H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 309
284
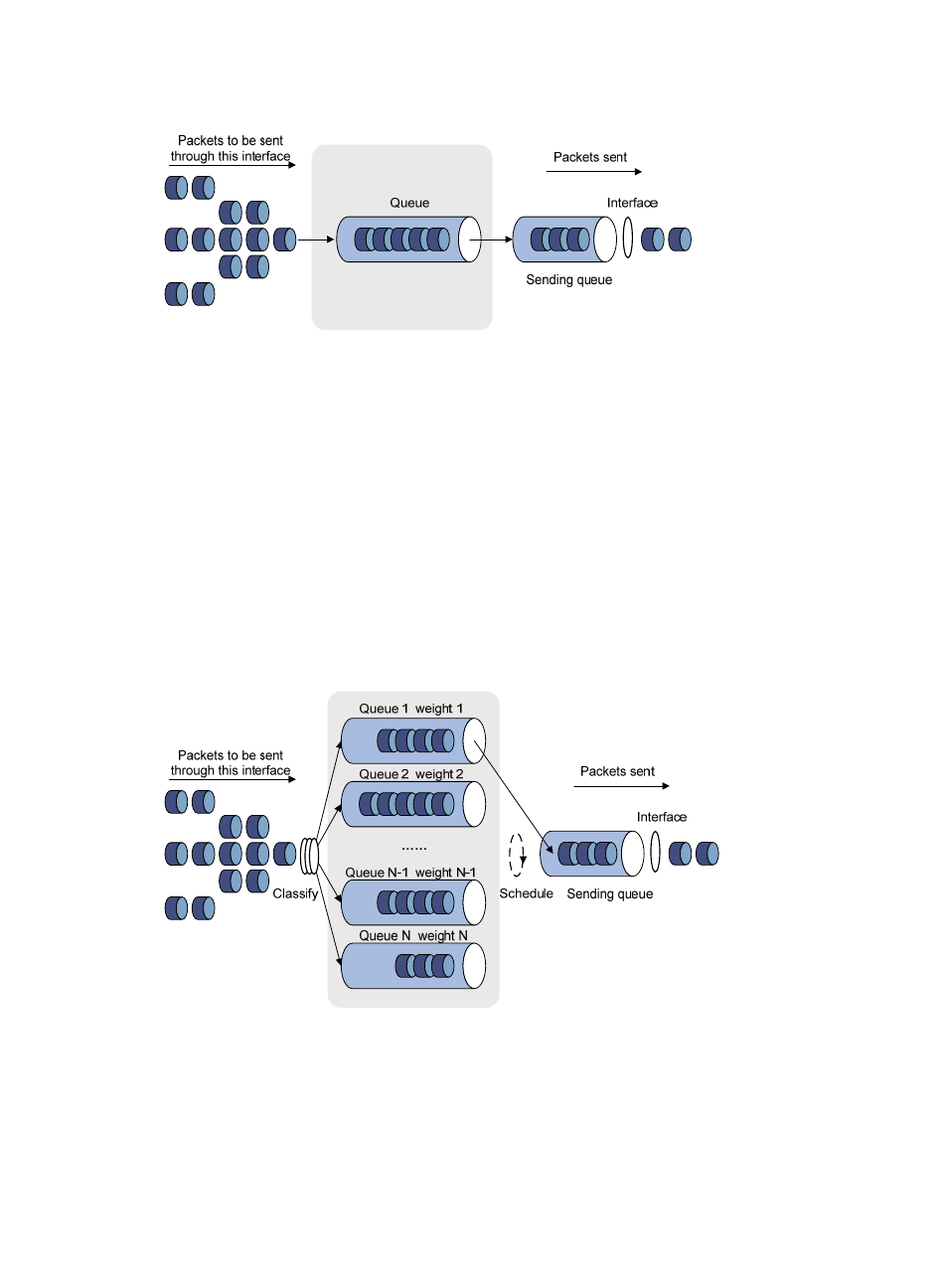
Figure 176 FIFO queuing
As shown in
, First In First Out (FIFO) uses a single queue and does not classify traffic
or schedule queues. FIFO delivers packets depending on their arrival order, with the one arriving
earlier scheduled first. The only concern of FIFO is queue length, which affects delay and packet
loss rate. On a device, resources are assigned for packets depending on their arrival order and
load status of the device. The best-effort service model uses FIFO queuing.
FIFO does not address congestion problems. If only one FIFO output/input queue exists on a port,
you can hardly ensure timely delivery of mission-critical or delay-sensitive traffic or smooth traffic
jitter. The situation gets worsened if malicious traffic is present to occupy bandwidth aggressively.
To control congestion and prioritize forwarding of critical traffic, you need to use other queue
scheduling mechanisms, where multiple queues can be configured. Within each queue, however,
FIFO is still used.
By default, FIFO queuing is used on interfaces.
2.
Weighted fair queuing
Figure 177 Weighted fair queuing (WFQ)
Before WFQ is introduced, you need to understand fair queuing (FQ). FQ is designed for fairly
allocating network resources to reduce delay and jitter of each traffic flow as possible. In an
attempt to balance the interests of all parties, FQ follows these principles:
{
Different queues have fair dispatching opportunities for delay balancing among streams.
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS H3C SecBlade LB Cards H3C SecPath L1000-A Load Balancer
