3 sci after reset, Sci after reset -5, Sci registers after reset -5 – Motorola DSP56301 User Manual
Page 241: 3 sci after reset, There are several different ways to reset the sci, Hardware, Signal
SCI After Reset
Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
8
-5
8.3
SCI After Reset
There are several different ways to reset the SCI:
n
Hardware
RESET
signal
n
Software RESET instruction:
Both hardware and software resets clear the port control register bits, which configure
all I/O as GPIO input. The SCI remains in the Reset state as long as all SCI signals are
programmed as GPIO (
PC2
,
PC1
, and
PC0
all are cleared); the SCI becomes active
only when at least one of the SCI I/O signals is not programmed as GPIO.
n
Individual reset:
During program execution, the PC2, PC1, and PC0 bits can all be cleared (that is,
individually reset), causing the SCI to stop serial activity and enter the Reset state. All
SCI status bits are set to their reset state. However, the contents of the SCR remain
unaffected so the DSP program can reset the SCI separately from the other internal
peripherals. During individual reset, internal DMA accesses to the data registers of the
SCI are not valid, and the data is unknown.
n
Stop processing state reset (that is, the STOP instruction)
Executing the STOP instruction halts operation of the SCI until the DSP is restarted,
causing the SCI Status Register (SSR) to be reset. No other SCI registers are affected
by the STOP instruction.
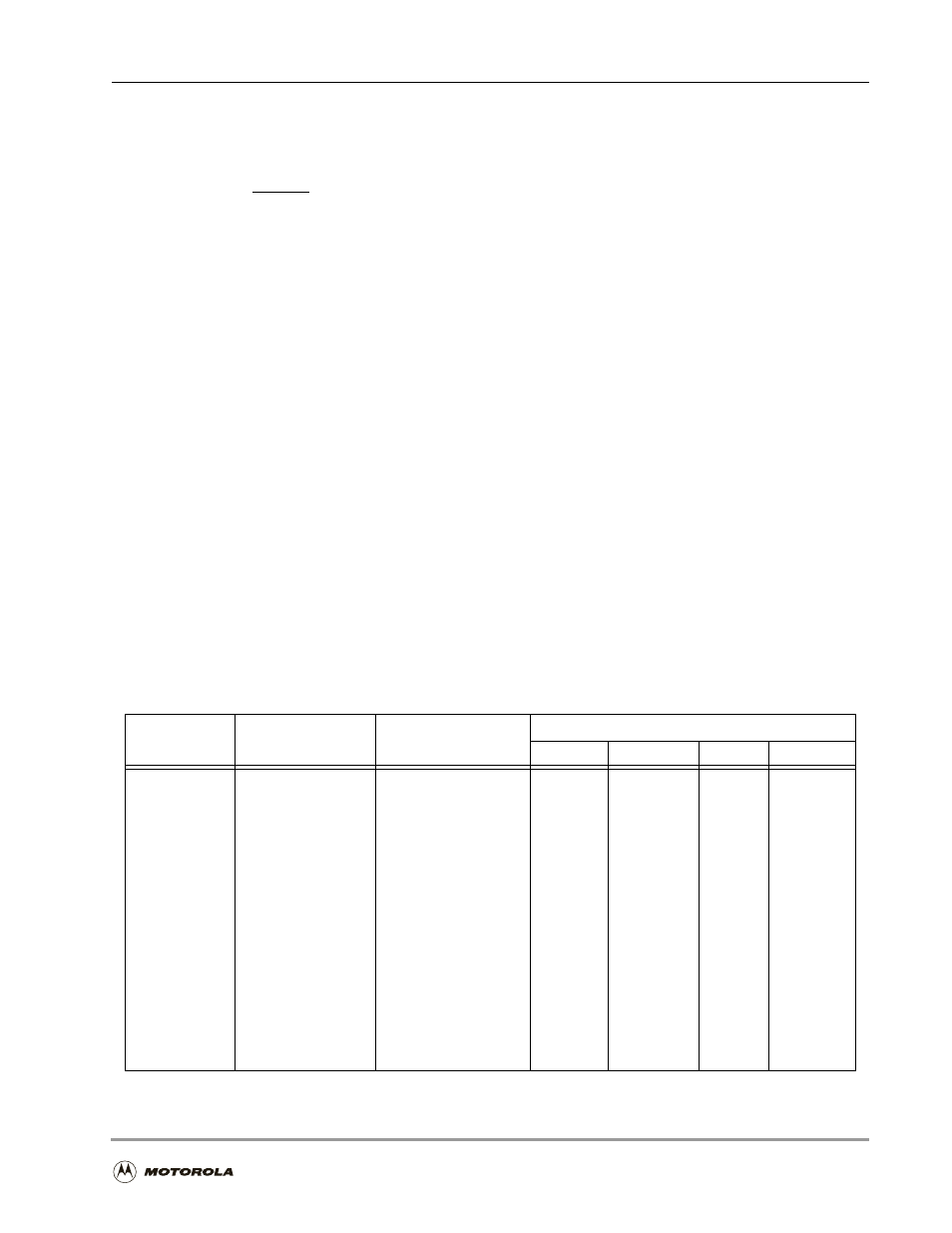
Table 8-1 illustrates how each type of reset affects each register in the SCI.
Table 8-1. SCI Registers After Reset
Register
Bit Mnemonic
Bit Number
Reset Type
HW Reset
SW Reset
IR Reset
ST Reset
SCR
REIE
16
0
0
—
—
SCKP
15
0
0
—
—
STIR
14
0
0
—
—
TMIE
13
0
0
—
—
TIE
12
0
0
—
—
RIE
11
0
0
—
—
ILIE
10
0
0
—
—
TE
9
0
0
—
—
RE
8
0
0
—
—
WOMS
7
0
0
—
—
RWU
6
0
0
—
—
WAKE
5
0
0
—
—
SBK
4
0
0
—
—
SSFTD
3
0
0
—
—
WDS[2–0]
2–0
0
0
—
—
