Dldp fundamentals, Dldp packets, Figure 1-2 – H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 222: The hollo
1-2
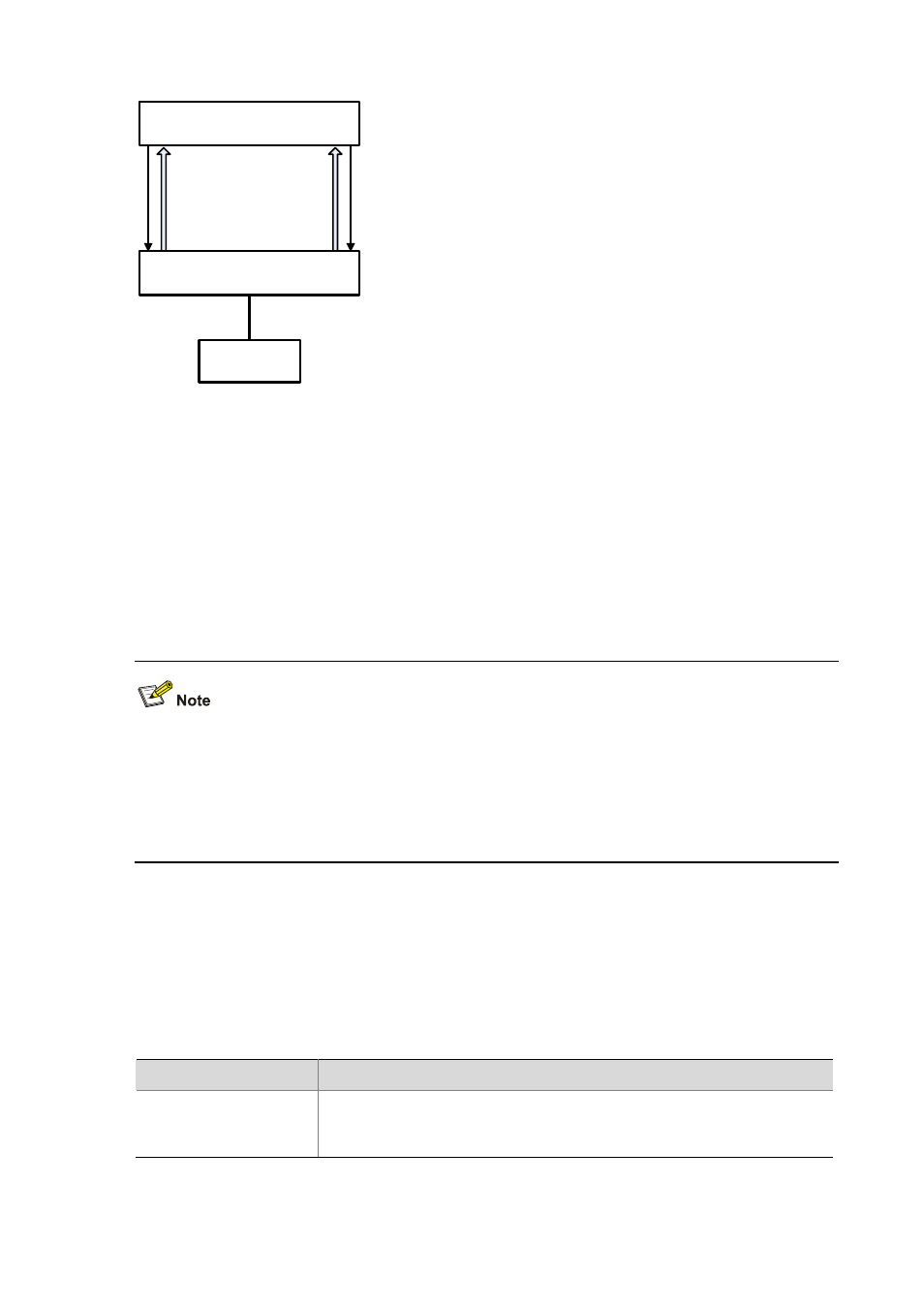
Figure 1-2 Fiber broken or not connected
Switch A
GE1/1/3
GE1/1/4
Switch B
GE1/1/3
GE1/1/4
Host
DLDP provides the following features:
z
As a link layer protocol, it works together with the physical layer protocols to monitor the link status
of a device.
z
The auto-negotiation mechanism at the physical layer detects physical signals and faults. DLDP
identifies peer devices and unidirectional links, and disables unreachable ports.
z
Even if both ends of links can work normally at the physical layer, DLDP can detect whether these
links are connected correctly and whether packets can be exchanged normally at both ends.
However, the auto-negotiation mechanism cannot implement this detection.
z
In order for DLDP to detect fiber disconnection in one direction, you need to configure the port to
work in mandatory full duplex mode at a mandatory rate.
z
When the port determines the duplex mode and speed through auto-negotiation, even if DLDP is
enabled, it does not take effect when the fiber in one direction is disconnected. In this case, the port
is considered down.
DLDP Fundamentals
DLDP packets
DLDP detects link status by exchanging the following types of packets.
Table 1-1 DLDP packet types
DLDP packet type
Function
Advertisement
Notifies the neighbor devices of the existence of the local device. An
advertisement packet carries only the local port information, and it does
not require response from the peer end.
