Introduction to qos functions, Traffic classification, Priority trust mode – H3C Technologies H3C S3600 Series Switches User Manual
Page 734: Introduction to precedence types
1-4
Introduction to QoS Functions
Traffic Classification
Traffic here refers to service traffic; that is, all the packets passing the switch.
Traffic classification means identifying packets that conform to certain characteristics according to
certain rules. It is the foundation for providing differentiated services.
In traffic classification, the priority bit in the type of service (ToS) field in IP packet header can be used to
identify packets of different priorities. The network administrator can also define traffic classification
policies to identify packets by the combination of source address, destination address, MAC address, IP
protocol or the port number of an application. Normally, traffic classification is done by checking the
information carried in packet header. Packet payload is rarely adopted for traffic classification. The
identifying rule is unlimited in range. It can be a quintuplet consisting of source address, source port
number, protocol number, destination address, and destination port number. It can also be simply a
network segment.
Priority Trust Mode
Introduction to precedence types
1) IP precedence, ToS precedence, and DSCP precedence
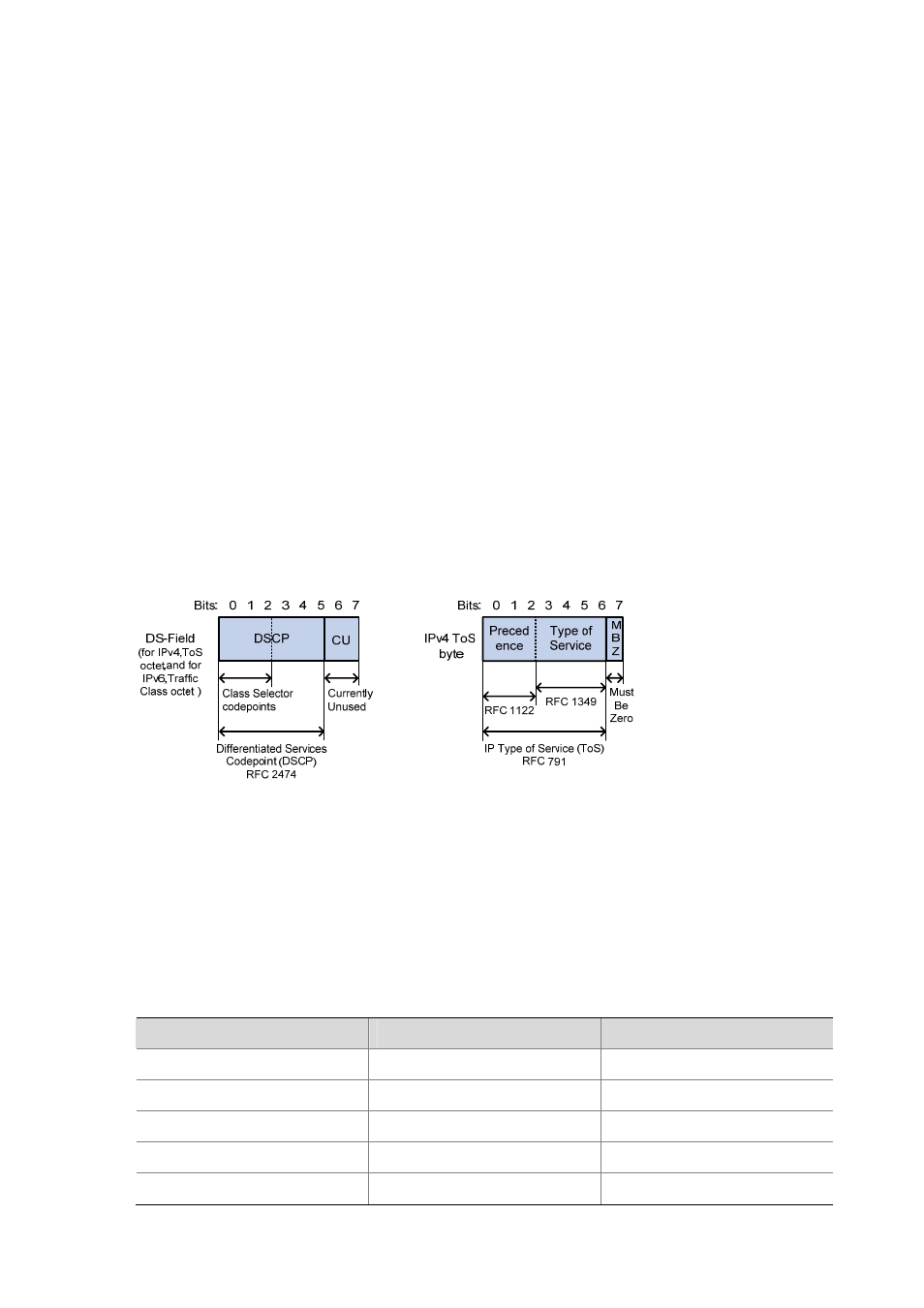
Figure 1-2 DS field and ToS byte
The ToS field in an IP header contains eight bits numbered 0 through 7, among which,
z
The first three bits indicate IP precedence in the range 0 to 7.
z
Bit 3 to bit 6 indicate ToS precedence in the range of 0 to 15.
z
In RFC2474, the ToS field in IP packet header is also known as DS field. The first six bits (bit 0
through bit 5) of the DS field indicate differentiated service codepoint (DSCP) in the range of 0 to 63,
and the last two bits (bit 6 and bit 7) are reserved.
Table 1-2 Description on IP Precedence
IP Precedence (decimal)
IP Precedence (binary)
Description
0 000
Routine
1 001
priority
2 010
immediate
3 011
flash
4 100
flash-override
