Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 5.5.0.0 and later) User Manual
Page 840
828
Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide
53-1003099-01
15
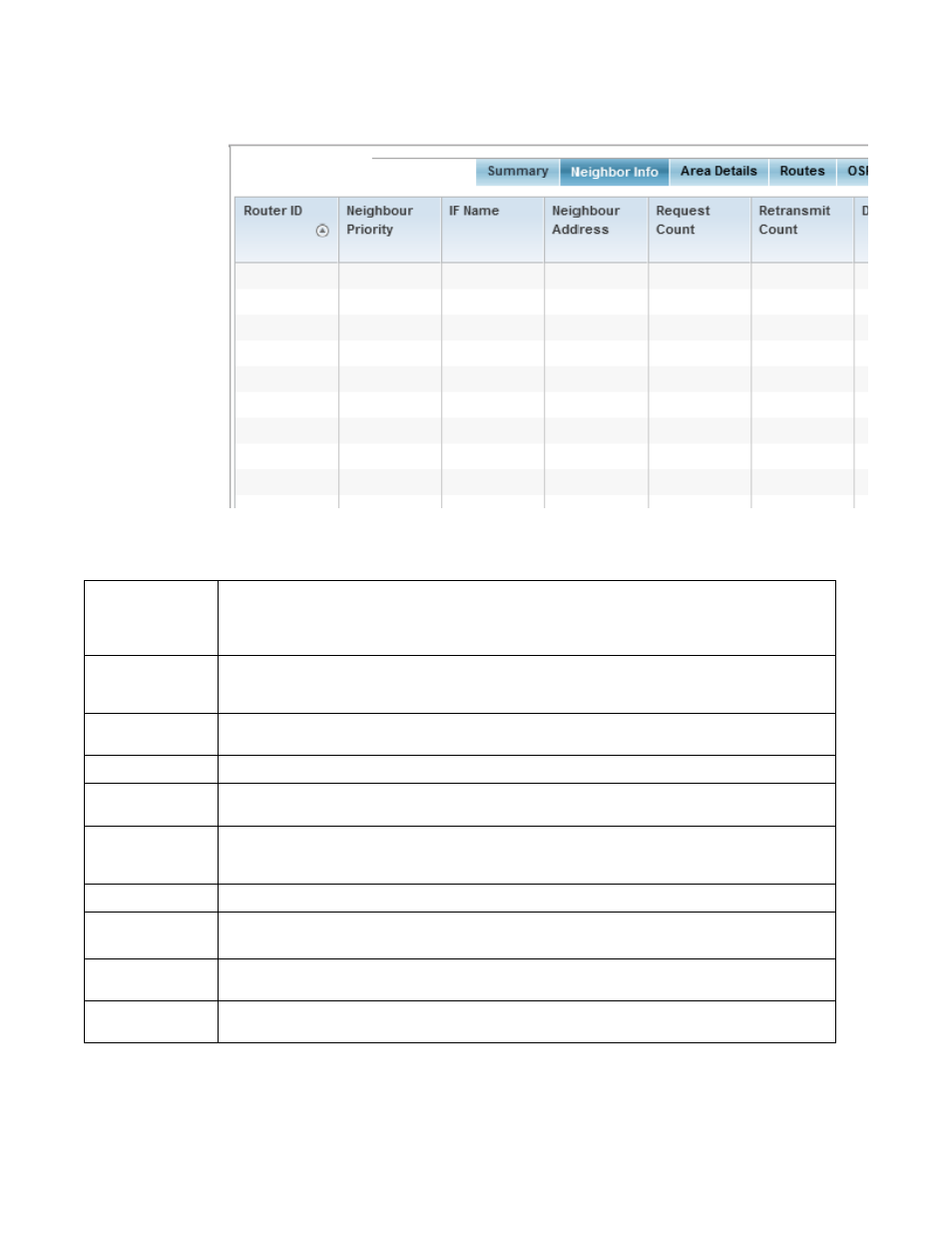
FIGURE 53
Wireless Controller - OSPF Neighbor Info tab
The Neighbor Info tab describes the following:
5. Select the Refresh button to update the statistics counters to their latest values.
Router ID
Displays the router ID assigned for this OSPF connection. The router is a level three Internet Protocol packet
switch. This ID must be established in every OSPF instance. If not explicitly configured, the highest logical IP
address is duplicated as the router identifier. However, since the router identifier is not an IP address, it does
not have to be a part of any routable subnet in the network.
Neighbor Priority
Displays each listed neighbor’s priority in respect to becoming the designated router managing the OSPF
connection. The designated router is the router interface elected among all routers on a particular
multi-access network segment.
IF Name
Lists the name assigned to the router interface used to support connections amongst OSPF enabled
neighbors.
Neighbor Address
Lists the IP address of the neighbor sharing the router interface with each listed router ID.
Request Count
Lists the connection request count (hello packets) to connect to the router interface, discover neighbors and
elect a designated router.
Retransmit Count
Lists the connection retransmission count attempted in order to connect to the router interface, discover
neighbors and elect a designated router. A designated router (DR) is the router interface elected among all
routers on a particular multi-access network segment, generally assumed to be broadcast.
Dead Time
Lists the dead time between neighbors in the network topology that are currently utilizing the listed router ID.
Self Neighbor
State
Displays the self-neighbor status assessment used to discover neighbors and elect a designated router.
Source Address
Displays the single source address used by all neighbor routers to obtain topology and connection status. This
form of multicasting significantly reduces network load.
Summary Count
Routes that originate from other areas are called summary routes. Summary routes are not flooded in a
totally stubby or NSSA totally stubby area.
