4 power management, 4 power management -4 – Motorola ColdFire MCF5281 User Manual
Page 112
Static RAM (SRAM)
5-4
Freescale Semiconductor
The following loop initializes the entire SRAM to zero
lea.l
RAMBASE,A0
;load pointer to SRAM
move.l
#16384,D0
;load loop counter into D0
SRAM_INIT_LOOP:
clr.l
(A0)+)
;clear 4 bytes of SRAM
subq.l
#1,D0
;decrement loop counter
bne.b
SRAM_INIT_LOOP
;if done, then exit; else continue looping
5.3.4
Power Management
As noted previously, depending on the configuration defined by the RAMBAR, instruction fetch and
operand read accesses may be sent to the SRAM and cache simultaneously. If the access is mapped to the
SRAM module, it sources the read data and the unified cache access is discarded. If the SRAM is used
only for data operands, asserting the ASn bits associated with instruction fetches can decrease power
dissipation. Additionally, if the SRAM contains only instructions, masking operand accesses can reduce
power dissipation.
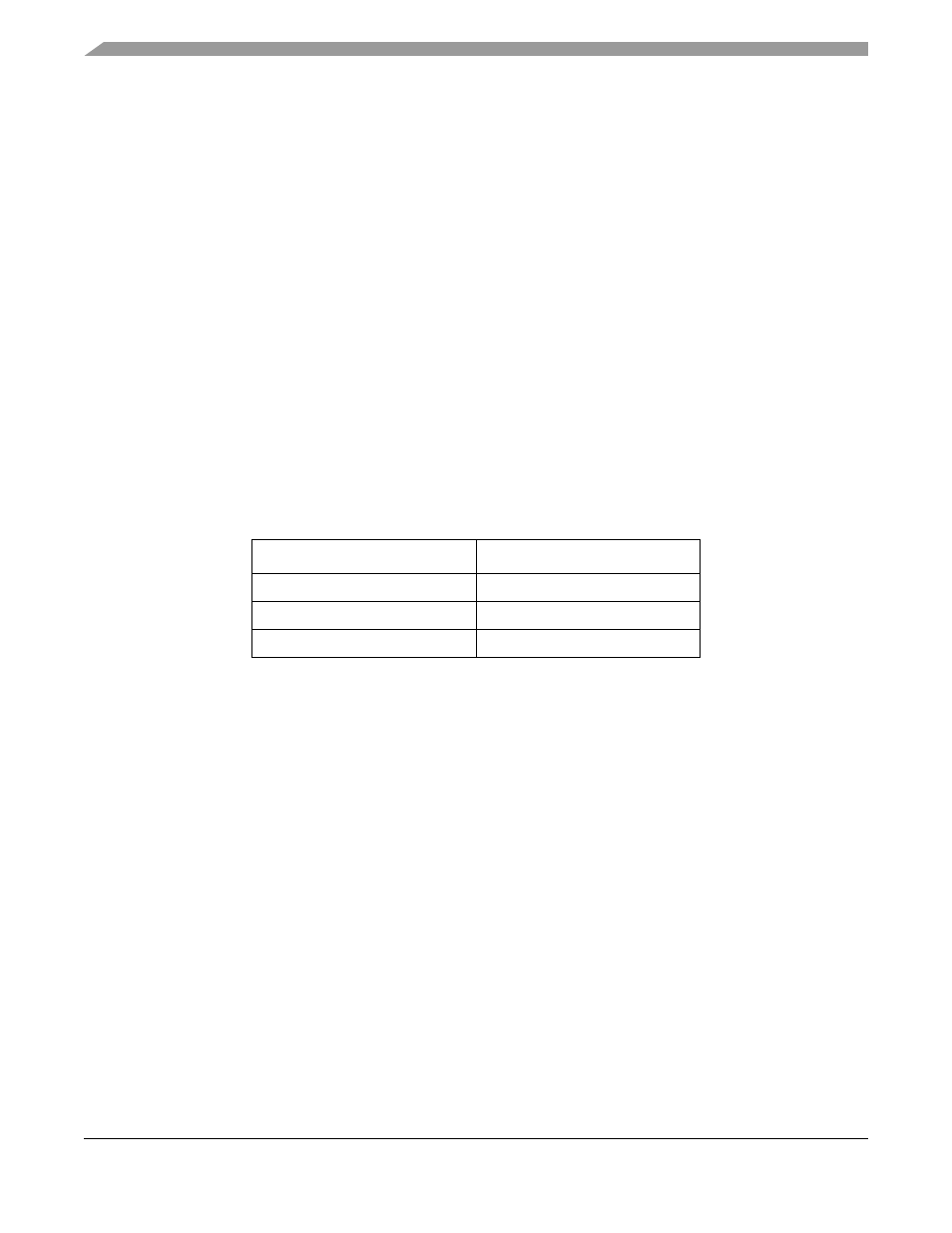
shows some examples of typical RAMBAR settings.
Table 5-2. Typical RAMBAR Setting Examples
Data Contained in SRAM
RAMBAR[7:0]
Code Only
0x2B
Data Only
0x35
Both Code And Data
0x21
MCF5282 and MCF5216 ColdFire Microcontroller User’s Manual, Rev. 3
