3 motion subcommands, 1 motion subcommand table, 2 motion subcommand settings – Yaskawa MP2000 Series: Built-in SVB or SVB-01 Motion Module User Manual
Page 261
6.3 Motion Subcommands
6.3.1 Motion Subcommand Table
6-100
6.3 Motion Subcommands
6.3.1 Motion Subcommand Table
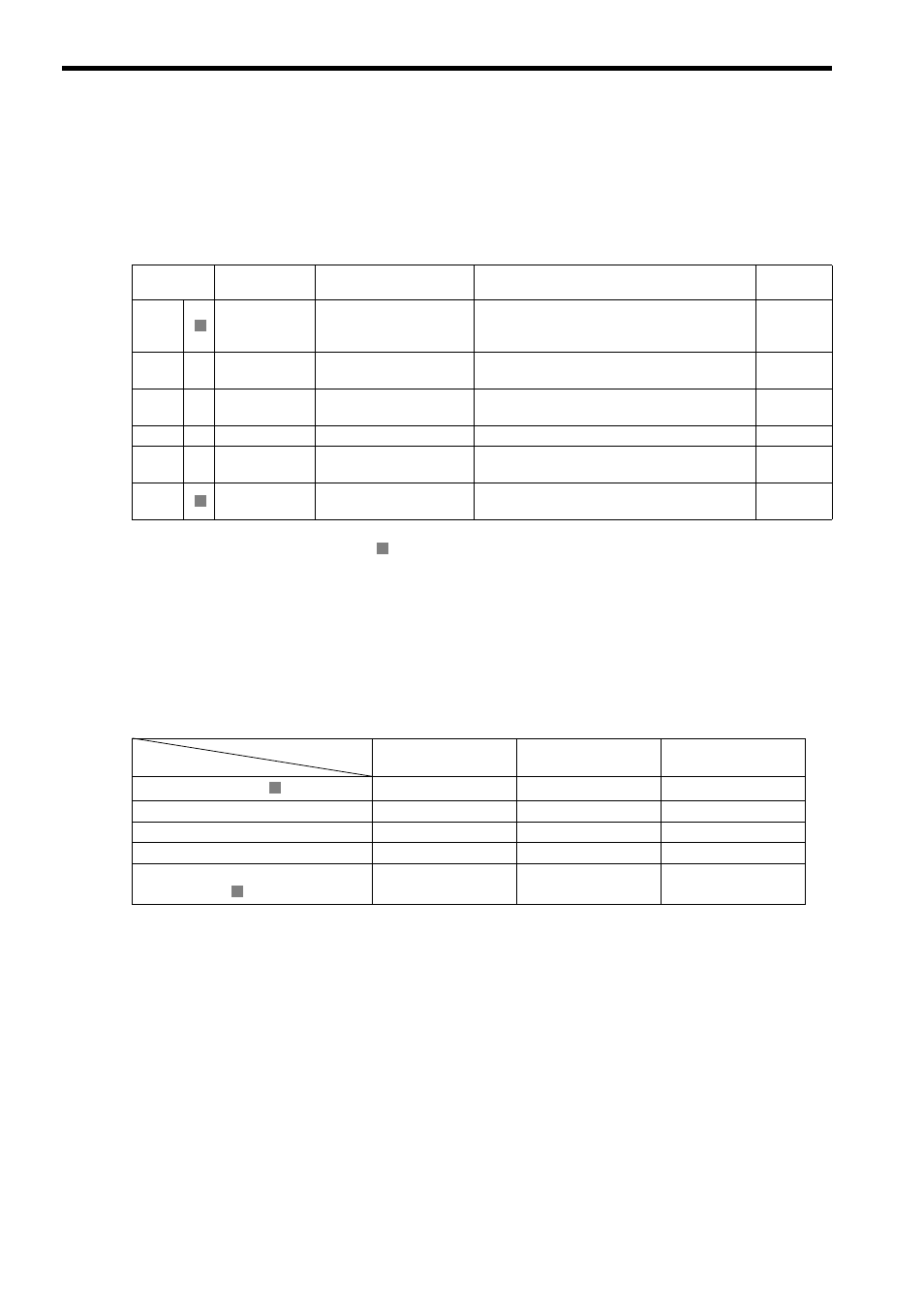
This table shows the motion subcommands that are supported by the MP2000-series Machine Controller. Refer to the
section numbers indicated in the Reference column for additional command information.
Commands in the table displaying an
are supported by the Virtual Motion Module (SVR).
6.3.2 Motion Subcommand Settings
It may not be possible to execute some subcommands, depending on the motion command and motion subcommand
combination being used. Refer to 7.1 Switchable Motion Commands and Subcommands for details on which command
combinations are allowed.
In addition, some motion subcommands can not be executed with the MECHATROLINK-I and MECHATROLINK-II
communication. See the following table.
: Can be executed.
×: Cannot be executed.
Command
Code
Command
Name
Function
Reference
0
NOP
No Command
This is a null command.
When a subcommand is not being specified, set
this “no command” code.
6.4.1
1
−
PRM_RD
Read User Constant
Reads the specified SERVOPACK parameter and
stores it in the monitoring parameters.
6.4.2
2
−
PRM_WR
Write User Constant
Changes the specified SERVOPACK parameter's
set value.
6.4.3
3
−
Reserved
Reserved by system.
−
−
4
−
SMON
Status Monitor
Stores the servo driver's status in the monitoring
parameters.
6.4.4
5
FIXPRM_RD
Read Fixed Parameters
Reads the specified fixed parameter’s current
value and stores it in the monitoring parameters.
6.4.5
R
R
R
Communication method
Subcommand
MECHATROLINK-I
MECHATROLINK-II
(17-byte)
MECHATROLINK-II
(32-byte)
No Command (NOP)
Read User Constant (PRM_RD)
×
×
Write User Constant (PRM_WR)
×
×
Status Monitor (SMON)
×
×
Read Fixed Parameters
(FIXPRM_RD)
R
R
