Multicast addresses, Eui-64 address-based interface identifiers – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 705
680
•
A loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 (or ::1). It may never be assigned to any physical interface
and can be used by a node to send an IPv6 packet to itself in the same way as the loopback
address in IPv4.
•
An unspecified address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 (or ::). It cannot be assigned to any node. Before
acquiring a valid IPv6 address, a node fills this address in the source address field of IPv6 packets.
The unspecified address cannot be used as a destination IPv6 address.
Multicast addresses
IPv6 multicast addresses listed in
are reserved for special purposes.
Table 83 Reserved IPv6 multicast addresses
Address Application
FF01::1
Node-local scope all-nodes multicast address
FF02::1
Link-local scope all-nodes multicast address
FF01::2
Node-local scope all-routers multicast address
FF02::2
Link-local scope all-routers multicast address
FF05::2
Site-local scope all-routers multicast address
Multicast addresses also include solicited-node addresses. A node uses a solicited-node multicast
address to acquire the link-layer address of a neighboring node on the same link and to detect duplicate
addresses. Each IPv6 unicast or anycast address has a corresponding solicited-node address. The format
of a solicited-node multicast address is FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FFXX:XXXX where FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FF is fixed and
consists of 104 bits, and XX:XXXX is the last 24 bits of an IPv6 unicast address or anycast address.
EUI-64 address-based interface identifiers
An interface identifier is 64 bits and uniquely identifies an interface on a link.
Interfaces generate EUI-64 address-based interface identifiers differently.
•
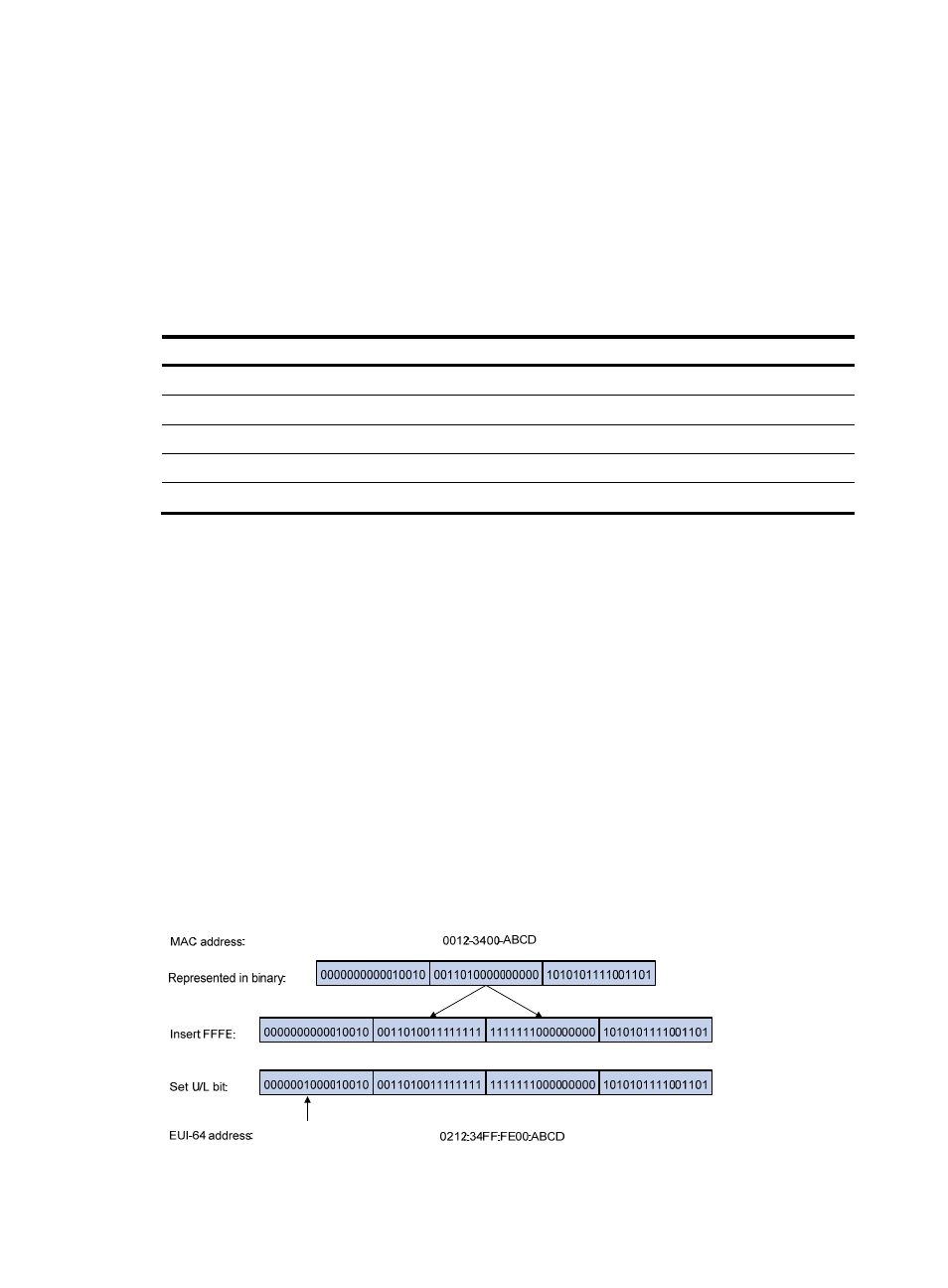
On an IEEE 802 interfaces (such as an Ethernet interface)
The interface identifier is derived from the link-layer address (typically a MAC address) of the
interface. To expand the 48-bit MAC address to a 64-bit interface identifier, the hexadecimal
number FFFE (16 bits of 1111111111111110) is inserted into the MAC address (behind the 24th
high-order bit). To make sure that the obtained interface identifier is globally unique, the
universal/local (U/L) bit (which is the seventh high-order bit) is set to 1. Thus, an EUI-64
address-based interface identifier is obtained.
Figure 354 Converting a MAC address into an EUI-64 address-based interface identifier
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS H3C SecBlade LB Cards H3C SecPath L1000-A Load Balancer
