Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 5.5.0.0 and later) User Manual
Page 64
52
Brocade Mobility RFS Controller System Reference Guide
53-1003099-01
5
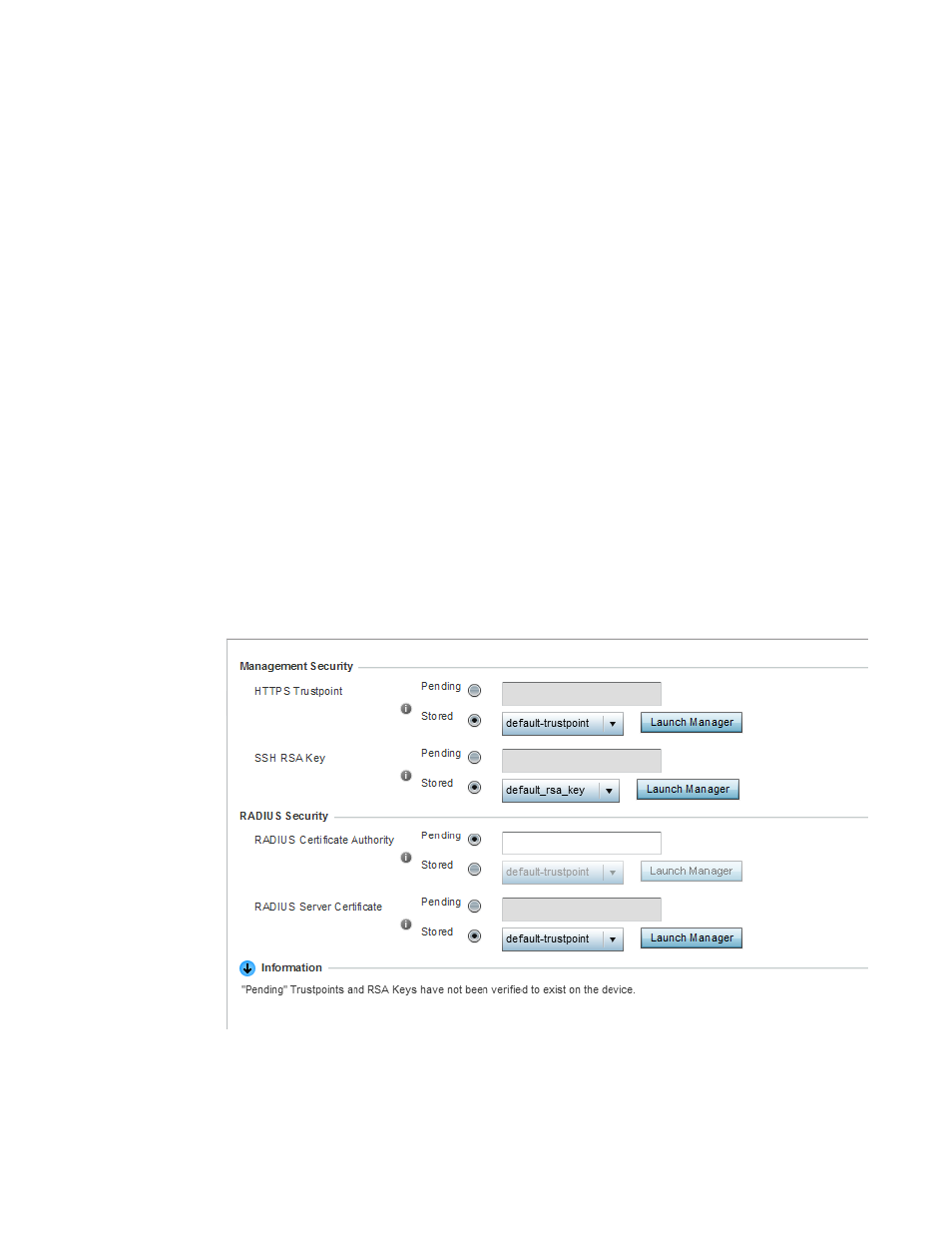
A certificate authority (CA) is a network authority that issues and manages security credentials and
public keys for message encryption. The CA signs all digital certificates it issues with its own private
key. The corresponding public key is contained within the certificate and is called a CA certificate. A
browser must contain the CA certificate in its Trusted Root Library so it can trust certificates signed
by the CA's private key.
Depending on the public key infrastructure, the digital certificate includes the owner's public key,
the certificate expiration date, the owner's name and other public key owner information.
Each certificate is digitally signed by a trustpoint. The trustpoint signing the certificate can be a
certificate authority, corporation or individual. A trustpoint represents a CA/identity pair containing
the identity of the CA, CA-specific configuration parameters, and an association with an enrolled
identity certificate.
SSH keys are a pair of cryptographic keys used to authenticate users instead of, or in addition to, a
username/password. One key is private and the other is public key. Secure Shell (SSH) public key
authentication can be used by a requesting client to access resources, if properly configured. A RSA
key pair must be generated on the client. The public portion of the key pair resides with the
controller or service platform, while the private portion remains on a secure local area of the client.
To configure certificate usage:
1. Select the Configuration tab from the Web UI.
2. Select Devices from the Configuration tab.
The Device Configuration screen displays a list of managed devices or peer controllers, service
platforms or Access Points.
3. Select Certificates from the Device menu.
FIGURE 4
Device Certificates screen
