3 transparent synchronization example, Transparent synchronization example -4, Sending transparent frames between mpc8260s -4 – Motorola MPC8260 User Manual
Page 924
32-4
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual
MOTOROLA
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
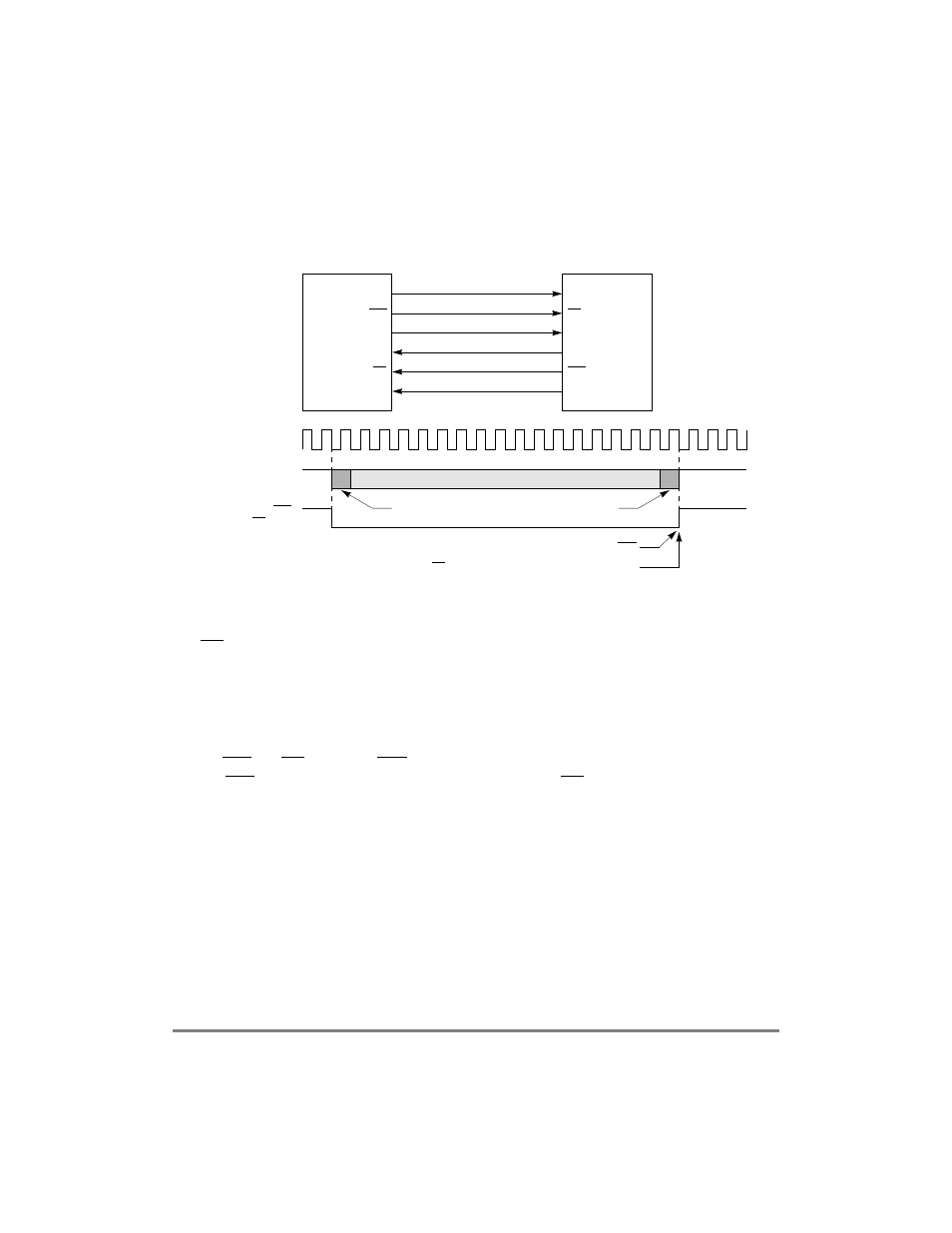
32.3.3 Transparent Synchronization Example
Figure 32-2 shows an example of synchronization using external signals.
Figure 32-2. Sending Transparent Frames between MPC8260s
MPC8260(A) and MPC8260(B) exchange transparent frames and synchronize each other
using RTS and CD. However, CTS is not required because transmission begins at any time.
Thus, RTS is connected directly to the other MPC8260Õs CD. GFMR[SYNL] is not used
and transmission and reception from each MPC8260 are independent.
RXD
CD
CLKx
TXD
RTS
CD
RXD
BRGOx
RTS
TXD
CLKx
BRGOx
BRGOx
Last Bit of Frame Data
First Bit of Frame Data
(Output is CLKx Input)
TXD
(Output is RXD Input)
RTS
(Output is CD Input)
or CRC
TxBD[L] = 1 Causes Negation of RTS
CD Lost Condition Terminates Reception of Frame
MPC8260 A
MPC8260 B
Notes:
1. Each MPC8260 generates its own transmit clocks. If the transmit and receive clocks are the same, one can
generate transmit and receive clocks for the other MPC8260. For example, CLKx on MPC8260 (B) could be used to
clock the transmitter and receiver.
2. CTS should be conÞgured as always asserted in the parallel I/O port or connected to ground externally.
3. The required GSMR conÞgurations are DIAG= 00, CTSS=1, CTSP is a donÕt care, CDS=1, CDP=0, TTX=1, and
TRX=1. REVD and TCRC are application-dependent.
4. The transparent frame contains a CRC if TxBD[TC] is set.
