Hierarchal tree – Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 5.5.0.0 and later) User Manual
Page 695
Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide
683
53-1003099-01
12
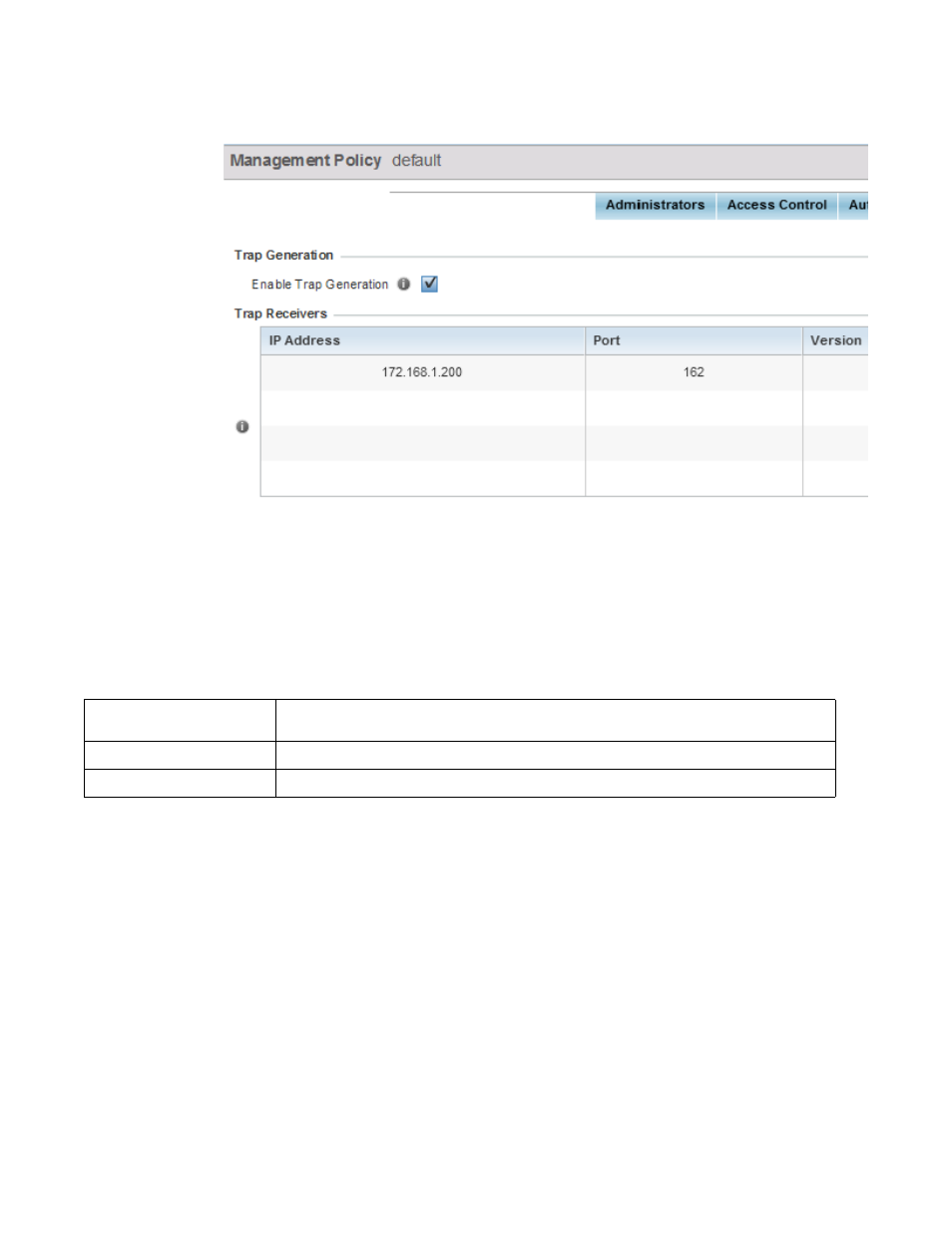
FIGURE 8
Management Policy screen - SNMP Traps tab
2. Select the Enable Trap Generation checkbox to enable trap generation using the trap receiver
configuration defined. This feature is disabled by default.
3. Refer to the Trap Receiver table to set the configuration of the external resource dedicated to
receiving trap information. Select Add Row + as needed to add additional trap receivers. Select
the Delete icon to permanently remove a trap receiver.
4. Select OK to update the SNMP Trap configuration. Select Reset to revert to the last saved
configuration.
Hierarchal Tree
Tree Setup is unique because it is not a policy (which is reused in other objects), but rather a global
configuration that represents the tree displayed for Dashboard, Operations and Statistics. However
since it is set as a configuration, it follows the standard configuration methods, and requires a
Commit before it taking effect and a Save to become persistent across reboots.
ADSP can run as a virtual machine on RFS9510 model service platforms. Mobility communicates
with ADSP using a single sign-on (SSO) authentication mechanism. Once the user is logged in,
Mobility gains access to ADSP without being prompted to login again at ADSP. There is no
synchronization between the Mobility and ADSP databases. ADSP has its own user database stored
locally within its virtual machine. This local database is accessed if a user logs directly into ADSP.
IP Address
Sets the IP address of the external server resource dedicated to receiving the SNMP traps on
behalf of the controller or service platform.
Port
Set the port of the server resource dedicated to receiving SNMP traps. The default port is port 162.
Version
Sets the SNMP version to use to send SNMP traps. SNMPv2 is the default.
