H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 295
1-42
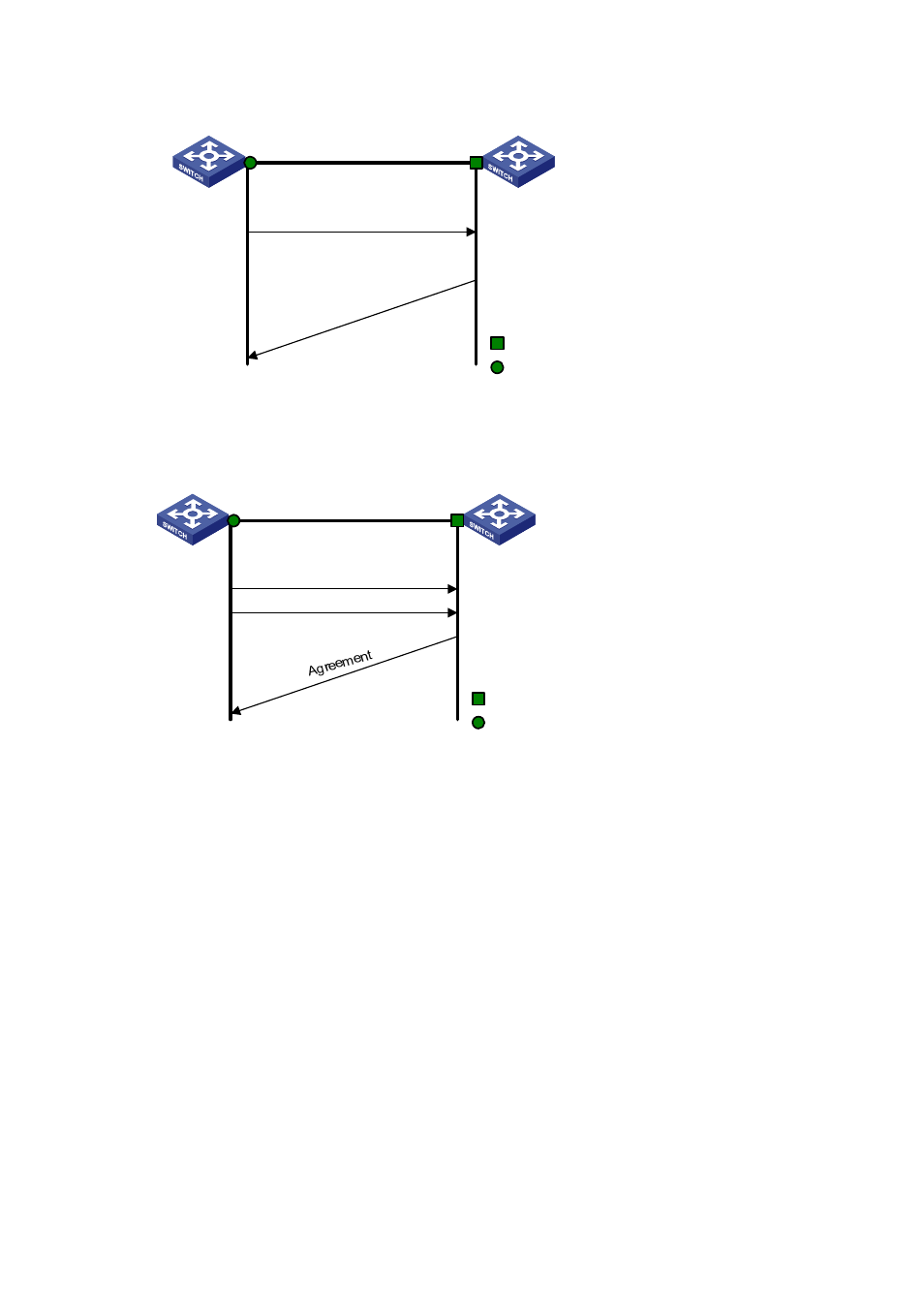
Figure 1-6
The RSTP rapid transition mechanism
Root port blocks other non-
edge ports, changes to
forwarding state and sends
Agreement to upstream device
Downstream switch
Upstream switch
Proposal for rapid transition
Agree
ment
Designated port
changes to
forwarding state
Root port
Designated port
Figure 1-7
The MSTP rapid transition mechanism
Downstream switch
Root port blocks other
non- edge ports
Root port changes to
forwarding state and
sends Agreement to
upstream switch
Designated port
changes to
forwarding state
Upstream switch
Proposal for rapid transition
Agreement
Root port
Designated port
The cooperation between MSTP and RSTP is limited in the process of rapid transition. For example,
when the upstream switch adopts RSTP, the downstream switch adopts MSTP and the downstream
switch does not support RSTP-compatible mode, the root port on the downstream switch receives no
agreement packet from the upstream switch and thus sends no agreement packets to the upstream
switch. As a result, the designated port of the upstream switch fails to transit rapidly and can only turn to
the forwarding state after a period twice the forward delay.
Some other manufacturers' switches adopt proprietary spanning tree protocols that are similar to RSTP
in the way to implement rapid transition on designated ports. When a switch of this kind operating as the
upstream switch connects with a H3C series switch running MSTP, the upstream designated port fails to
change its state rapidly.
The rapid transition feature is developed to resolve this problem. When a H3C series switch running
MSTP is connected in the upstream direction to another manufacturer's switch running proprietary
spanning tree protocols, you can enable the rapid transition feature on the ports of the H3C series
switch operating as the downstream switch. Among these ports, those operating as the root ports will
then send agreement packets to their upstream ports after they receive proposal packets from the
upstream designated ports, instead of waiting for agreement packets from the upstream switch. This
enables designated ports of the upstream switch to change their states rapidly.
