Apple Soundtrack Pro 3 User Manual
Page 499
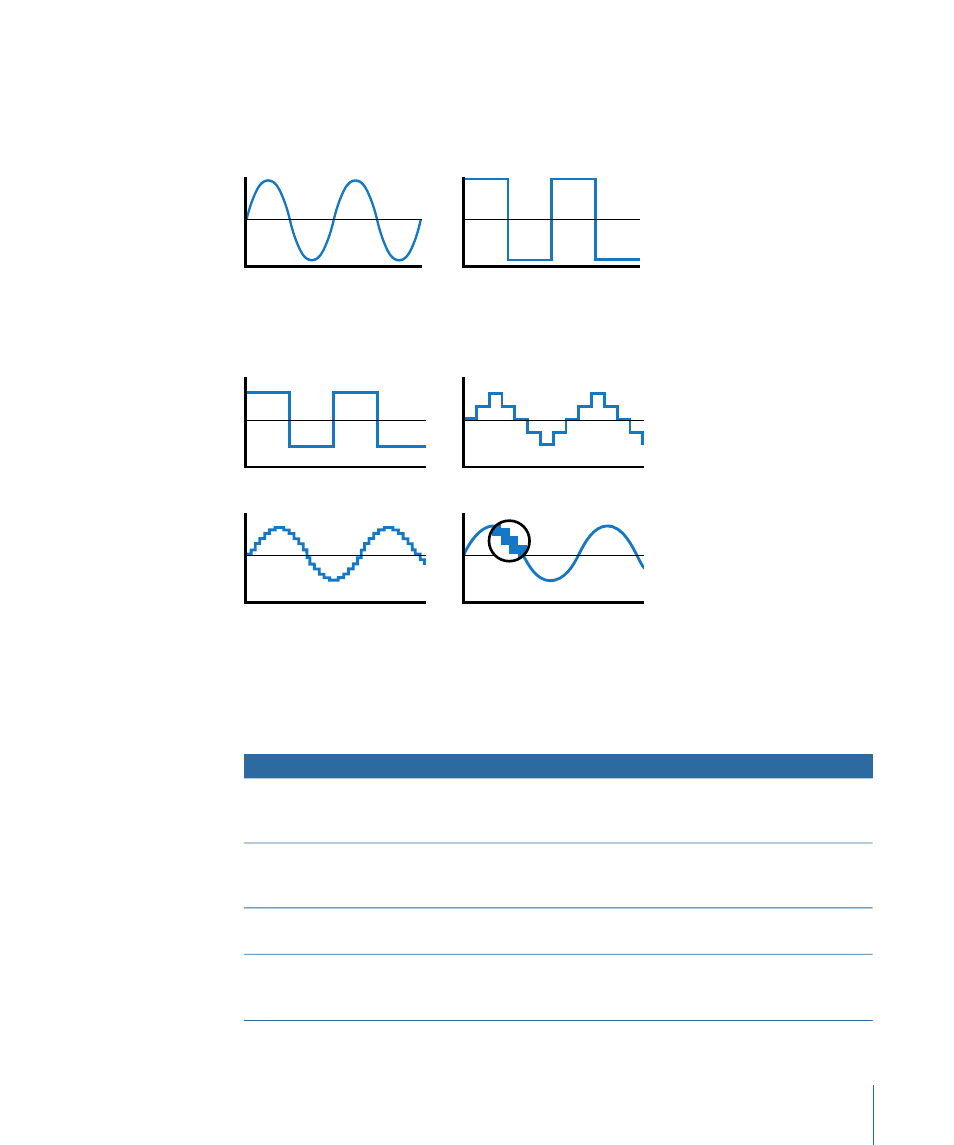
For example, a 1-bit system (a ladder with only two rungs) can represent either silence
or full volume, and nothing in between. Any audio sample that falls between these rungs
must be rounded to full volume or silence. Such a system would have absolutely no
subtlety, rounding smooth analog signals to a square-shaped waveform.
Sine
Square
When the number of bits per sample is increased, each sample can more accurately
represent the audio signal.
2-bit
1-bit
16-bit
4-bit
To avoid rounding errors, you should always use the highest bit depth your equipment
supports. Most digital video devices use 16- or 20-bit audio, so you may be limited to
one of these bit depths. However, professional audio recording devices usually support
24-bit audio, which has become the industry standard.
When used
Bit depth
This allows audio calculations, such as fader levels and effects
processing, to be performed at very high resolution with a minimum
of error, which preserves the quality of your digital audio.
32-bit floating point
This has become the audio industry standard for most audio
recording formats. Most professional audio interfaces and computer
audio editing systems can record with 24-bit precision.
24-bit
Used in some video formats such as Digital Betacam and audio
formats such as ADAT Type II.
20-bit
DAT recorders, Tascam DA-88 and ADAT Type I multitracks, and
audio CDs all use 16-bit samples. Many digital video formats, such
as DV, use 16-bit audio.
1
16-bit
499
Appendix B
Audio Fundamentals
