Profinet communication, And diagnostic alarm, Example – Lenze I/O system 1000 System Manual User Manual
Page 666
PROFINET communication
Parameterising the counter
One counter 32 bits, 24 V DC − EPM−S600
l
666
EDSIO1000 EN 7.0
Diagnostic alarm
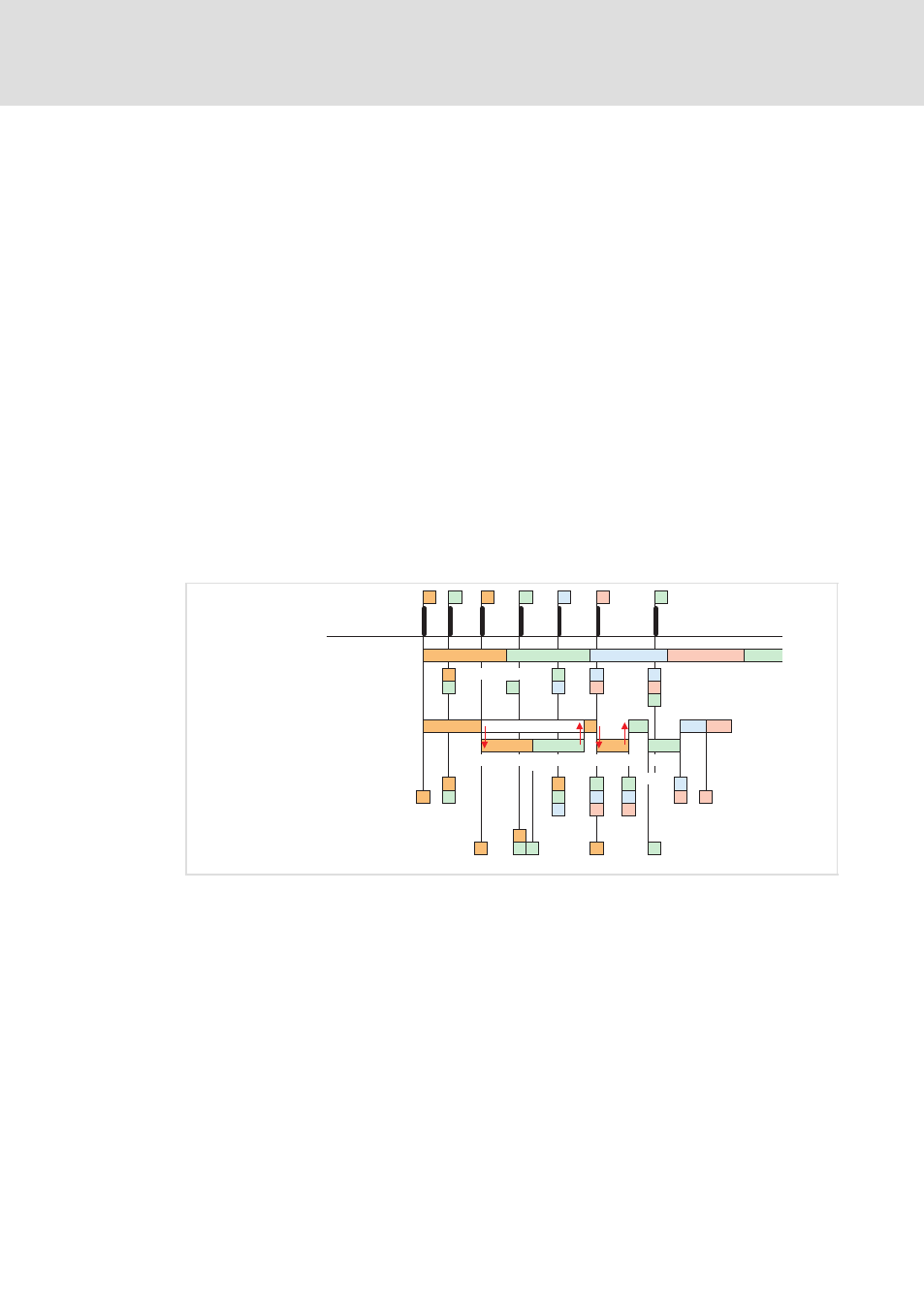
You have the possibility of globally activating a diagnostic alarm for the module via
parameterisation (data set 00h). A diagnostic alarm occurs if a further process alarm is
triggered for the same event during a process alarm processing in the OB 40.
By activation of a diagnostic alarm the current process alarm processing in the OB 40 is
interrupted and branched to the diagnostic alarm processing
incoming
in OB 82. If further
events occur on other channels during the diagnostic alarm processing, which can trigger
a process or diagnostic alarm, they are buffered. At the end of the diagnostic alarm
processing, first all buffered diagnostic alarms are processed in order of their occurrence,
and afterwards all process alarms.
If further process alarms occur on a channel for which a diagnostic alarm
incoming
is
currently processed or buffered, they are lost. If a process alarm for which a diagnostic
alarm
incoming
has been triggered is processed, the diagnostic alarm processing is called
again as diagnostic alarm
outgoing
.
All events of a channel between the diagnostic alarm
incoming
and diagnostic alarm
outgoing
are not buffered and are lost. During this time (first diagnostic alarm
incoming
to the last
diagnostic alarm
outgoing
) the MF−LED of the module is lit. Additionally an entry in the
diagnostic buffer of the CPU is made for every diagnostic alarm
incoming/outgoing
.
Example:
Process alarm:
OB40:
Without diagnostic alarm:
OB40:
OB82:
OB40_1
OB82_1
OB82_2
OB82_1
OB82_2
Buffer memory proc. (FIFO):
OB40_2
OB40_3
OB40_4
2
2
3
2
3
4
3
4
4
Buffer memory (FIFO):
2
3
4
OB40_1
OB40_2
OB40_3
OB40_4
With diagnostic alarm:
lost
2
Buffer memory diag. (FIFO):
2
1
4
incomming incomming
outgoing
outgo.
1
1
2
1
2
3
4
2
1
1
1
2
3
4
OB40_2
1
2
2
3
3
2
1
2
lost
lost
SLIO044
