Vlan mapping, Queue scheduling – H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 740
1-10
VLAN Mapping
VLAN mapping identifies traffics using ACLs and maps the VLAN tags carrier in matched packets to
specific VLAN tags. By employing VLAN mapping on a switch connecting user networks to the carrier
network, you can map the VLAN tags of specific user network packets to those of specific VLANs in the
carrier network, thus meeting the requirements of the carrier network.
Queue Scheduling
When the network is congested, the problem that many packets compete for resources must be solved,
usually through queue scheduling.
The S3600 series switches support three queue scheduling algorithms: Strict Priority (SP) queuing,
Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ), and Weighted Round Robin (WRR) queuing.
1) SP
queuing
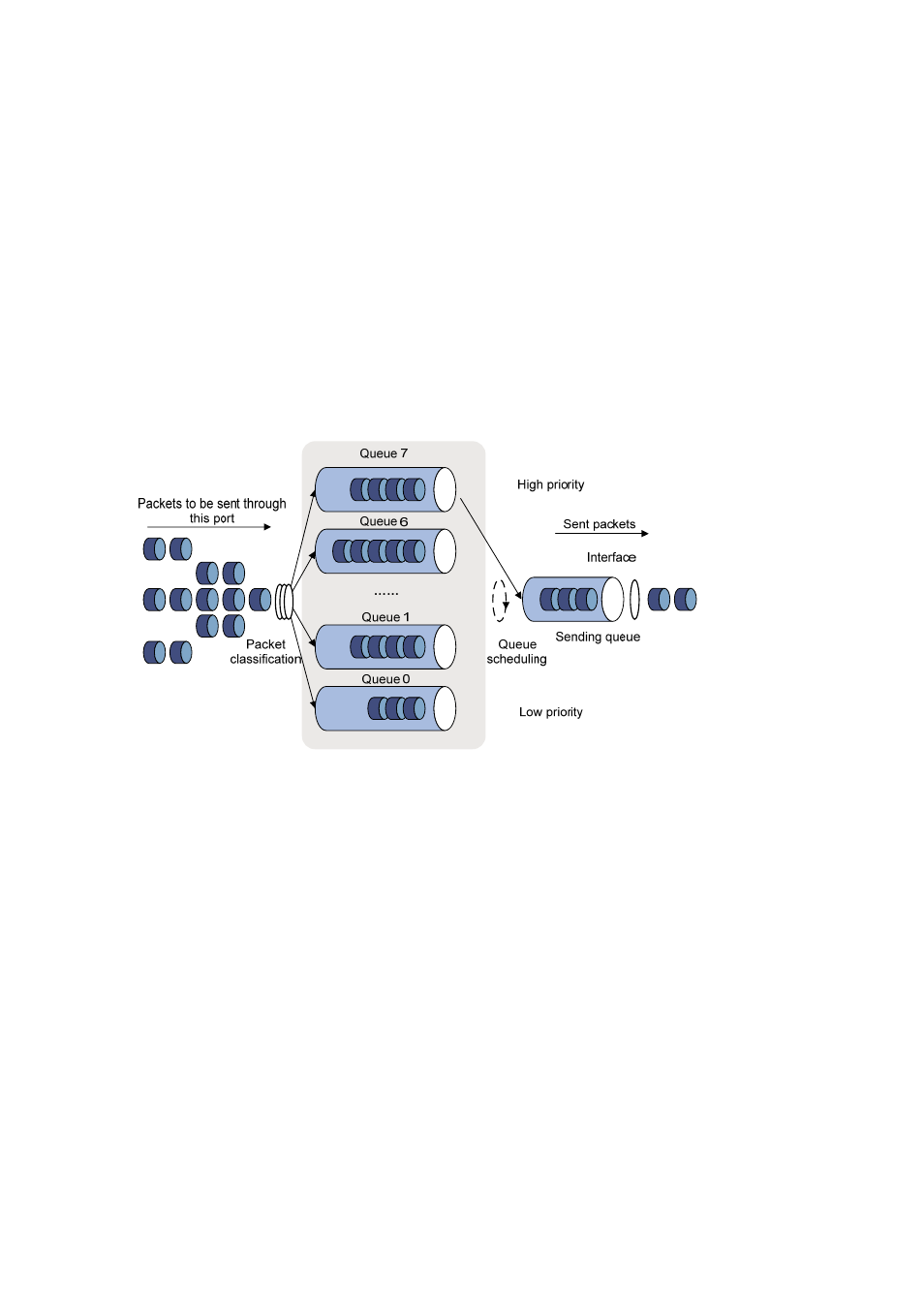
Figure 1-6 Diagram for SP queuing
SP queue-scheduling algorithm is specially designed for critical service applications. An important
feature of critical services is that they demand preferential service in congestion in order to reduce the
response delay. Assume that there are eight output queues on the port and the preferential queue
classifies the eight output queues on the port into eight classes, which are queue7, queue6, queue5,
queue4, queue3, queue2, queue1, and queue0. Their priorities decrease in order.
In queue scheduling, SP sends packets in the queue with higher priority strictly following the priority
order from high to low. When the queue with higher priority is empty, packets in the queue with lower
priority are sent. You can put critical service packets into the queues with higher priority and put
non-critical service (such as e-mail) packets into the queues with lower priority. In this case, critical
service packets are sent preferentially and non-critical service packets are sent when critical service
groups are not sent.
The disadvantage of SP queue is that: if there are packets in the queues with higher priority for a long
time in congestion, the packets in the queues with lower priority will be “starved” because they are not
served.
2) WFQ
queuing
