6 back-to-back bus cycles, 6 back-to-back bus cycles -9, Figure 13-10 – Motorola ColdFire MCF5281 User Manual
Page 233
External Interface Module (EIM)
Freescale Semiconductor
13-9
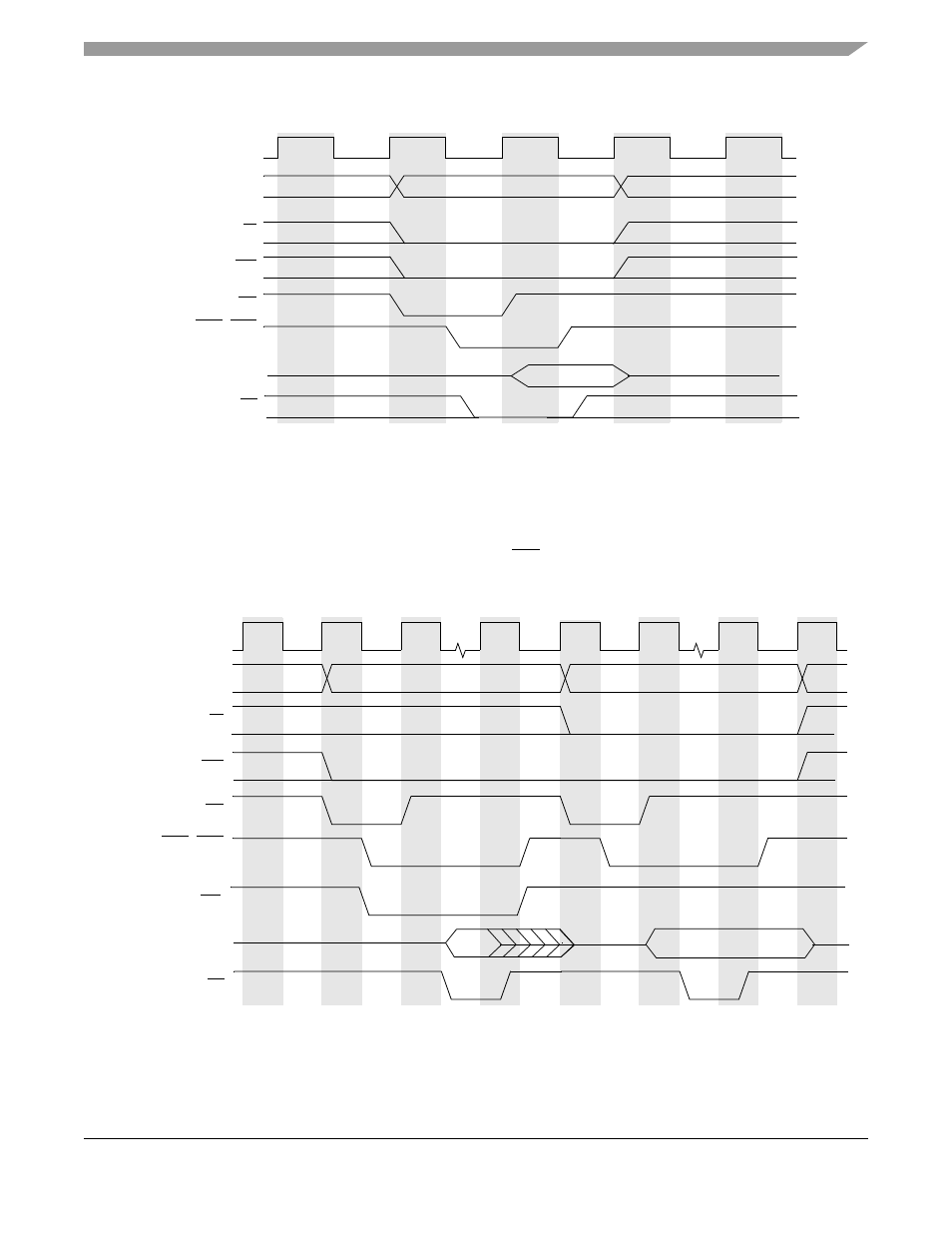
Figure 13-10. Write Cycle with Fast Termination
13.4.6
Back-to-Back Bus Cycles
The processor runs back-to-back bus cycles whenever possible. For example, when a longword read is
started on a word-size bus, the processor performs two back-to-back word read accesses. Back-to-back
accesses are distinguished by the continuous assertion of TIP throughout the cycle.
shows a
read back-to-back with a write.
Figure 13-11. Back-to-Back Bus Cycles
Basic read and write cycles are used to show a back-to-back cycle, but there is no restriction as to the type
of operations to be placed back to back. The initiation of a back-to-back cycle is not user definable.
R/W
TIP
TS
CSn, BSn
D[31:0]
TA
S0
S1
S4
S5
Write
CLKOUT
A[31:0], SIZ[1:0]
R/W
TIP
TS
CSn, BSn
D[31:0]
TA
Read
S0
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S0
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
Write
OE
CLKOUT
A[31:0], SIZ[1:0]
MCF5282 and MCF5216 ColdFire Microcontroller User’s Manual, Rev. 3
