8 cpu core interrupts, 1 non-maskable interrupt (nmi), 2 ordinary interrupts – NEC Network Controller uPD98502 User Manual
Page 182: 3 software interrupts generated in cpu core, 4 timer interrupt
CHAPTER 2 V
R
4120A
182
Preliminary User’s Manual S15543EJ1V0UM
2.8 CPU Core Interrupts
Four types of interrupt are available on the CPU core. These are:
one non-maskable interrupt, NMI
five ordinary interrupts
two software interrupts
one timer interrupt
For the interrupt request input to the CPU core.
2.8.1 Non-maskable interrupt (NMI)
The non-maskable interrupt is acknowledged by asserting the NMI signal (internal), forcing the processor to branch
to the Reset Exception vector. This signal is latched into an internal register at the rising edge of MasterOut signal
(internal), as shown in Figure 2-87.
NMI only takes effect when the processor pipeline is running.
This interrupt cannot be masked.
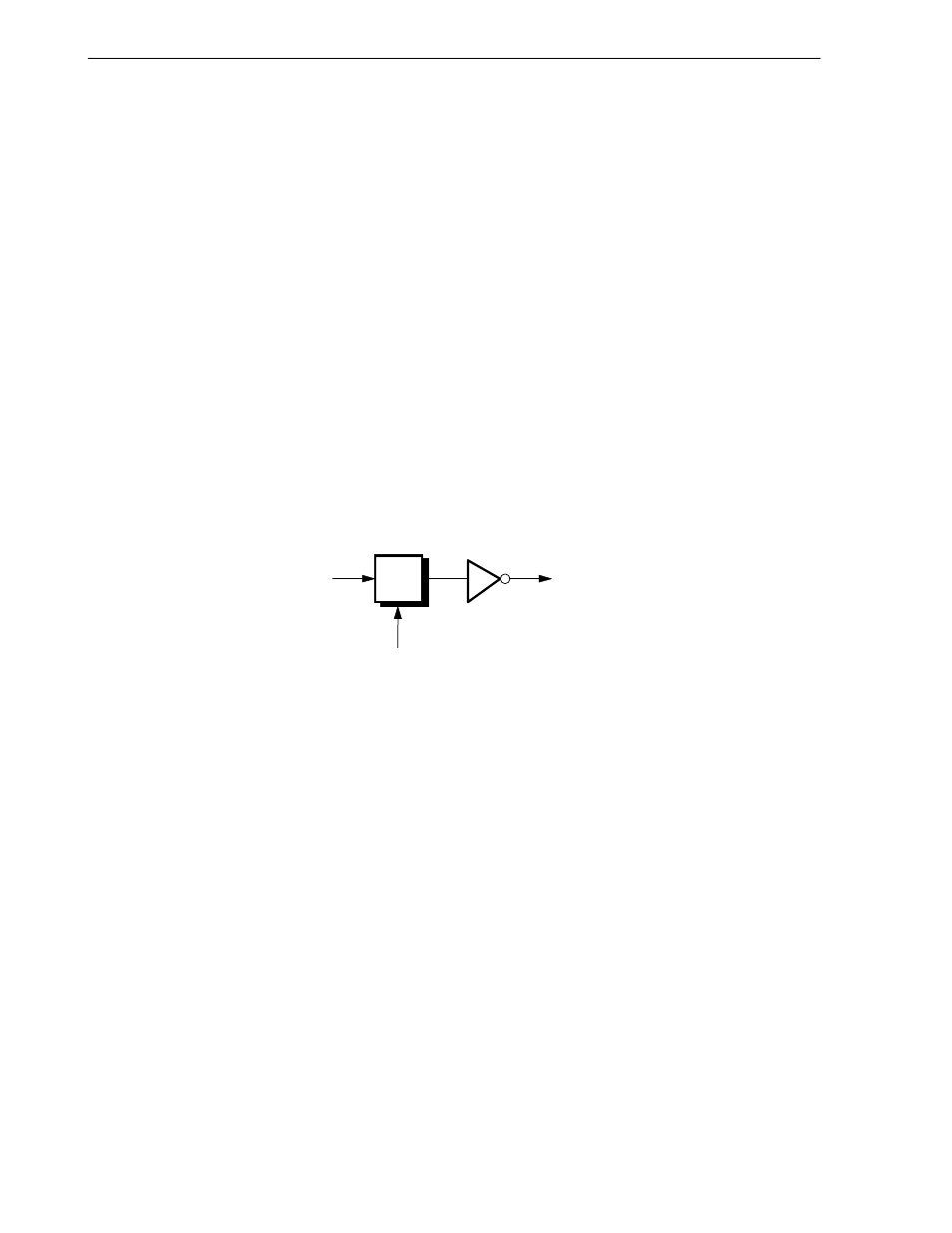
Figure 2-87 shows the internal service of the NMI signal. The NMI signal is latched into an internal register by the
rising edge of MasterOut. The latched signal is inverted to be transferred to inside the device as an NMI request.
Figure 2-87. Non-maskable Interrupt Signal
NMI request
NMI signal
MasterOut
(Internal register)
2.8.2 Ordinary interrupts
Ordinary interrupts are acknowledged by asserting the Int(4:0) signals (internal). However, Int4 never occurs in the
V
R
4120A.
This interrupt request can be masked with the IM (6:2), IE, and EXL fields of the Status register.
2.8.3 Software interrupts generated in CPU core
Software interrupts generated in the CPU core use bits 1 and 0 of the IP (interrupt pending) field in the Cause
register. These may be written by software, but there is no hardware mechanism to set or clear these bits.
After the processing of a software interrupt exception, corresponding bit of the IP field in the Cause register must
be cleared before returning to ordinary routine or enabling multiple interrupts until the operation returns to normal
routine.
This interrupt request is maskable through the IM (1:0), IE, and EXL fields of the Status register.
2.8.4 Timer interrupt
The timer interrupt uses bit 7 of the IP (interrupt pending) field of the Cause register. This bit is set automatically
whenever the value of the Count register equals the value of the Compare register, and an interrupt request is
acknowledged.
This interrupt is maskable through IM7 of the IM field of the Status register.
