Rf domain overrides – Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 5.5.0.0 and later) User Manual
Page 83
Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide
71
53-1003099-01
5
5. Set the following Port Mirroring values to define the ports and directions data is spanned on
the NX4524 or NX6524 model service platform:
6. Select + Add Row to add different sources, destinations and directions for additional GE port
spanning configurations.
7. Select OK to save the changes made to the NX4524 or NX6524 port mirroring configuration.
Selecting Reset reverts the screen to its last saved configuration.
RF Domain Overrides
Use RF Domain Overrides to define configurations overriding the configuration set by the target
device’s original RF Domain assignment.
RF Domains allow administrators to assign configuration data to multiple devices deployed in a
common coverage area (floor, building or site). In such instances, there’s many configuration
attributes these devices share, since their general client support roles are quite similar. However,
device configurations may need periodic refinement from their original RF Domain administered
design.
A controller or service platform configuration contains (at a minimum) one default RF Domain, but
can optionally use additional user defined RF Domains:
•
Default RF Domain - Automatically assigned to each controller, service platform and
associated Access Points by default. A default RF Domain is unique to a specific model.
•
User Defined RF Domains - Created by administrators and manually assigned to individual
controllers, service platforms or Access Points, but can be automatically assigned to Access
Points using adoption policies.
Each controller, service platform and Access Point is assigned one RF Domain at a time. However, a
user defined RF Domain can be assigned to multiple devices as required. User defined RF Domains
can be manually assigned or automatically assigned to Access Points using an auto provisioning
policy. The more devices assigned a single RF Domain, the greater the likelihood one of the
device’s configurations will require an override deviating that device’s configuration from the
original RF Domain assignment shared by the others.
To review the RF Domain’s original configuration requirements and the options available for a
target device, refer to
.
To define a device’s RF Domain override configuration:
1. Select the Configuration tab from the Web UI.
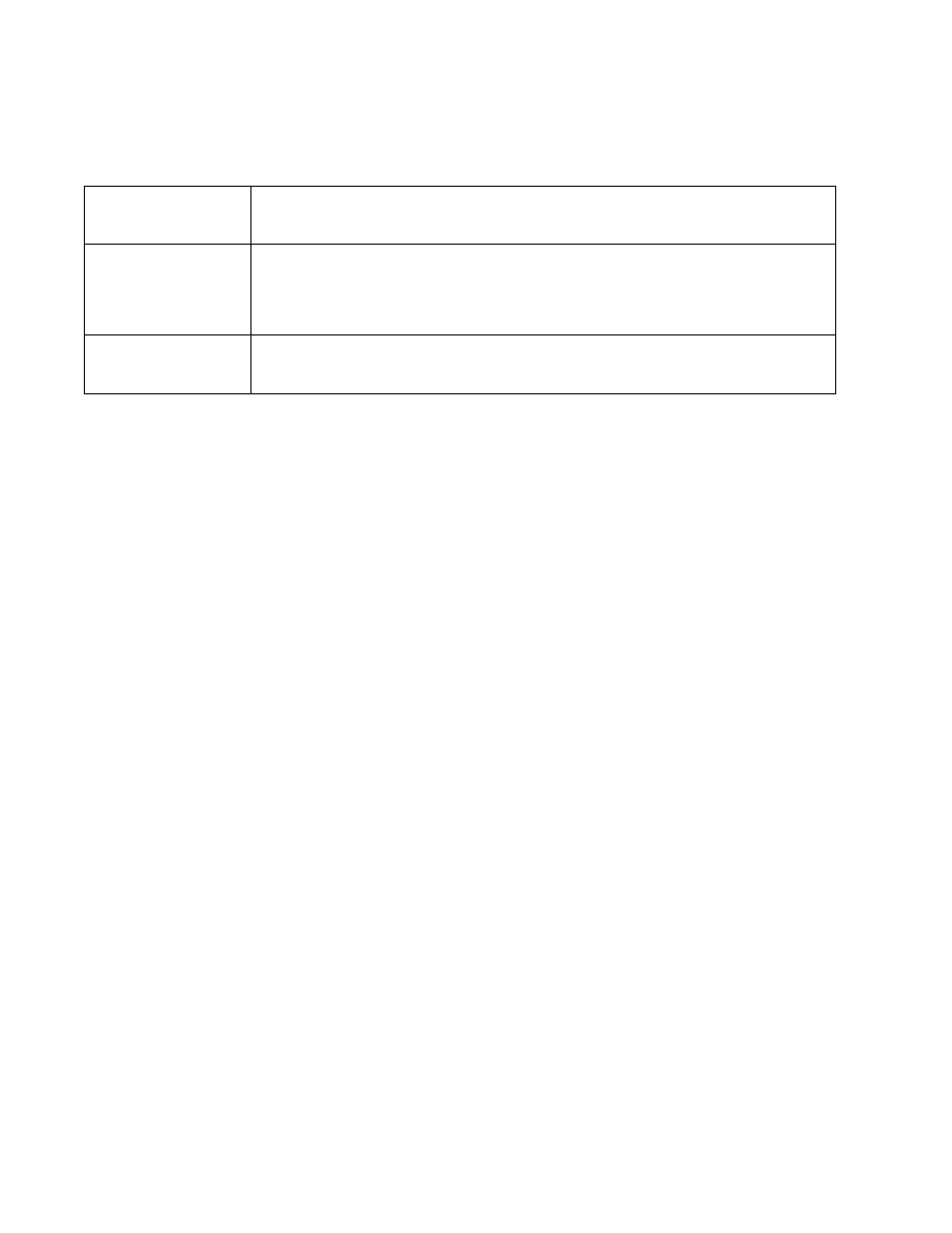
Source
Select the GE port (1 - 24) used as the data source to span packets to the selected destination port.
The packets spanned from the selected source to the destination depend on whether Inbound,
Outbound or Any is selected as the direction. A source port cannot be a destination port.
Destination
Select the GE port (1 - 24) used as the port destination to span packets from the selected source. The
destination port serves as a duplicate image of the source port and can be used to send packets to a
network diagnostic without disrupting the behavior on the original port. The destination port transmits
only mirrored traffic and does not forward received traffic. Additionally, address learning is disabled on
the destination port.
Direction
Define the direction data packets are spanned from the selected source to the defined destination.
Packets spanned from the source to the destination depend on whether Inbound (received packets
only), Outbound (transmitted packets only) or Any (packets in either direction) is selected.
