Memory controller machine selection -6 – Motorola MPC8260 User Manual
Page 282
10-6
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual
MOTOROLA
Part III. The Hardware Interface
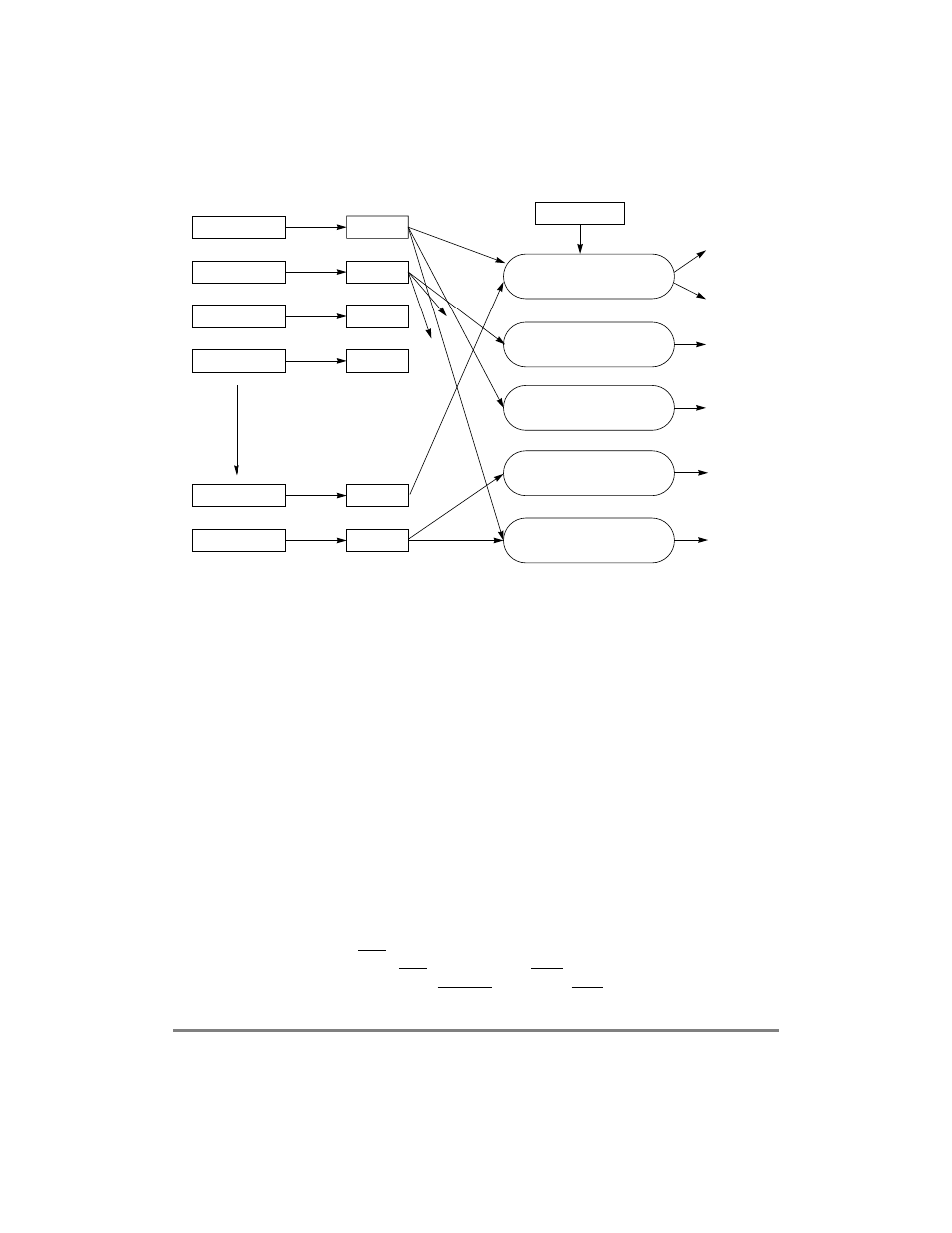
Figure 10-2. Memory Controller Machine Selection
Some features are common to all machines.
¥
A 17-bit most-signiÞcant address decode on each memory bank
¥
The block size of each memory bank can vary between 32 Kbytes (1 Mbyte for
SDRAM) and 4 Gbytes (128 Mbytes for SDRAM).
¥
Normal parity may be generated and checked for any memory bank.
¥
Read-modify-write parity may be generated and checked for any memory bank with
either 32- or 64-bit port size. Using RMW parity on 32-bit port size bank, requires
the bus to be in strict 60x mode (BCR[ETM] = 0. See Section 4.3.2.1, ÒBus
ConÞguration Register (BCR).Ó
¥
ECC may be generated and checked for any memory bank with a 64-bit port size
¥
Each memory bank can be selected for read-only or read/write operation.
¥
Each memory bank can use data pipelining, which reduces the required data setup
time for synchronous devices.
¥
Each memory bank can be controlled by an external memory controller or bus slave.
The memory controller functionality minimizes the need for glue logic in MPC8260-based
systems. In Figure 10-3, CS0 is used with the 16-bit boot EPROM with BR0[MS]
defaulting to select the GPCM. CS1 is used as the RAS signal for 64-bit DRAM with
BR1[MS] conÞgured to select UPMA. BS[0Ð7] are used as CAS signals on the DRAM.
User-Programmable
Local General-Purpose
Bank 0
Bank 1
Bank 2
Bank 3
Bank 10
Bank11
MS
MS
MS
MS
MS
MS
Chip-Select Machine
Local SDRAM
Local
60x
Local
MxMR[BS]
60x SDRAM
60x
Local
60x General-Purpose
Chip-Select Machine
60x
Machine (A/B/C)
Machine
Machine
