Rpc request, Rpc reply, Rpc request rpc reply – Brocade Network OS NETCONF Operations Guide v4.1.1 User Manual
Page 37: Figure 2, N in
Network OS NETCONF Operations Guide
5
53-1003231-02
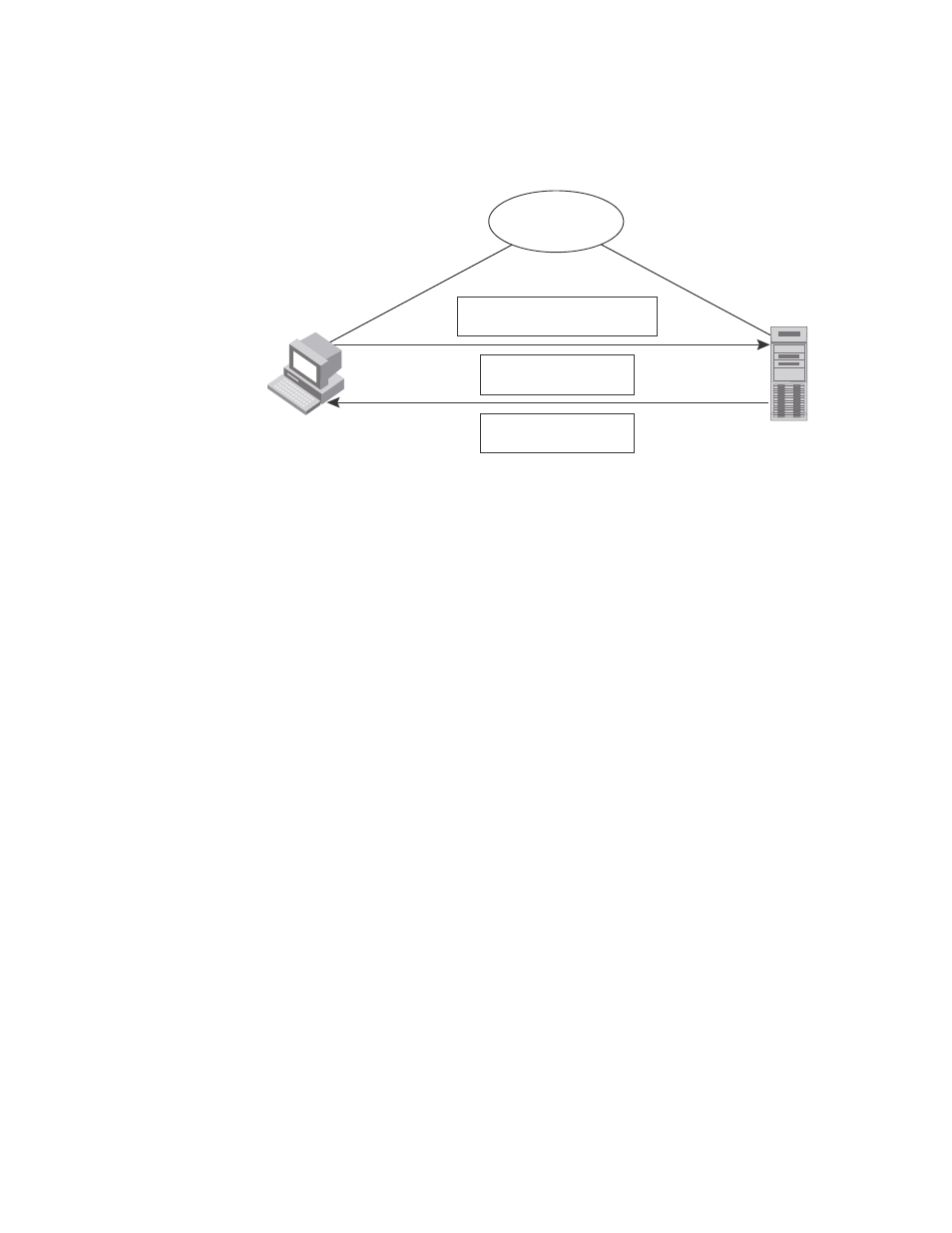
NETCONF in client/server architecture
1
FIGURE 2
NETCONF communication
The communication between the client and server consists of a series of alternating request and
reply messages. The NETCONF peers use
protocol-independent framing of NETCONF requests and responses. The NETCONF server
processes the RPC requests sequentially in the order in which they are received.
RPC request
The
Every
value for every RPC request, and is used to associate every RPC request with the corresponding
response. The message-id value is a monotonically increasing integer string. The maximum length
of the string is 4095 characters. If the message-id is not present in the RPC request, the server
rejects the request by returning an
“missing-attribute”.
If there are any additional attributes present in the RPC request, the NETCONF server returns them
unmodified in the corresponding RPC reply.
RPC reply
An
the mandatory attribute message-id copied from the corresponding RPC request, along with any
additional attributes that are present in the RPC request.
For successfully processed
content of the
For successfully processed
encoded as the content of the
For unsuccessful RPC requests, one or more
NETCONF Client
(Manager)
NETCONF Server
(Device)
SSHv2 Transport,
NETCONF port, XML
RPC (For example:
Operation)
Configuration, State
data (YANG)
RPC-REPLY
