Modbus tcp kommunikation – Lenze I/O system 1000 System Manual User Manual
Page 714
Modbus TCP Kommunikation
About Modbus TCP
l
714
EDSIO1000 EN 7.0
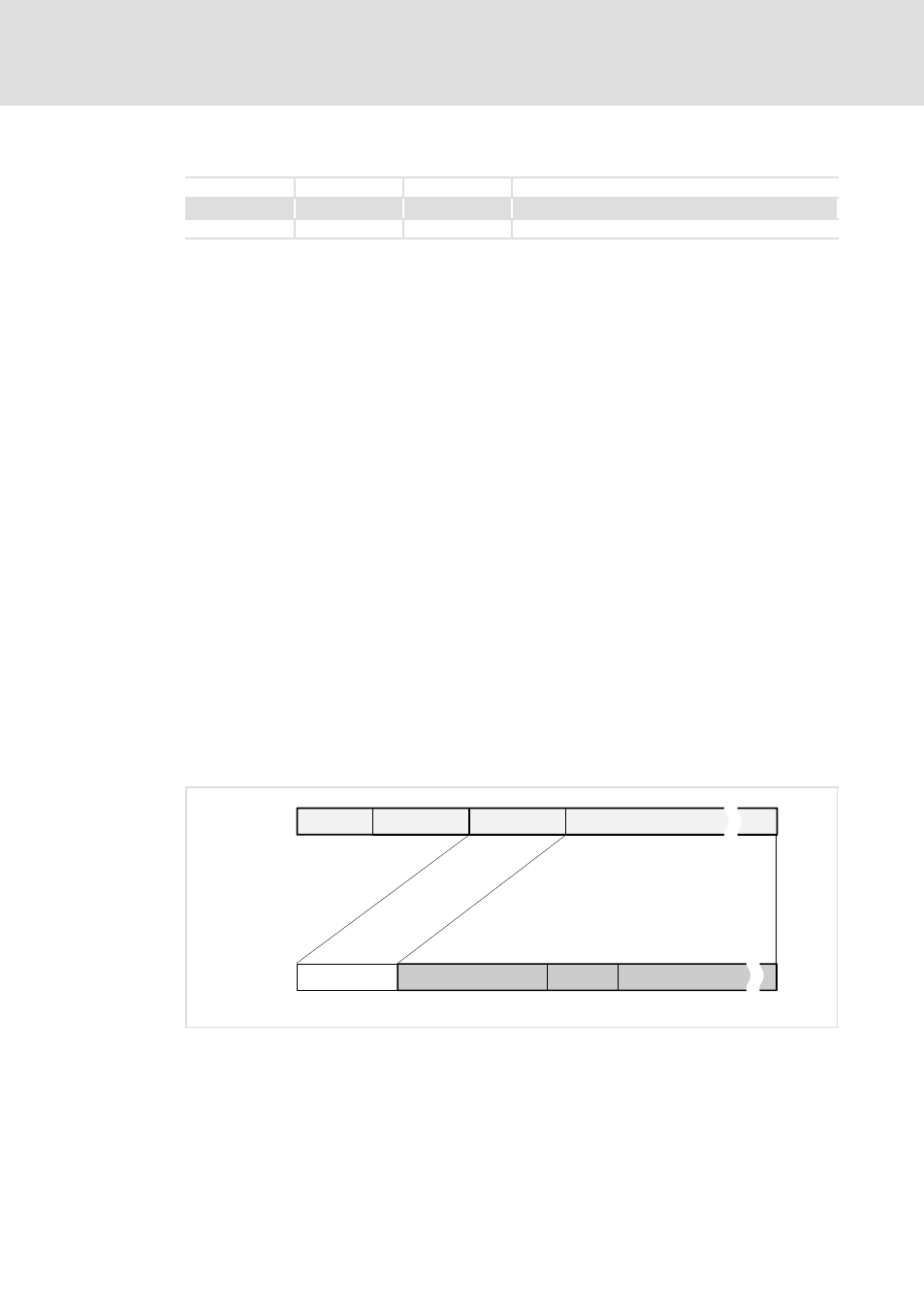
Telegram structure
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Layer 7
MAC/DLL
IP
TCP
API
...
14 bytes
20 bytes
20 bytes
Length depends on protocol
MAC/DLL: While the Ethernet physics with its standardised signal levels covers layer 1,
MAC/DLL complies with the specifications for the data link layer (layer 2). With MAC
(Medium Access Control) / DLL (Data Link Layer), communication takes place on the lowest
Ethernet level using MAC addresses. Every Ethernet−capable station has a non−ambiguous
MAC address that may only exist once. When MAC addresses are used, source and target
are clearly specified.
IP: The internet protocol covers the network layer (layer 3) of the SO/OSI layer model. The
task of the IP is to send data packets from one computer to the receiver via several
computers. These data packets are datagrams. The IP neither ensures the correct order of
datagrams nor the delivery at the receiver. For a clear distinction between sender and
receiver, 32−bit addresses (IP addresses) are used that usually are written in four octets
(exactly 8 bits), e.g. 172.16.192.11. In an octet, figures between 0 and 255 can be displayed.
A part of the address specifies the network, the rest serves to identify the computer in the
network. The transition between network part and host part is smooth and depends on the
network size.
TCP: The TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is directly based on the IP and thus covers the
transport layer (layer 4) on the OSI layer model. TCP is a connection−oriented end−to−end
protocol and serves as a logical connection between two partners. TCP ensures a logical
and reliable data transfer. Each datagram is provided with a header of min. 20 bytes which,
among other things, contains a sequence number for the correct order. Thus, the single
datagrams in a network are able to reach the target in various ways.
API: API stands for Application Programming Interface. API fulfills the requirements for the
application layer (layer 7). Here, header and user data of the corresponding protocols are
stored. In the Modbus TCP bus coupler, the Modbus TCP protocol is used which will be
explained in detail in the following section.
MAC/DLL
IP
TCP
API
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Layer 7
14 Byte
20 Byte
20 Byte
Depending of length
...
Port 502
Modbus TCP header Modbus User data
6 Byte
...
max. 254 Byte
Modbus TCP
SLIO068
Fig. 13−1
API structure
