Chapter 44 a/d converter, Overview of a/d converter – FUJITSU MB91460 SERIES FR60 User Manual
Page 901
885
Chapter 44 A/D Converter
1.Overview of A/D Converter
Chapter 44 A/D Converter
This chapter provides an overview of the A/D converter, describes the register structure and functions, and
describes the operation of the A/D converter.
•
•
2. Block Diagram of A/D Converter
•
• 4. Operation of A/D Converter
1. Overview of A/D Converter
The A/D converter converts analog input voltage into digital values and provides the following features.
Features of A/D converter:
Conversion time: minimum 3 us per channel.
RC type successive approximation conversion with sample & hold circuit
10-bit or 8-bit resolution
Program section analog input from 32 channels
Single conversion mode: conversion of one selected channel
Scan conversion mode: continuous conversion of multiple channels, programmable for up to 32 channels
Single conversion mode:
Convert the specified channel only once.
Continuous mode:
Repeatedly convert the specified channels.
Stop mode:
Convert one channel then temporarily halt until the next activation.
(Enables synchronization of the conversion start timing.)
A/D conversion can be followed by an A/D conversion interrupt request to CPU. This interrupt, an option that
is ideal for continuous processing can be used to start a DMA transfer of the results of A/D conversion to
memory.
Startup may be by software, external trigger (falling edge) or timer (rising edge).
■
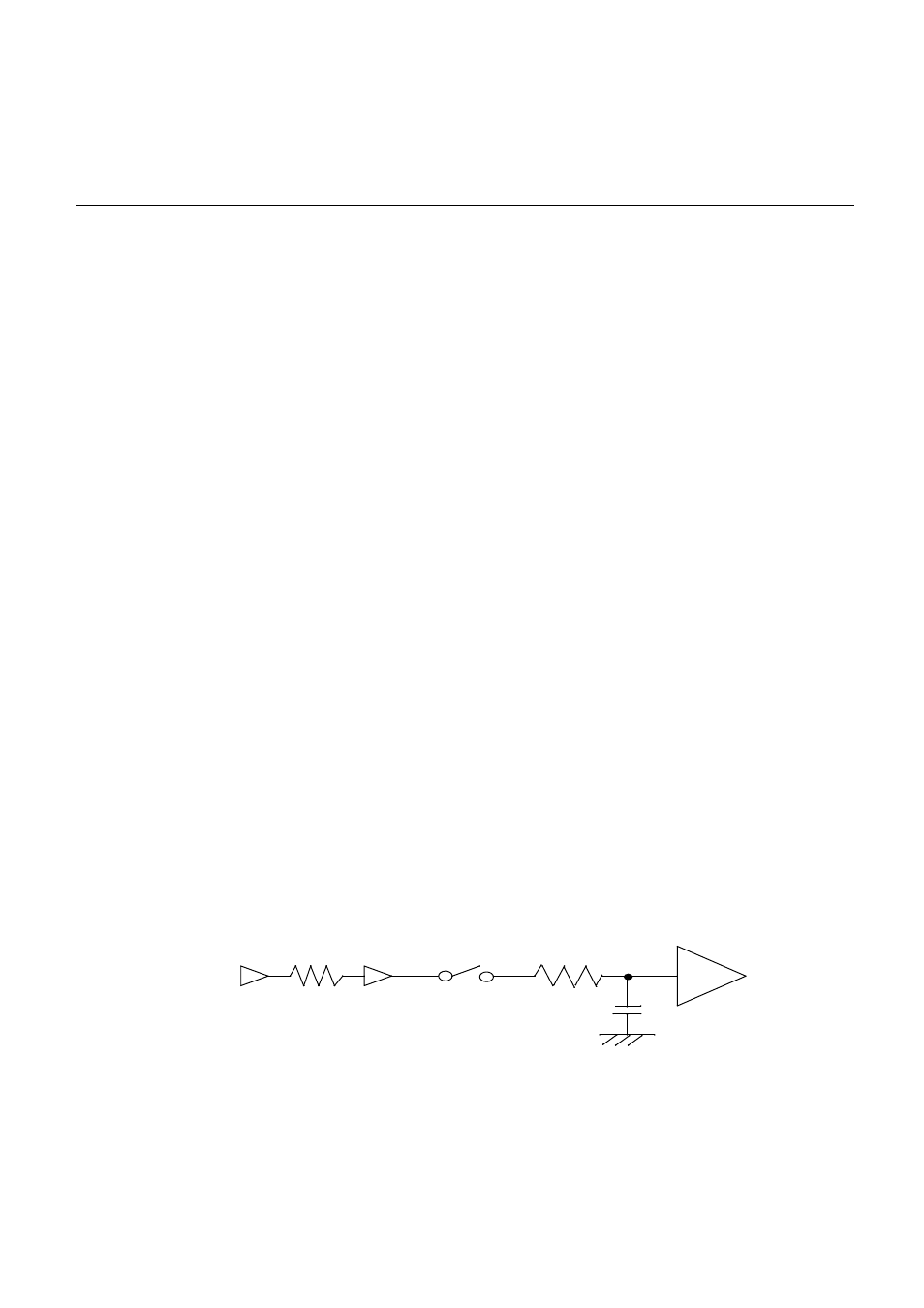
Input impedance
Sampling circuit of A/D converter is expressed in
Figure 1-1 Input Impedance
Don•ft set Rext over maximum sampling time (Tsamp).
Re xt = Ts amp/ (7*Cin) - Rin
Cin:max 10.7pF
Rin
13.6kƒ¶ (AVCC•† 4.0V)
2.52kƒ¶ (AVCC•† 4.5V)
ADC
Analog S W
ANx
Analog
s ignal
s ourc e
Re xt
