Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 5.5.0.0 and later) User Manual
Page 515
Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide
503
53-1003099-01
8
Use Bridge NAT to manage Internet traffic originating at a remote site. In addition to traditional NAT
functionality, Bridge NAT provides a means of configuring NAT for bridged traffic through an Access
Point. NAT rules are applied to bridged traffic through the Access Point, and matching packets are
NATed to the WAN link instead of being bridged on their way to the router.
Using Bridge NAT, a tunneled VLAN (extended VLAN) is created between the NoC and a remote
location. When a remote client needs to access the Internet, Internet traffic is routed to the NoC,
and from there routed to the Internet. This increases the access time for the end user on the client.
To resolve latency issues, Bridge NAT identifies and segregates traffic heading towards the NoC and
outwards towards the Internet. Traffic towards the NoC is allowed over the secure tunnel. Traffic
towards the Internet is switched to a local WLAN link with access to the Internet.
To define a NAT configuration that can be applied to a profile:
1. Select the Configuration tab from the Web UI
2. Select Profiles from the Configuration tab.
3. Select Manage Profiles from the Configuration > Profiles menu
4. Select Security.
5. Select Bridge NAT.
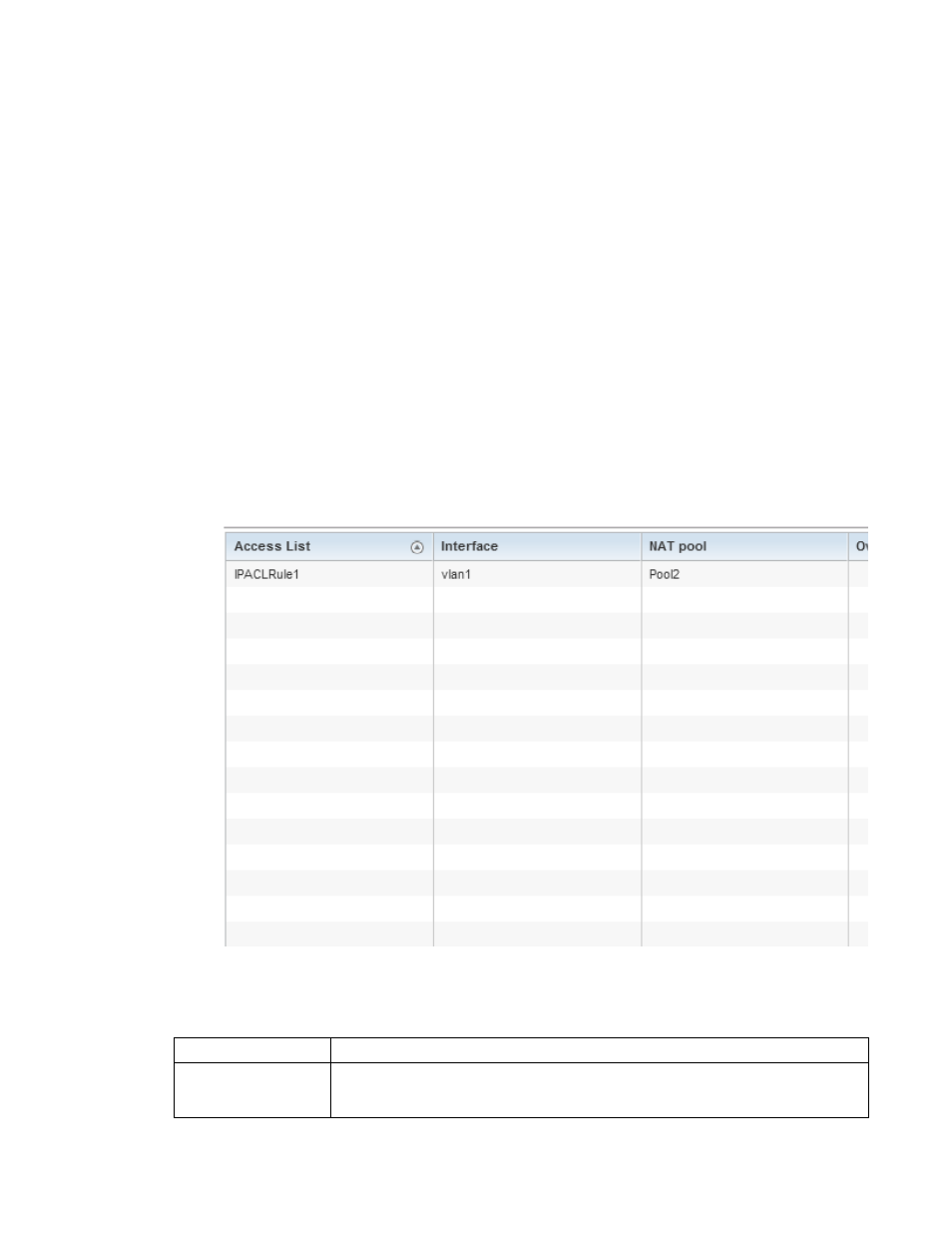
FIGURE 81
Security Bridge NAT screen
6. Review the following Bridge NAT configurations to determine whether a new Bridge NAT
configuration requires creation or an existing configuration be modified or removed.
Access List
Lists the ACL applying IP address access/deny permission rules to the Bridge NAT configuration.
Interface
Lists the communication medium (outgoing layer 3 interface) between source and destination
points. This is either the Access Point’s pppoe1 or wwan1 interface or the VLAN used as the
redirection interface between the source and destination.
