Roles in multicast – H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 378
1-4
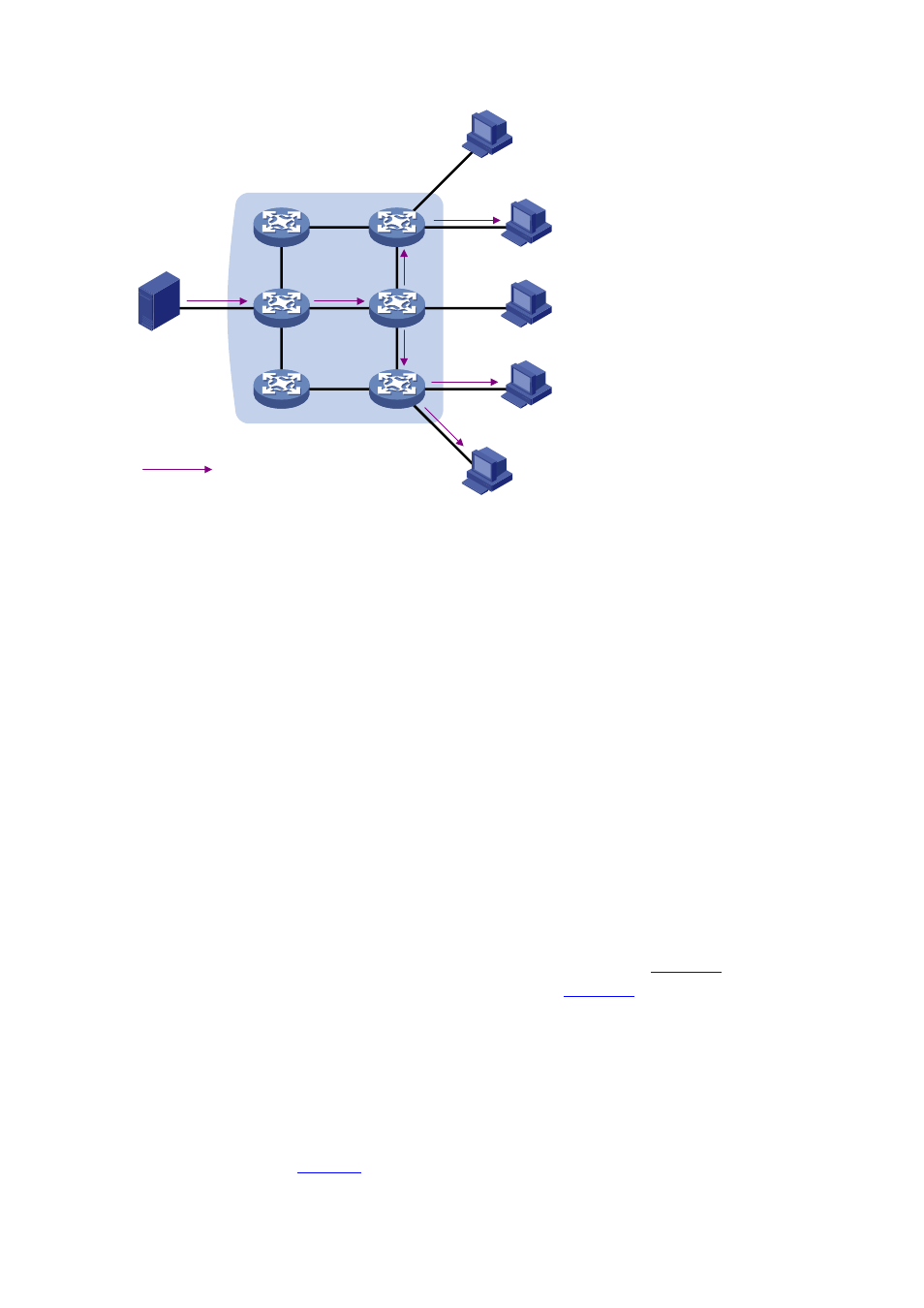
Figure 1-3 Information transmission in the multicast mode
Source
Server
Receiver
Receiver
Receiver
Host A
Host B
Host C
Host D
Host E
Packets for the multicast group
Assume that Hosts B, D and E need the information. To transmit the information to the right users, it is
necessary to group Hosts B, D and E into a receiver set. The routers on the network duplicate and
distribute the information based on the distribution of the receivers in this set. Finally, the information is
correctly delivered to Hosts B, D, and E.
The advantages of multicast over unicast are as follows:
z
No matter how many receivers exist, there is only one copy of the same multicast data flow on each
link.
z
With the multicast mode used to transmit information, an increase of the number of users does not
add to the network burden remarkably.
The advantages of multicast over broadcast are as follows:
z
A multicast data flow can be sent only to the receiver that requires the data.
z
Multicast brings no waste of network resources and makes proper use of bandwidth.
Roles in Multicast
The following roles are involved in multicast transmission:
z
An information sender is referred to as a multicast source (“Source” in
).
z
Each receiver is a multicast group member (“Receiver” in
z
All receivers interested in the same information form a multicast group. Multicast groups are not
subject to geographic restrictions.
z
A router that supports Layer 3 multicast is called multicast router or Layer 3 multicast device. In
addition to providing multicast routing, a multicast router can also manage multicast group
members.
For a better understanding of the multicast concept, you can use the analogy of a transmission of TV
programs, as shown in
