1 hdlc bus features, 2 accessing the hdlc bus, Hdlc bus features -19 – Motorola MPC8260 User Manual
Page 627: Accessing the hdlc bus -19, Typical hdlc bus single-master configuration -19
MOTOROLA
Chapter 21. SCC HDLC Mode
21-19
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
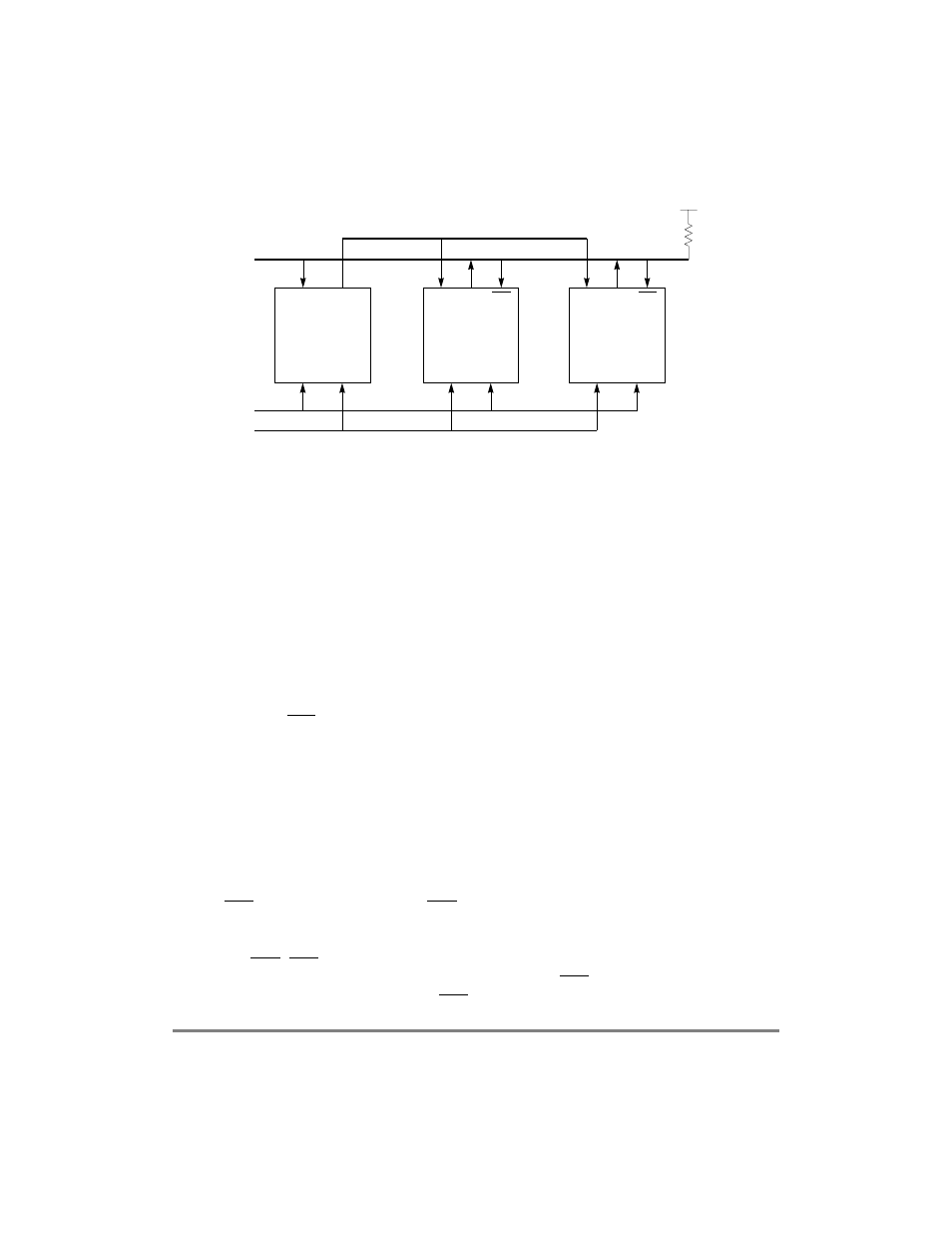
Figure 21-11. Typical HDLC Bus Single-Master Configuration
21.14.1 HDLC Bus Features
The main features of the HDLC bus are as follows:
¥
Superset of the HDLC controller features
¥
Automatic HDLC bus access
¥
Automatic retransmission in case of collision
¥
May be used with the NMSI or a TDM bus
¥
Delayed RTS mode
21.14.2 Accessing the HDLC Bus
The HDLC bus protocol ensures orderly bus control when multiple transmitters attempt
simultaneous access. The transmitter sending a zero bit at the time of collision completes
the transmission. If a station sends out an opening ßag (0x7E) while another station is
already sending, the collision is always detected within the Þrst byte, because the
transmission in progress is using zero bit insertion to prevent ßag imitation.
While in the active condition (ready to transmit), the HDLC bus controller monitors the bus
using CTS. It counts the one bits on CTS. When eight consecutive ones are counted, the
HDLC bus controller starts transmitting on the line; if a zero is detected, the internal
counter is cleared. During transmission, data is continuously compared with the external
bus using CTS. CTS is sampled halfway through the bit time using the rising edge of the
Tx clock. If the transmitted bit matches the received CTS bus sample, transmission
continues. However, if the received CTS sample is 0 and the transmitted bit is 1,
HDLC
Controller
RXD
TXD
A
RCLK
HDLC Bus
Controller
RXD
CTS
TXD
B
HDLC Bus
Controller
RXD
CTS
TXD
C
Clock1
HDLC Bus LAN
+ 5 V
R
Slave
Slave
Master
NOTES:
1. Transceivers may be used to extend the LAN size.
2. The TXD pins of slave devices should be configured to open-drain in the port C parallel I/O port.
3. Clock1 is the master RCLK and the slave TCLK.
Clock2
TCLK
RCLK
TCLK
RCLK
TCLK
4. Clock2 is the master TCLK and the slave RCLK.
