2 queue priority schemes, 2 queue priority schemes -36 – Motorola ColdFire MCF5281 User Manual
Page 574
Queued Analog-to-Digital Converter (QADC)
28-36
Freescale Semiconductor
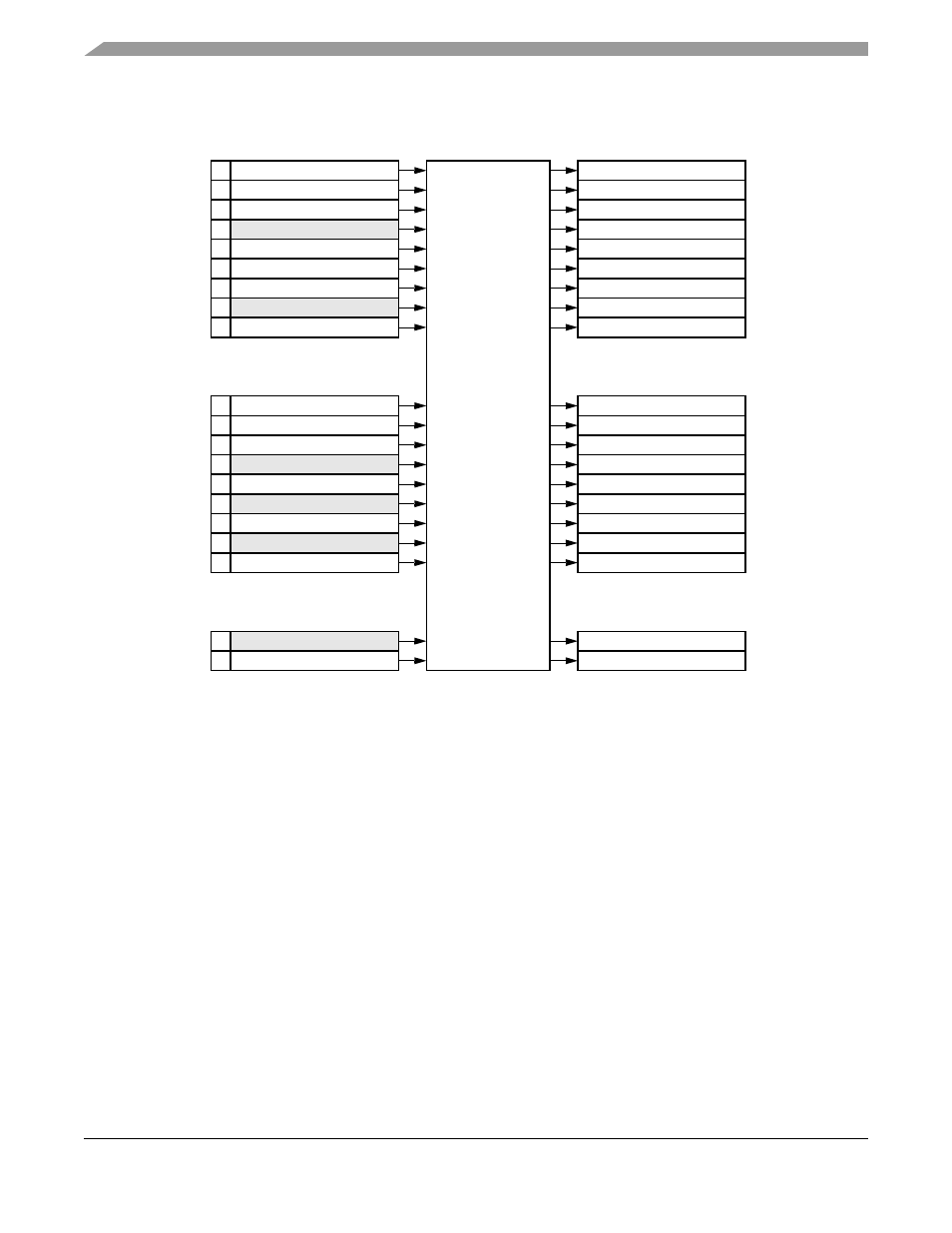
Figure 28-22. QADC Queue Operation with Pause
Trigger events which occur during the execution of a subqueue are ignored, but the trigger overrun flag is
set. When a continuous-scan mode is selected, a trigger event occurring after the completion of the last
subqueue (after the queue completion flag is set), causes the execution to continue with the first subqueue,
starting with the first CCW in the queue.
When the QADC encounters a CCW with the pause bit set, the queue enters the paused state after
completing the conversion specified in the CCW with the pause bit. The pause flag is set in QASR0, and
a pause interrupt may be requested. The status of the queue is shown to be paused, indicating completion
of a subqueue. The QADC then waits for another trigger event to again begin execution of the next
subqueue.
28.8.1.2
Queue Priority Schemes
Because there are two conversion command queues and only one A/D converter, a priority scheme
determines which conversion occurs. Each queue has a variety of trigger events that are intended to initiate
conversions, and they can occur asynchronously in relation to each other and other conversions in
progress. For example, a queue can be idle awaiting a trigger event; a trigger event can have occurred, but
the first conversion has not started; a conversion can be in progress; a pause condition can exist awaiting
another trigger event to continue the queue; and so on.
Beginning of Queue 1
00
Channel Select,
Sample, Hold,
A/D Conversion
Conversion Command
Result Word Table
0
Pause
Word (CCW) Table
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
Pause
00
P
0
Pause
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Pause
P
End of Queue 1
Beginning of Queue 2
BQ2
Pause
Pause
End of Queue 2
P
1
0
63
63
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
MCF5282 and MCF5216 ColdFire Microcontroller User’s Manual, Rev. 3
