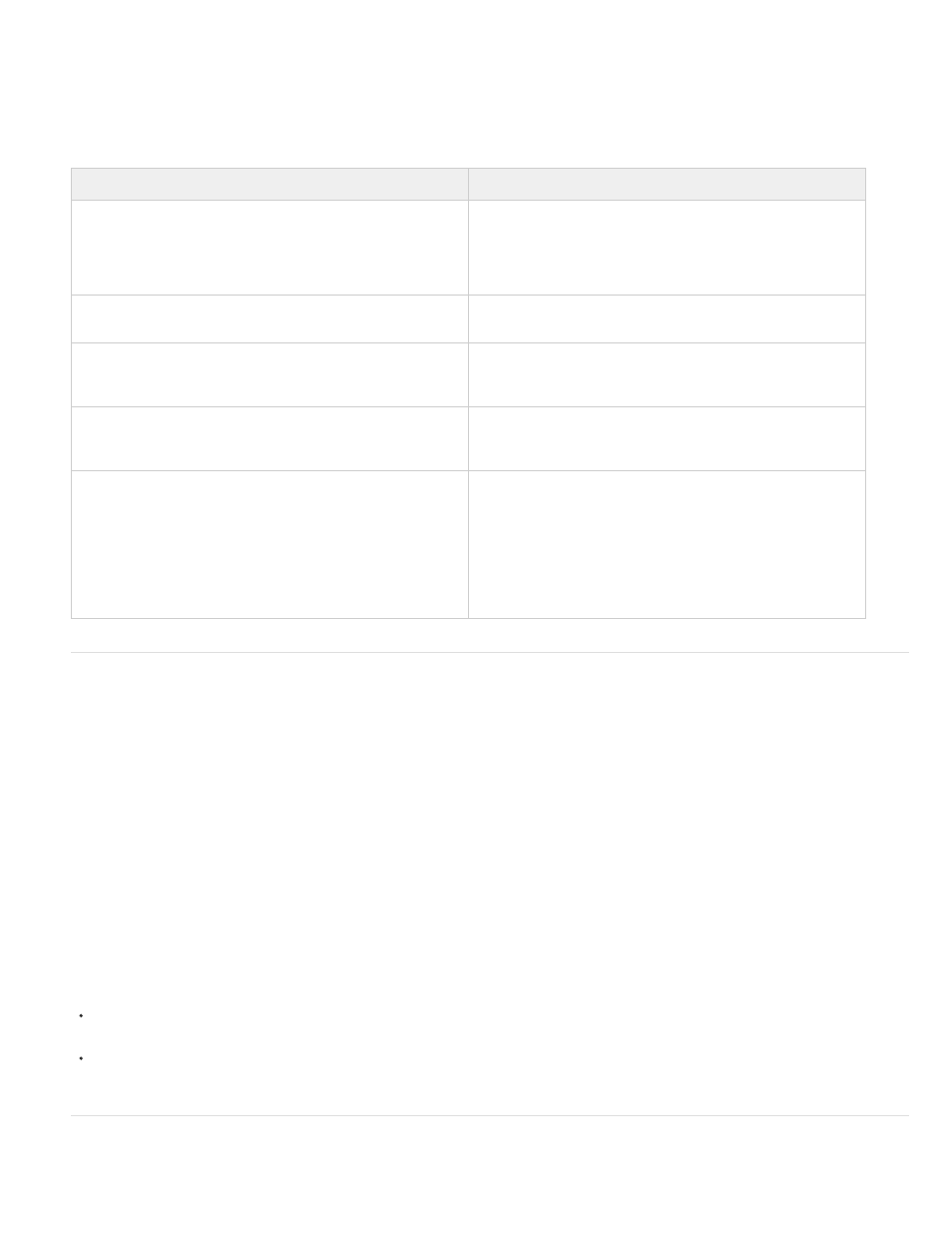
The following table shows you several options for sending data to a server and receiving data using Flash Professional:
Send data
Description
LoadVars.send and LoadVars.sendAndLoad
Sends name-value pairs to a server-side script for processing.
LoadVars.send sends variables to a remote script and ignores
any response. LoadVar.sendAndLoad sends name-value pairs to
a server and loads or parses the response into a target LoadVars
object.
XML.send and XML.sendAndLoad
Similar to LoadVars, but XML.send and XML.sendAndLoad send
XML packets instead of name-value pairs.
getURL
Using the getURL() function or MovieClip.getURL method, you
can send variables from Flash Professional to a frame or pop-up
window.
Flash Remoting
Lets you easily exchange complex information between Flash
Professional and ColdFusion, ASP.NET, Java, and more. You
can also use Flash Remoting to consume web services.
Web services
Adobe® Flash® Professional includes the WebServiceConnector
component that lets you connect to remote web services, send
and receive data, and bind results to components. This lets Flash
Professional developers quickly create Rich Internet Applications
without having to write a single line of ActionScript.
You can consume remote web services by using
WebServiceClasses, which can require writing complex
ActionScript.
Adding data loading and validation
Validate any information you retrieve before you send that data to a server. This reduces strain on the remote server, because it does not handle
as many requests when users do not fill in required fields. Never rely solely on client-side validation in any application; server-side validation must
also occur.
Even if you build a simple registration or login form, check that the user has entered their name and password. Perform this validation before
sending the request to the remote server-side script and waiting for a result. Do not rely only on server-side validation. If a user enters only a
username, the server-side script must receive the request, validate the data being sent, and return an error message to the Flash Professional
application, stating that it requires both the username and password. Likewise, if validation is performed only on the client side (within the SWF
file), a user might hack the SWF file, bypass the validation, and send data to your server in an attempt to post the bad data.
Client-side validation can be as simple as making sure that a form field is at least one character long, or that the user entered a numeric value and
not a string. To validate an e-mail address, for example, check that the text field in Flash Professional isn’t empty and contains at least the at sign
(@) and dot (.) characters. For the server-side validation, add more complex validation and check that the e-mail address belongs to a valid
domain.
You must write ActionScript to handle the data that loads into the SWF file from the server. After you finish loading data into a SWF file, the data
can be accessed from that location. Use ActionScript to check whether the data is fully loaded. You can use callback functions or listeners to send
a signal that the data is loaded into the document.
When you load data, it can be formatted in several ways:
You might load XML, in which case you use the XML class methods and properties to parse the data and use it. If you use name-value pairs,
the pairs turn into variables and you can manipulate them as variables.
You might receive data from a web service or from Flash Remoting.
In both cases, you could receive complex data structures, such as arrays, objects, or record sets, which you must parse and bind appropriately.
Using error handling and debugging
Your application needs to be robust enough to anticipate certain errors and handle them accordingly.
858
