Burst fly-by transfer, Demand transfer 2-cycle transfer – FUJITSU MB91460 SERIES FR60 User Manual
Page 374
358
Chapter 26 DMA Controller
3.DMA Controller (DMAC) Operation
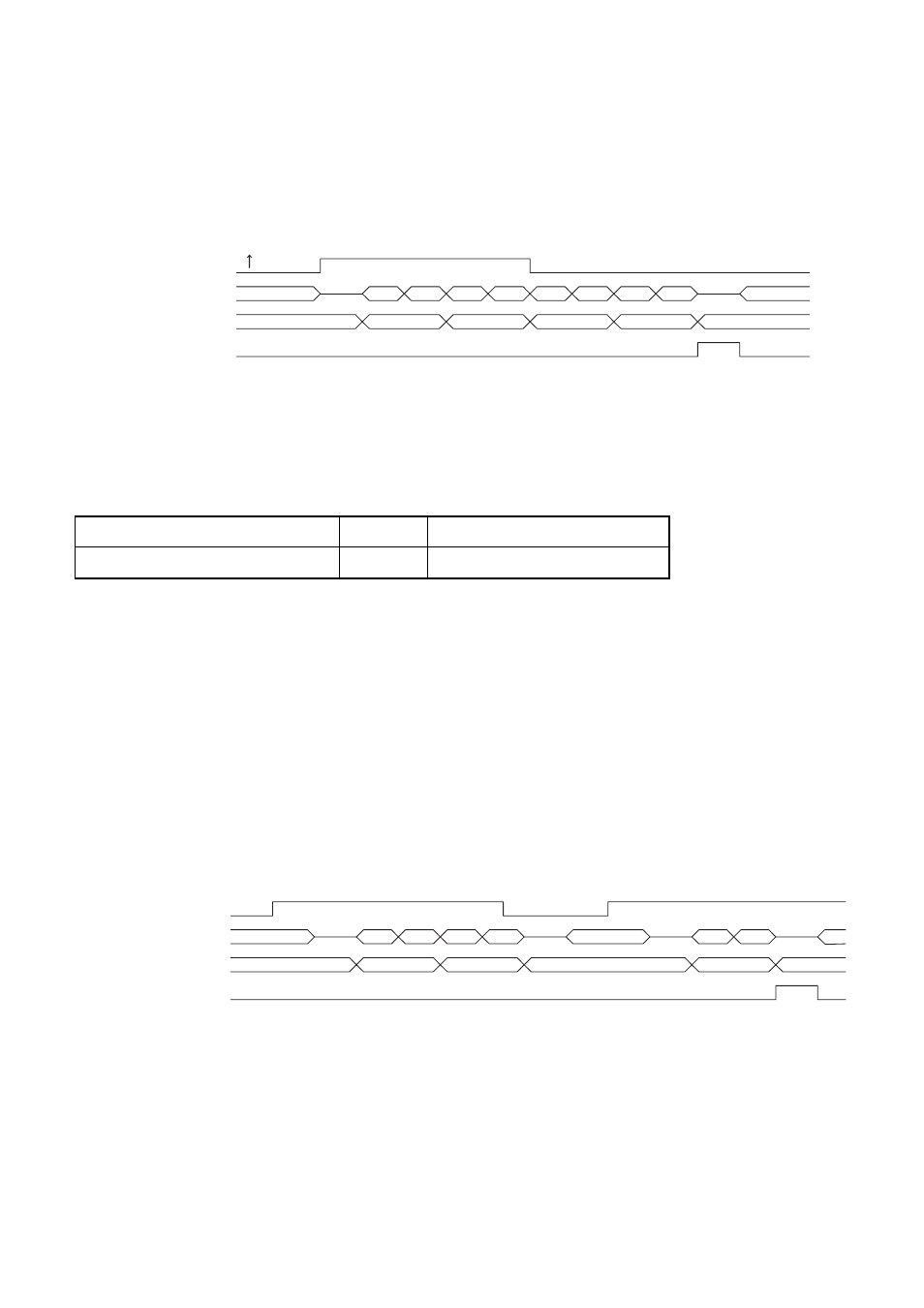
Figure 3-1 Example of burst transfer for a start on an external pin rising edge, number of blocks =1, and
transfer count = 4
●
Burst fly-by transfer
A burst fly-by transfer has the same features as a 2-cycle transfer except that the transfer area can only be
external areas, and the transfer unit is read (memory --> I/O) or write (I/O --> memory) only.
●
Demand Transfer 2-Cycle Transfer
A demand transfer sequence is generated only if H level or L level of an external pin is selected as a transfer
request. Select the level with IS[3:0] of DMACA.
The following are some features of a continuous transfer:
The following are some features of a continuous transfer:
•
Each transfer operation of a transfer request is checked. While the external input level is within the range of
the specified transfer request levels, transfer is performed continuously without the request being cleared. If
the external input changes, the request is cleared and the transfer stops at the transfer boundary. This
operation is repeated for the number of times specified by the transfer count.
•
Otherwise, operations are the same as those of a burst transfer.
Figure 3-2 Example of demand transfer for a start with the external pin at H level, number of blocks = 1,
and transfer count = 3
Table 3-2 Specifiable transfer addresses (burst fly-by transfer)
Transfer source addressing
Direction
Transfer destination addressing
Specification not required (invalid)
None
External area
Transfer count
Bus operation
CPU
SA
DA
SA
DA
SA
DA
SA
DA
CPU
4
3
1
2
Transfer end
0
Transfer request ( edge)
CPU
SA
DA
SA
DA
SA
DA
3
2
1
0
CPU
Transfer request (H level)
Bus operation
Transfer count
Transfer end
