Arp attack detection – H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 603
2-2
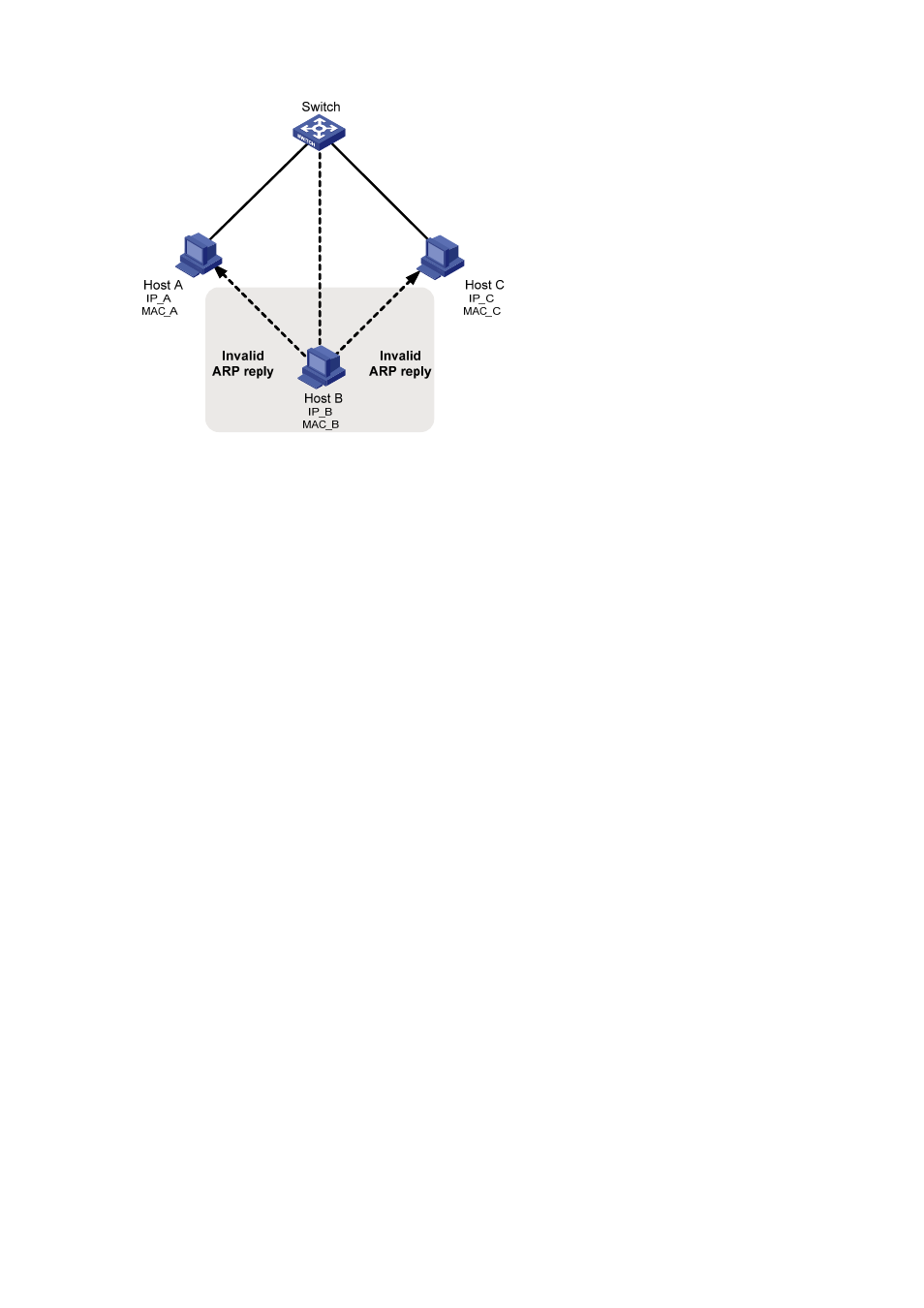
Figure 2-1 Network diagram for ARP man-in-the-middle attack
ARP attack detection
To guard against the man-in-the-middle attacks launched by hackers or attackers, S3600 series
Ethernet switches support the ARP attack detection function.
After you enable ARP attack detection for a VLAN,
z
When receiving an ARP request or response packet from an ARP untrusted port, the device
delivers the ARP packet to the CPU to check the validity of the packet. If the packet is considered to
be valid, it is forwarded; otherwise, it is discarded.
z
ARP packets received from a trusted port of the VLAN are forwarded without validity check.
After validity check, users are determined to be valid or invalid on the ports of the VLAN. Validity check
can be based on DHCP-snooping entries, IP static binding entries, or IP-to-MAC mappings of
authenticated 802.1x users, according to different network environments.
z
If all the clients connected to the switch use IP addresses obtained through DHCP, you are
recommended to enable DHCP snooping on the switch. The switch then checks validity of packets
based on DHCP-snooping entries.
z
If the clients connected to the switch use IP addresses configured manually and are few in number,
you are recommended to configure IP static binding entries on the switch. The switch then checks
validity of packets based on IP static binding entries.
z
If a large number of 802.1x clients connected to the switch use IP addresses configured manually,
you are recommended to enable ARP attack detection based on authenticated 802.1x clients on
the switch. The switch then records mappings between IP addresses (both static and dynamic IP
addresses) and MAC addresses of authenticated 802.1x clients and uses the mappings for ARP
attack detection together with DHCP-snooping entries and IP static binding entries.
