1 features, Features -2, Scc block diagram -2 – Motorola MPC8260 User Manual
Page 558
19-2
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual
MOTOROLA
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
Associated with each SCC is a digital phase-locked loop (DPLL) for external clock
recovery, which supports NRZ, NRZI, FM0, FM1, Manchester, and Differential
Manchester. If the clock recovery function is not required (that is, synchronous
communication), then the DPLL can be disabled, in which case only NRZ and NRZI are
supported.
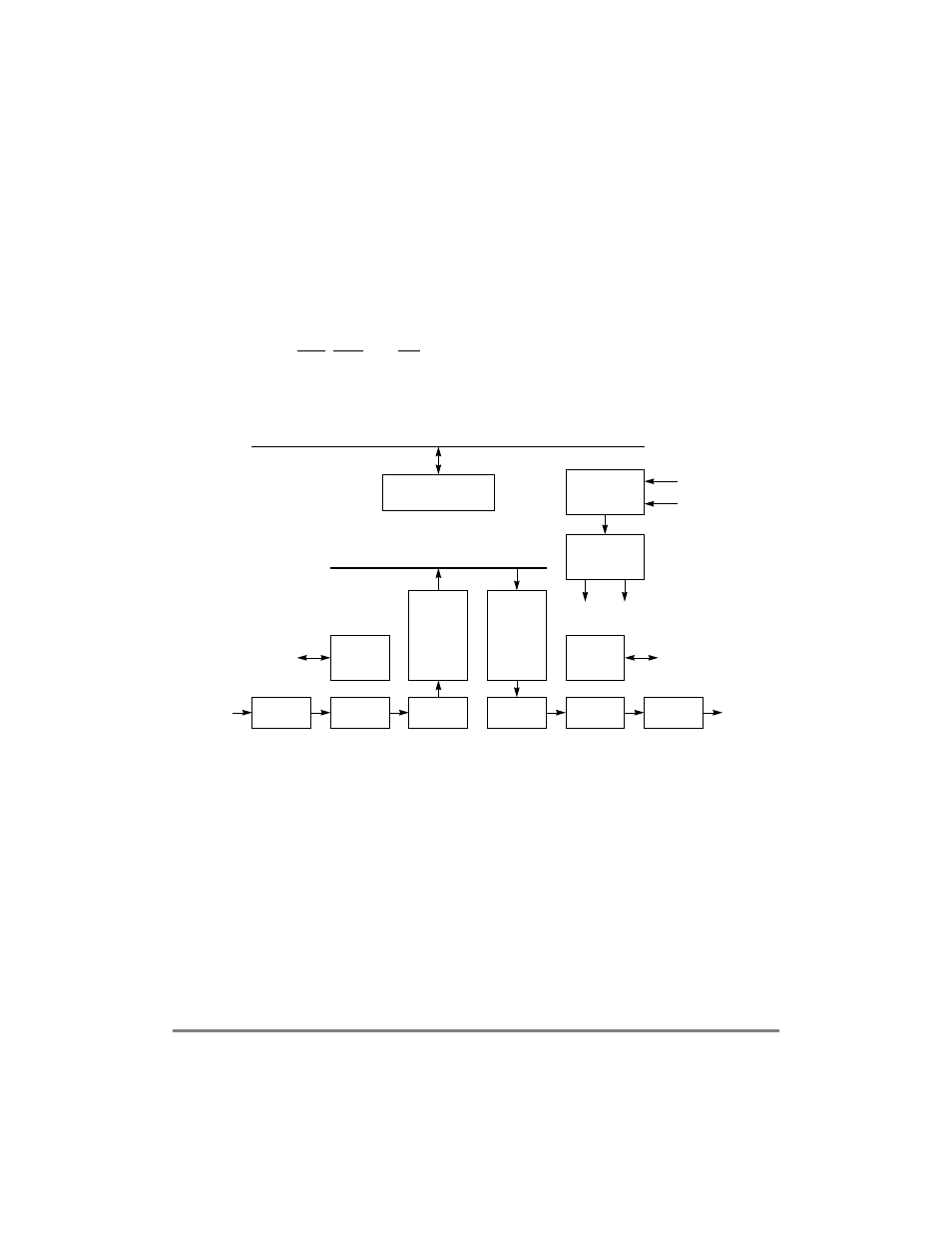
An SCC can be connected to its own set of pins on the MPC8260. This conÞguration is
called the non-multiplexed serial interface (NMSI) and is described in Chapter 14, ÒSerial
Interface with Time-Slot Assigner.Ó Using NMSI, an SCC can support standard modem
interface signals, RTS, CTS, and CD. If required, software and additional parallel I/O lines
can be used to support additional handshake signals. Figure 19-1 shows the SCC block
diagram.
Figure 19-1. SCC Block Diagram
19.1 Features
The following is a list of the main SCC features. (Performance Þgures assume a 25-MHz
system clock.)
¥
Implements HDLC/SDLC, HDLC bus, synchronous start/stop, asynchronous start/
stop (UART), AppleTalk/LocalTalk, and totally transparent protocols
¥
Supports 10-Mbps Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 (half- or full-duplex) on all SCCs
¥
Additional protocols supported through Motorola-supplied RAM microcodes:
ProÞbus, Signaling System#7 (SS7), ATM over T1/E1 (ATOM1)
¥
Additional protocols can be added in the future through the use of RAM microcodes.
Decoder
Delimiter
Shifter
Delimiter
Internal Clocks
Encoder
Modem Lines
Rx
Control
Unit
Rx
Data
FIFO
Tx
Data
FIFO
Tx
Control
Unit
RXD
Modem Lines
Clock
Generator
DPLL
and Clock
Recovery
TCLK
TXD
Control
Registers
Shifter
60x Bus
Peripheral Bus
RCLK
