3 address breakpoint registers (ablr, abhr), 3 address breakpoint registers (ablr, abhr) -9, P. 30-9 – Motorola ColdFire MCF5281 User Manual
Page 627
Debug Support
Freescale Semiconductor
30-9
30.4.3
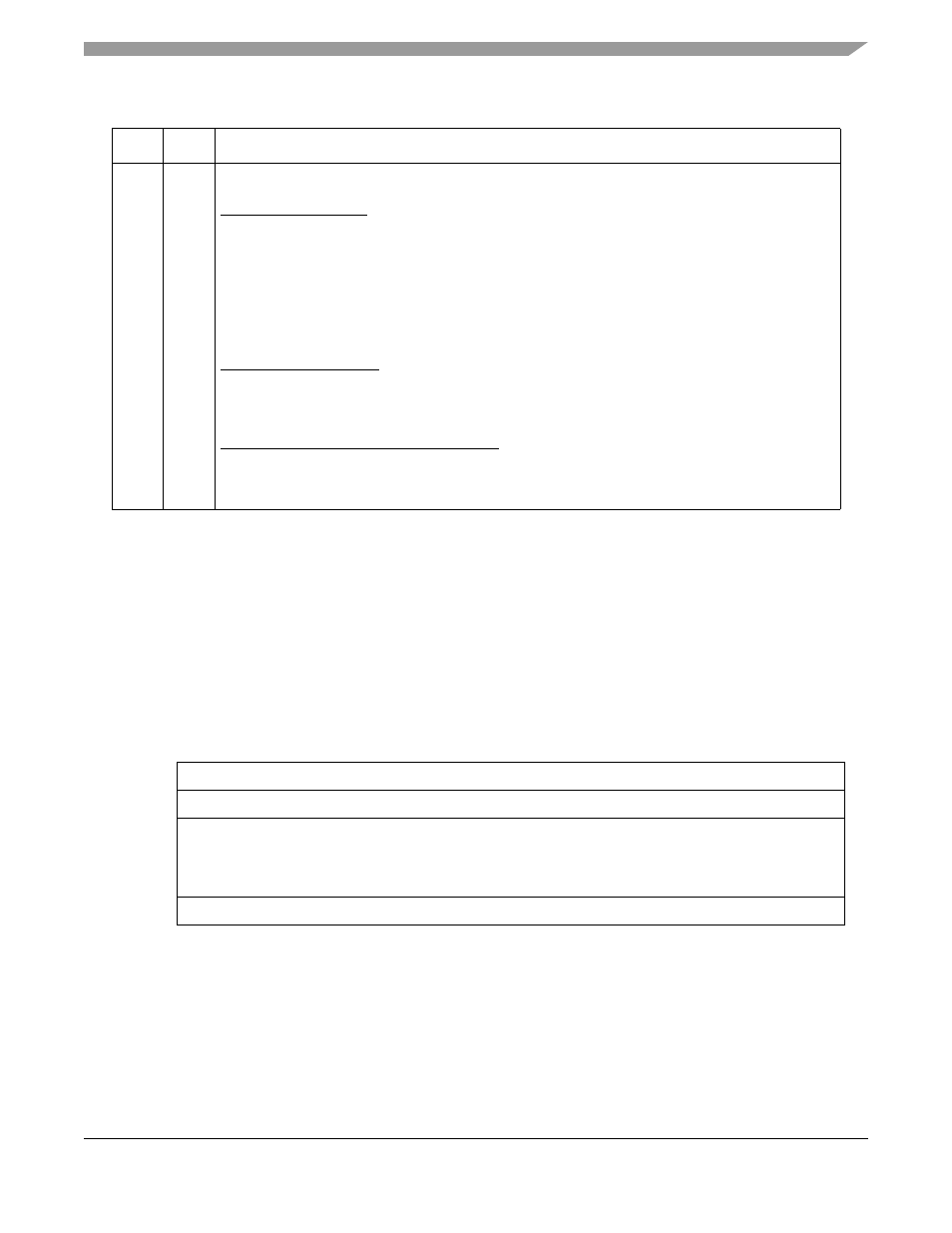
Address Breakpoint Registers (ABLR, ABHR)
The ABLR and ABHR, shown in
, define regions in the processor’s data address space that can
be used as part of the trigger. These register values are compared with the address for each transfer on the
processor’s high-speed local bus. The trigger definition register (TDR) identifies the trigger as one of three
cases:
1. Identical to the value in ABLR
2. Inside the range bound by ABLR and ABHR inclusive
3. Outside that same range
2–0
TM
Transfer modifier. Compared with the local bus transfer modifier signals, which give supplemental
information for each transfer type.
TT = 00 (normal mode):
000 Explicit cache line push
001 User data access
010 User code access
011 Reserved
100 Reserved
101 Supervisor data access
110 Supervisor code access
111 Reserved
TT = 10 (emulator mode):
0xx–100 Reserved
101 Emulator mode data access
110 Emulator mode code access
111 Reserved
TT = 11 (acknowledge/CPU space transfers):
000 CPU space access
001–111 Interrupt acknowledge levels 1–7
These bits also define the TM encoding for BDM memory commands (for backward compatibility).
31
0
Field
Address
Reset
—
R/W Write only. ABHR is accessible in supervisor mode as debug control register 0x0C using the WDEBUG
instruction and via the BDM port using the
RDMREG
and
WDMREG
commands.
ABLR is accessible in supervisor mode as debug control register 0x0D using the WDEBUG instruction and
via the BDM port using the
WDMREG
command.
DRc[4–0]
0x0D (ABLR); 0x0C (ABHR)
Figure 30-6. Address Breakpoint Registers (ABLR, ABHR)
Table 30-5. AATR Field Descriptions (continued)
Bits
Name Description
MCF5282 and MCF5216 ColdFire Microcontroller User’s Manual, Rev. 3
