Mac address replicating – H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 1039
2-2
telephone users (in VLAN 201 to VLAN 300). Packets of all these users are forwarded by Switch A to
the public network.
After the selective QinQ feature and the inner-to-outer tag mapping feature are enabled on the port
connecting Switch A to these users, the port will add different outer VLAN tags to the packets according
to their inner VLAN tags. For example, you can configure to add the tag of VLAN 1002 to the packets of
IP telephone users in VLAN 201 to VLAN 300 and forward the packets to the VoIP device, which is
responsible for processing IP telephone services.
To guarantee the quality of voice packet transmission, you can configure QoS policies in the public
network to reserve bandwidth for packets of VLAN 1002 and forward them preferentially.
In this way, you can configure different forwarding policies for data of different type of users, thus
improving the flexibility of network management. On the other hand, network resources are well utilized,
and users of the same type are also isolated by their inner VLAN tags. This helps to improve network
security.
MAC Address Replicating
Like the VLAN-VPN feature, a port with the selective QinQ enabled adds the source MAC addresses of
user packets to the MAC address table of the default VLAN on the port. However, the port with selective
QinQ enabled can insert an outer VLAN tag other than that of the default VLAN to the packets. Thus,
when packets are forwarded from the service provider to users, they may be broadcast if their
destination MAC addresses cannot be found in the MAC address table of the outer VLANs.
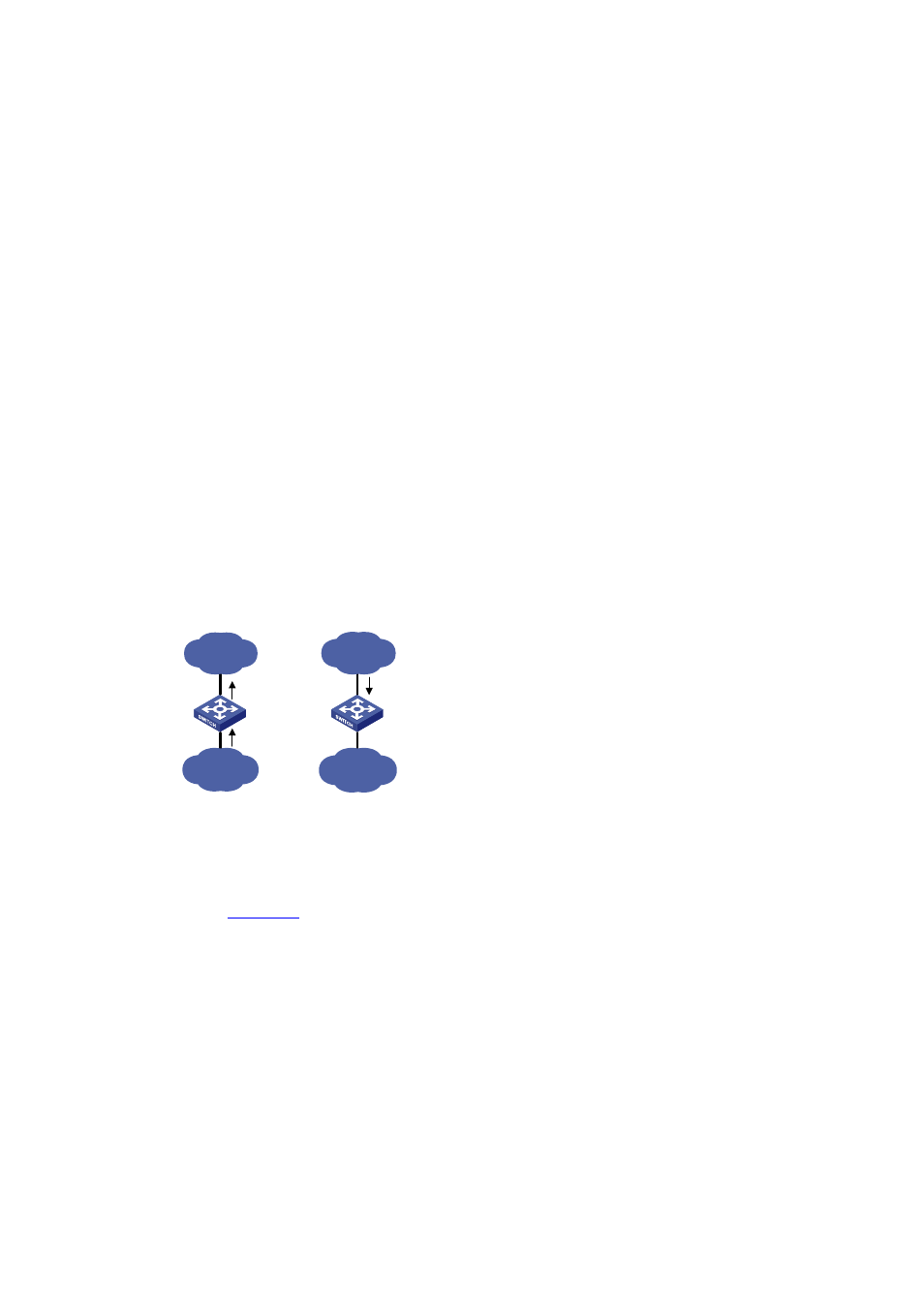
Figure 2-2 Learn MAC addresses of selective QinQ packets
VLAN3
MAC-A
VLAN4
MAC-A
PVID=2
Private
Network
Public
Network
Private
Network
Public
Network
PVID=2
VLAN4
MAC-A
Receives the data that the
private network sends to the
service provider’s network
Receives the data that the
service provider’s network
sends to the private network
As shown in
, the default VLAN of the port used to receive packets is VLAN 2. The port is
configured to receive packets of VLAN 3, tag the received packets with the outer tag of VLAN 4, and add
the source MAC addresses (MAC-A) of the packets to the MAC address table of its default VLAN (VLAN
2).
When a response packet is returned to the device from VLAN 4 of the service provider network, the
device searches the outbound port for MAC-A in the MAC address table of VLAN 4. However, because
the corresponding entry is not added to the MAC address table of VLAN 4, this packet is considered to
be a unicast packet with unknown destination MAC address. As a result, this packet will be broadcast to
all the ports in VLAN 4, which wastes the network resources and incurs potential security risks.
The S3600 series Ethernet switches provide the inter-VLAN MAC address replicating feature, which
can replicate the entries in the MAC address table of the default VLAN to that of the VLAN
corresponding to the outer tag. With the inter-VLAN MAC address replicating feature enabled, when a
device receives a packet from the service provider network, this device will find the path for the packet
