H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 137
1-2
z
Failover call routing
Refer to DHCP Operation for information about the Option184 field.
Following describes the way an IP phone acquires an IP address.
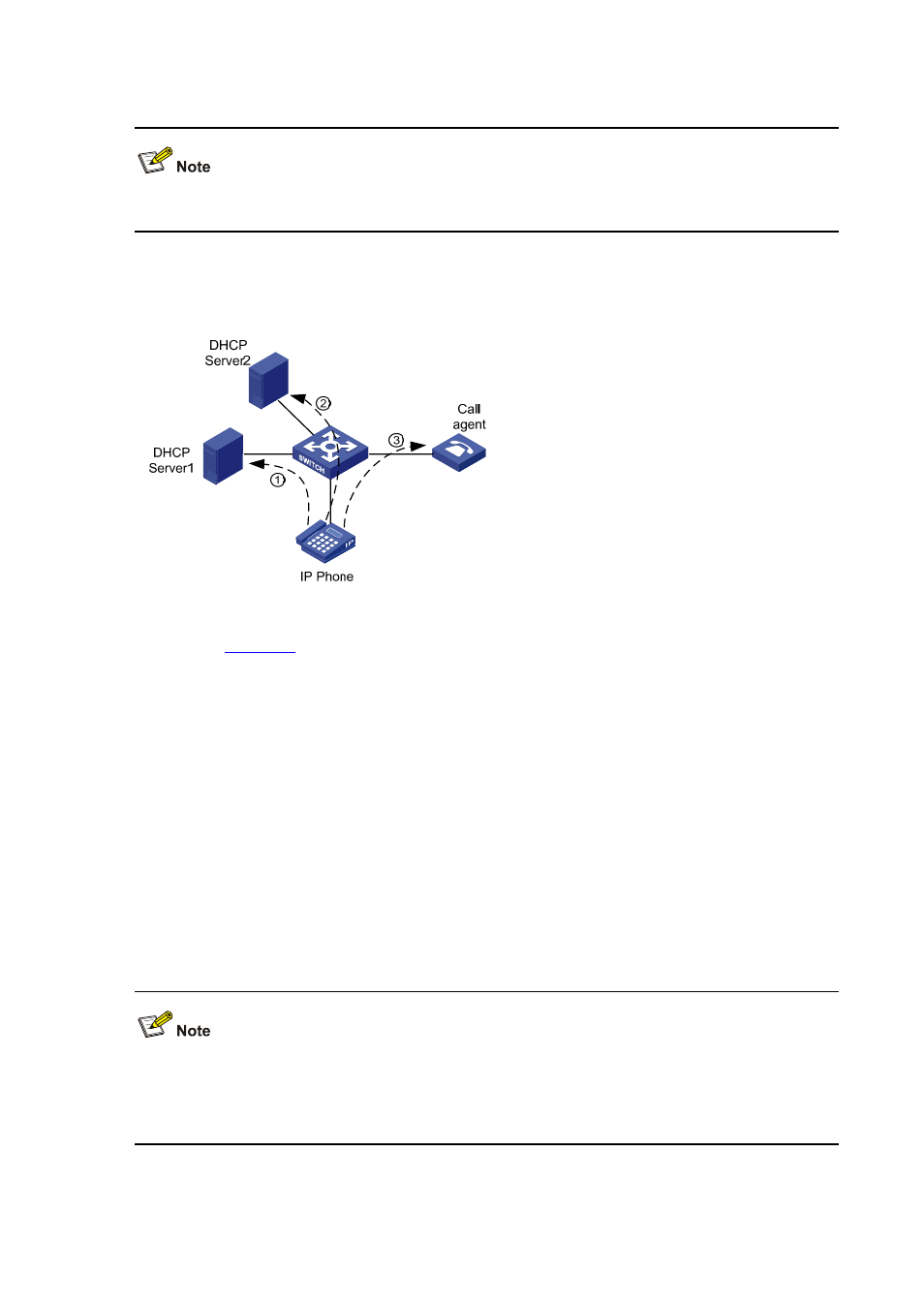
Figure 1-1 Network diagram for IP phones
As shown in
, the IP phone needs to work in conjunction with the DHCP server and the NCP
to establish a path for voice data transmission. An IP phone goes through the following three phases to
become capable of transmitting voice data.
2) After the IP phone is powered on, it sends an untagged DHCP request message containing four
special requests in the Option 184 field besides the request for an IP address. The message is
broadcast in the default VLAN of the receiving port. After receiving the DHCP request message,
DHCP Server 1, which resides in the default VLAN of the port receiving the message, responds as
follows:
z
If DHCP Server 1 does not support Option 184, it returns the IP address assigned to the IP phone
but ignores the other four special requests in the Option 184 field. Without information about voice
VLAN, the IP phone can only send untagged packets in the default VLAN of the port the IP phone is
connected to. In this case, you need to manually configure the default VLAN of the port as a voice
VLAN.
In cases where an IP phone obtains an IP address from a DHCP server that does not support Option
184, the IP phone directly communicates through the gateway after it obtains an IP address. It does not
go through the steps described below.
z
If DHCP Server 1 supports Option 184, it returns the IP address assigned to the IP phone, the IP
address of the NCP, the voice VLAN ID, and so on.
