How a cluster works – H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 807
1-3
Role
Configuration
Function
Member device
Normally, a
member device is
not assigned an
external IP
address
z
Members of a cluster
z
Discovers the information about its neighbors, processes
the commands forwarded by the management device,
and reports log. The member devices of a luster are
under the management of the management device.
Candidate
device
Normally, a
candidate device
is not assigned an
external IP
address
Candidate device refers to the devices that do not belong to
any clusters but are cluster-capable.
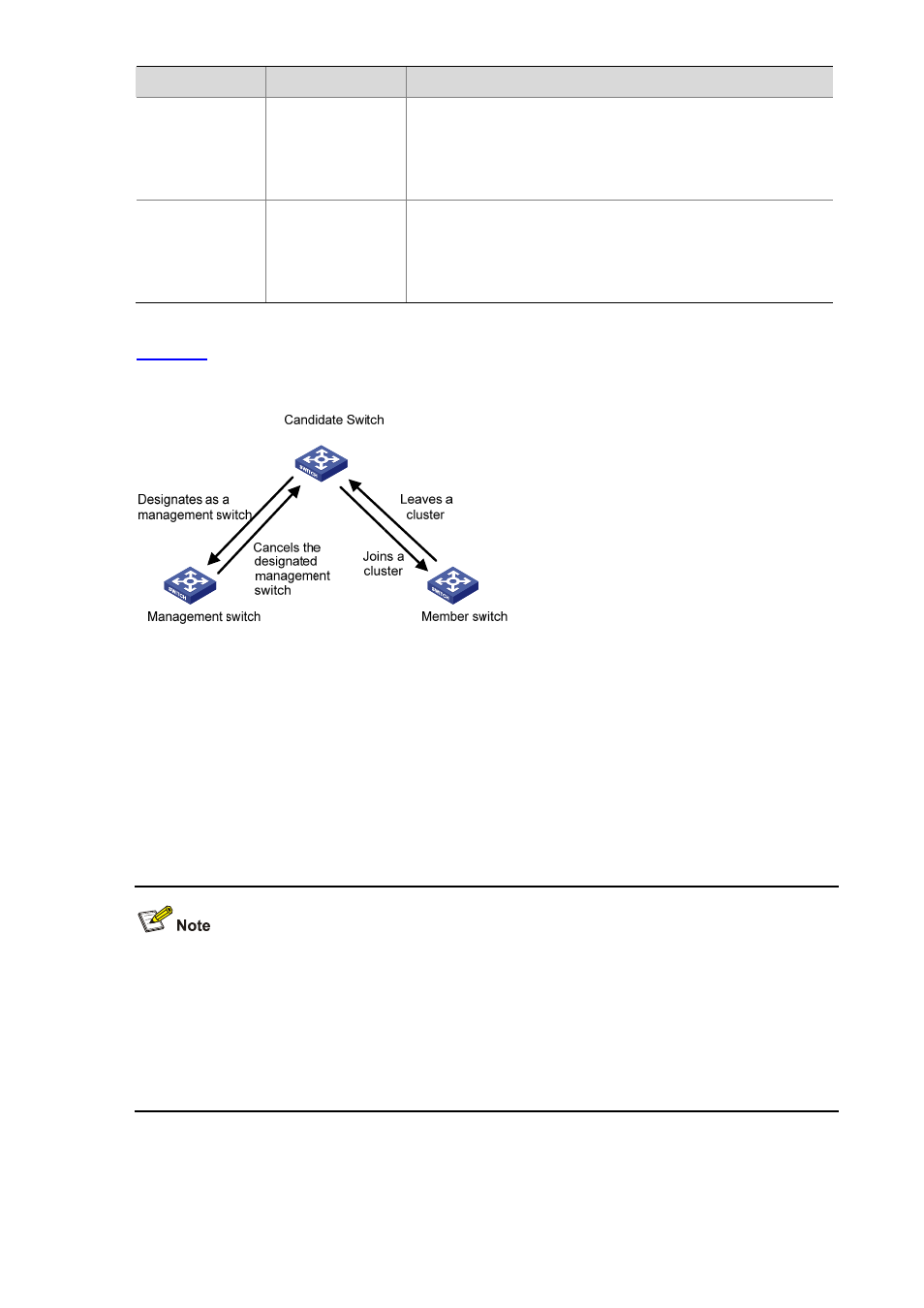
illustrates the state machine of cluster role.
Figure 1-2 State machine of cluster role
z
A candidate device becomes a management device when you create a cluster on it. Note that a
cluster must have one (and only one) management device. On becoming a management device,
the device collects network topology information and tries to discover and determine candidate
devices, which can then be added to the cluster through configurations.
z
A candidate device becomes a member device after being added to a cluster.
z
A member device becomes a candidate device after it is removed from the cluster.
z
A management device becomes a candidate device only after the cluster is removed.
After you create a cluster on an S3600 switch, the switch collects the network topology information
periodically and adds the candidate switches it finds to the cluster. The interval for a management
device to collect network topology information is determined by the NTDP timer. If you do not want the
candidate switches to be added to a cluster automatically, you can set the topology collection interval to
0 by using the ntdp timer command. In this case, the switch does not collect network topology
information periodically.
How a Cluster Works
HGMPv2 consists of the following three protocols:
