4 delayed rts mode, Delayed rts mode -21, Hdlc bus transmission line configuration -21 – Motorola MPC8260 User Manual
Page 629
MOTOROLA
Chapter 21. SCC HDLC Mode
21-21
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
Figure 21-13. Nonsymmetrical Tx Clock Duty Cycle for Increased Performance
21.14.4 Delayed RTS Mode
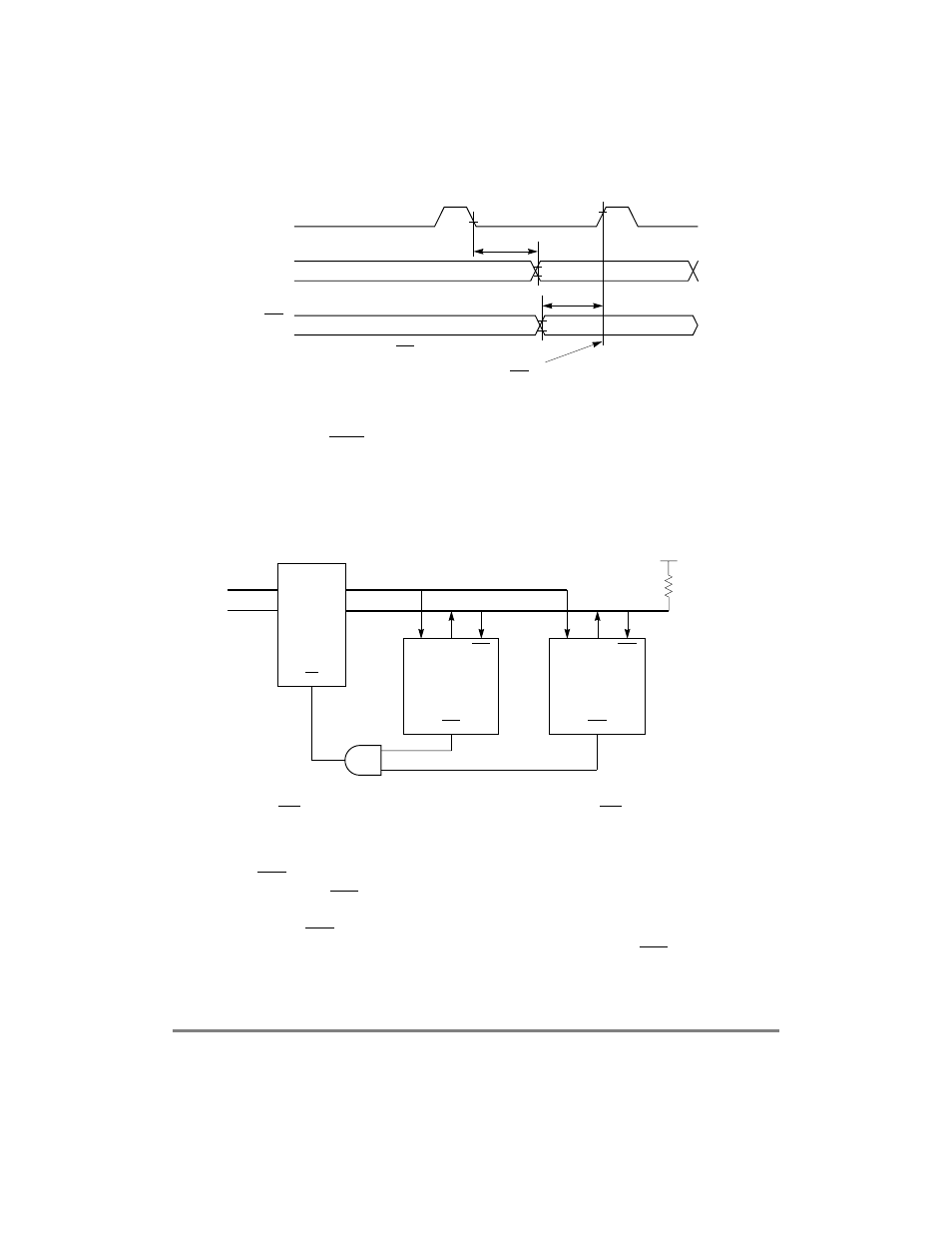
Figure 21-14 shows local HDLC bus controllers using a standard transmission line and a
local bus. The controllers do not communicate with each other but with a station on the
transmission line; yet the HDLC bus protocol controls access to the transmission line.
Figure 21-14. HDLC Bus Transmission Line Configuration
Normally, RTS goes active at the beginning of the opening ßagÕs Þrst bit. Setting
PSMR[BRM] delays RTS by one bit, which is useful when the HDLC bus connects
multiple local stations to a transmission line. If the transmission line driver has a one-bit
delay, the delayed RTS can be used to enable the output of the line driver. As a result, the
electrical effects of collisions are isolated locally. Figure 21-15 shows RTS timing.
TCLK
CTS
(Input)
TXD
(Output)
CTS sampled at three quarter point.
Collision detected when
TXD=1, but CTS=0.
Local HDLC Bus
HDLC Bus
Controller
RXD
CTS
TXD
A
HDLC Bus
Controller
RXD
CTS
TXD
B
RTS
+ 5 V
R
NOTES:
1. The TXD pins of slave devices should be configured to open-drain in the port C parallel I/O port.
2. The RTS pins of each HDLC bus controller are configured to delayed RTS mode.
RTS
Tx
Rx
EN
(1-Bit Delay)
Line Driver
