Signal (shown as ~ss0 ) – Motorola DSP56301 User Manual
Page 19
Manual Conventions
Overview
1
-3
n
Pins or signals that are asserted low (made active when pulled to ground) are indicated
like this:
— In text, they have an overbar: for example,
RESET
is asserted low.
— In code examples, they have a tilde in front of their names. In Example 1-1, line 3
refers to the
SS0
signal (shown as
~SS0
).
n
Sets of signals are indicated by the first and last signals in the set, for instance
HA[0–2
].
n
“Input/Output” indicates a bidirectional signal. “Input or Output” indicates a signal
that is exclusively one or the other.
n
Code examples are displayed in a monospaced font, as shown in Example 1-1.
n
Hexadecimal values are indicated with a dollar sign ($) preceding the value. For
example, $FFFFFF is the X memory address for the core interrupt priority register.
n
The word “reset” appears in four different contexts in this manual:
— the reset signal, written as
RESET
— the reset instruction, written as RESET
— the reset operating state, written as Reset
— the reset function, written as reset
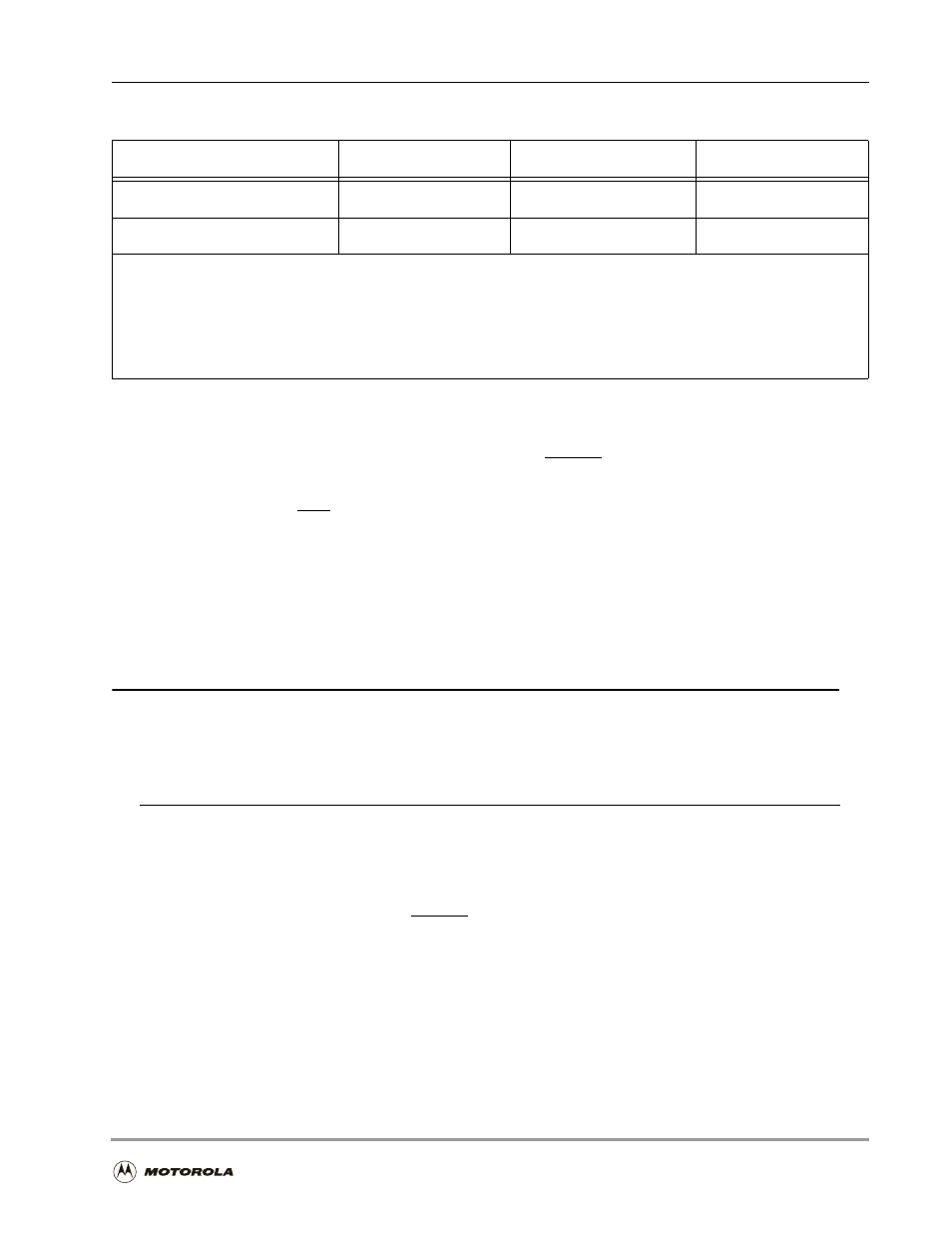
PIN
True
Asserted
V
CC
3
PIN
False
Deasserted
Ground
2
1.
PIN is a generic term for any pin on the chip.
2.
Ground is an acceptable low voltage level. See the appropriate data sheet for the range of acceptable low
voltage levels (typically a TTL logic low).
3.
V
CC
is an acceptable high voltage level. See the appropriate data sheet for the range of acceptable high
voltage levels (typically a TTL logic high).
Example 1-1. Sample Code Listing
BFSET
#$0007,X:PCC; Configure:
line 1
; MISO0, MOSI0, SCK0 for SPI master
line 2
; ~SS0 as PC3 for GPIO
line 3
Table 1-1. High True/Low True Signal Conventions
Signal/Symbol
Logic State
Signal State
Voltage
