Graft – H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 408
4-3
corresponding interface from the outgoing interface list in the (S, G) entry and stop forwarding
subsequent packets addressed to that multicast group down to this node.
z
An (S, G) entry contains the multicast source address S, multicast group address G, outgoing
interface list, and incoming interface.
z
For a given multicast stream, the interface that receives the multicast stream is referred to as
“upstream”, and the interfaces that forward the multicast stream are referred to as “downstream”.
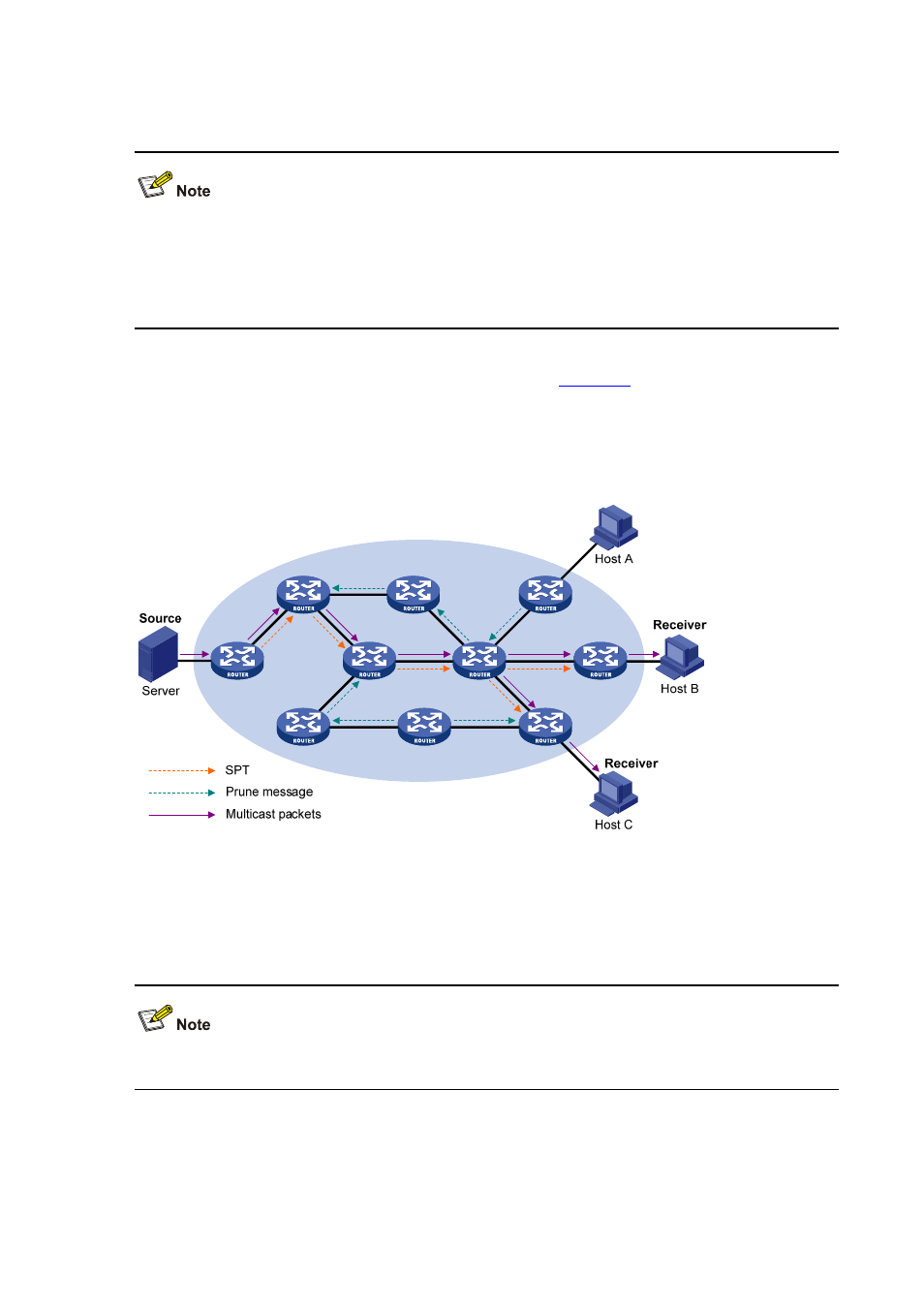
A prune process is first initiated by a leaf router. As shown in
, a router without any receiver
attached to it (the router connected with Host A, for example) sends a prune message, and this prune
process goes on until only necessary branches are left in the PIM-DM domain. These branches
constitute the SPT.
Figure 4-1 SPT building
The “flood and prune” process takes place periodically. A pruned state timeout mechanism is provided.
A pruned branch restarts multicast forwarding when the pruned state times out and then is pruned again
when it no longer has any multicast receiver.
Pruning has a similar implementation in PIM-SM.
Graft
When a host attached to a pruned node joins a multicast group, to reduce the join latency, PIM-DM uses
a graft mechanism to resume data forwarding to that branch. The process is as follows:
