4 stop mode, Stop mode – FUJITSU F2MCTM-16LX User Manual
Page 168
152
CHAPTER 8 LOW-POWER CONSUMPTION MODE
8.5.4
Stop Mode
Because this mode causes oscillation clock (HCLK) and subclock (SCLK) to stop during
operation in each clock mode, data can be retained by the lowest power consumption.
■
Stop Mode
When 1 is written to the STP bit of the low-power consumption mode control register (LPMCR) during
operation in the PLL clock mode (CKSCR: MCS=1, SCS=0), the mode transits to the stop mode according
to the settings of the MCS bit and SCS bit in the clock selection register (CKSCR).
Table 8.5-3 shows the settings of the MCS and SCS bits in the clock selection register (CKSCR) and the
stop modes.
Note:
If both the STP and SLP bits in the low-power consumption mode control register (LPMCR) are set to
"1" simultaneously, the STP bit is preferred and the mode transits to the stop mode.
●
Data retention function
In the stop mode, the contents of the dedicated registers, such as accumulators, and the internal RAM are
retained.
●
Operation during an interrupt request
Writing 1 in the STP bit of the low-power consumption mode control register (LPMCR) during an interrupt
request does not trigger a switch to the stop mode.
If the CPU is not ready to accept any interrupt request, the instruction next to currently executing
instruction is executed. If the CPU is ready to accept any interrupt request, an interrupt operation
immediately branches to the interrupt processing routine.
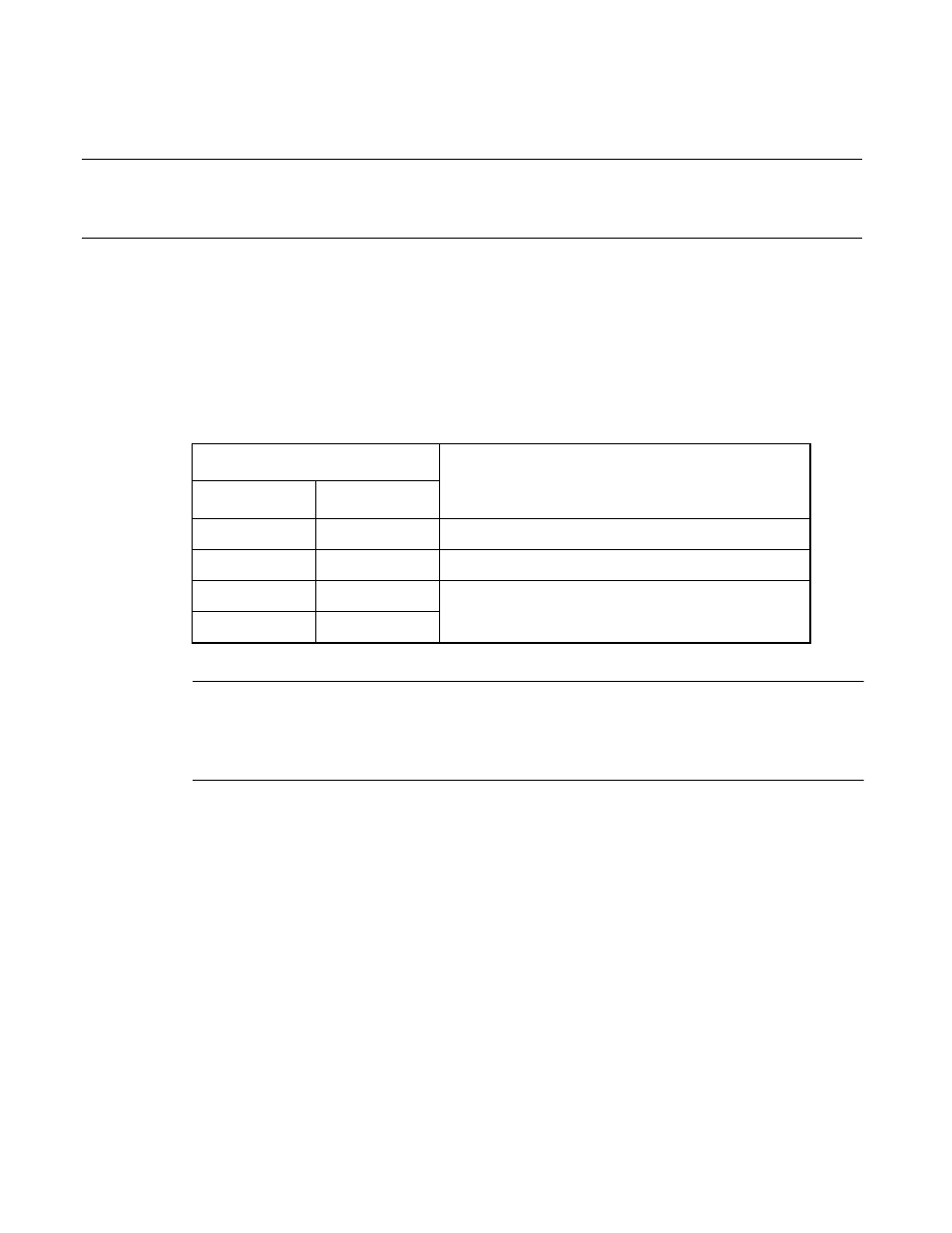
Table 8.5-3 Clock Selection Register (CKSCR) Settings and Stop Modes
Clock selection register (CKSCR)
Stop Mode to be Transited
MCS
SCS
1
1
Main stop mode
0
1
PLL stop mode
1
0
Sub-stop mode
0
0
