Own in, Figure 13-4 – Motorola ColdFire MCF5281 User Manual
Page 229
External Interface Module (EIM)
Freescale Semiconductor
13-5
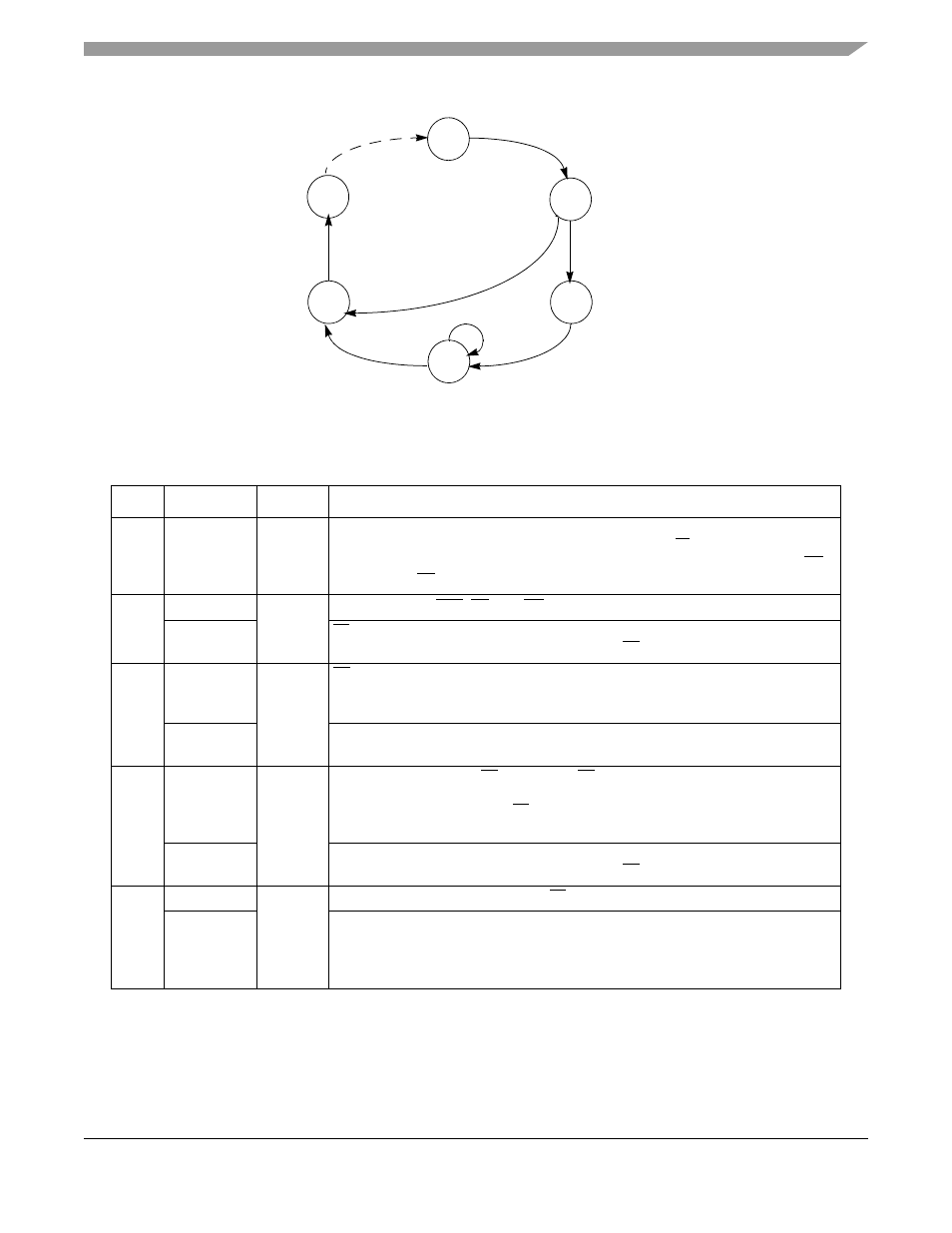
Figure 13-4. Data Transfer State Transition Diagram
describes the states as they appear in subsequent timing diagrams.
Table 13-3. Bus Cycle States
State
Cycle
CLKOUT
Description
S0
All
High
The read or write cycle is initiated in S0. On the rising edge of CLKOUT, the device
places a valid address on the address bus and drives R/W high for a read and low
for a write, if it is not already in the appropriate state. The processor asserts TIP,
SIZ[1:0], and TS on the rising edge of CLKOUT.
S1
All
Low
The appropriate CSn, BS, and OE signals assert on the CLKOUT falling edge.
Fast
Termination
TA must be asserted during S1. Data is made available by the external device and
is sampled on the rising edge of CLKOUT with TA asserted.
S2
Read/write
(skipped fast
termination)
High
TS is negated on the rising edge of CLKOUT in S2.
Write
The data bus is driven out of high impedance as data is placed on the bus on the
rising edge of CLKOUT.
S3
Read/write
(skipped for
fast
termination)
Low
The processor waits for TA assertion. If TA is not sampled as asserted before the
rising edge of CLKOUT at the end of the first clock cycle, the processor inserts wait
states (full clock cycles) until TA is sampled as asserted.
Read
Data is made available by the external device on the falling edge of CLKOUT and
is sampled on the rising edge of CLKOUT with TA asserted.
S4
All
High
The external device should negate TA.
Read
(including
fast-terminati
on)
The external device can stop driving data after the rising edge of CLKOUT.
However data could be driven through the end of S5.
S0
S3
S5
S4
S1
S2
Basic
Next Cycle
Wait
States
Read/Write
Fast
Termination
MCF5282 and MCF5216 ColdFire Microcontroller User’s Manual, Rev. 3
