Path vectors – Grass Valley Kalypso User Manual V.15.0 User Manual
Page 118
118
Kalypso — User Manual
Section 2 — Concepts
The path concept can also be applied to functions that do not move a
picture across the screen, like matte hue changes. For these functions, the
rate of change of the parameter follows the same path types above. For
example, an S-Linear hue rotation will accelerate and decelerate the speed
of the hue change at the beginning and end of the keyframe.
Tension, Continuity, and Bias Controls
When the
CURVE
parameter is selected, additional fine-tuning path controls
become available:
TENSION
— Controls the length of the tension vector. At a setting of 0.0,
this imaginary line extends an equal distance into and out of the key-
frame, and the path through the middle keyframe is curved.
CONTINUITY
—
Determines the angle of the path into and out of the key-
frame.
BIAS
— Determines whether the path will be pulled towards the pre-
vious or the following keyframe.
In the following examples, a physical path is shown between three key-
frames. The first keyframe (KF1) is the upper left square; the last keyframe
(KF3) is the lower right square. The adjustments in these examples are
applied to the middle keyframe only (KF2).
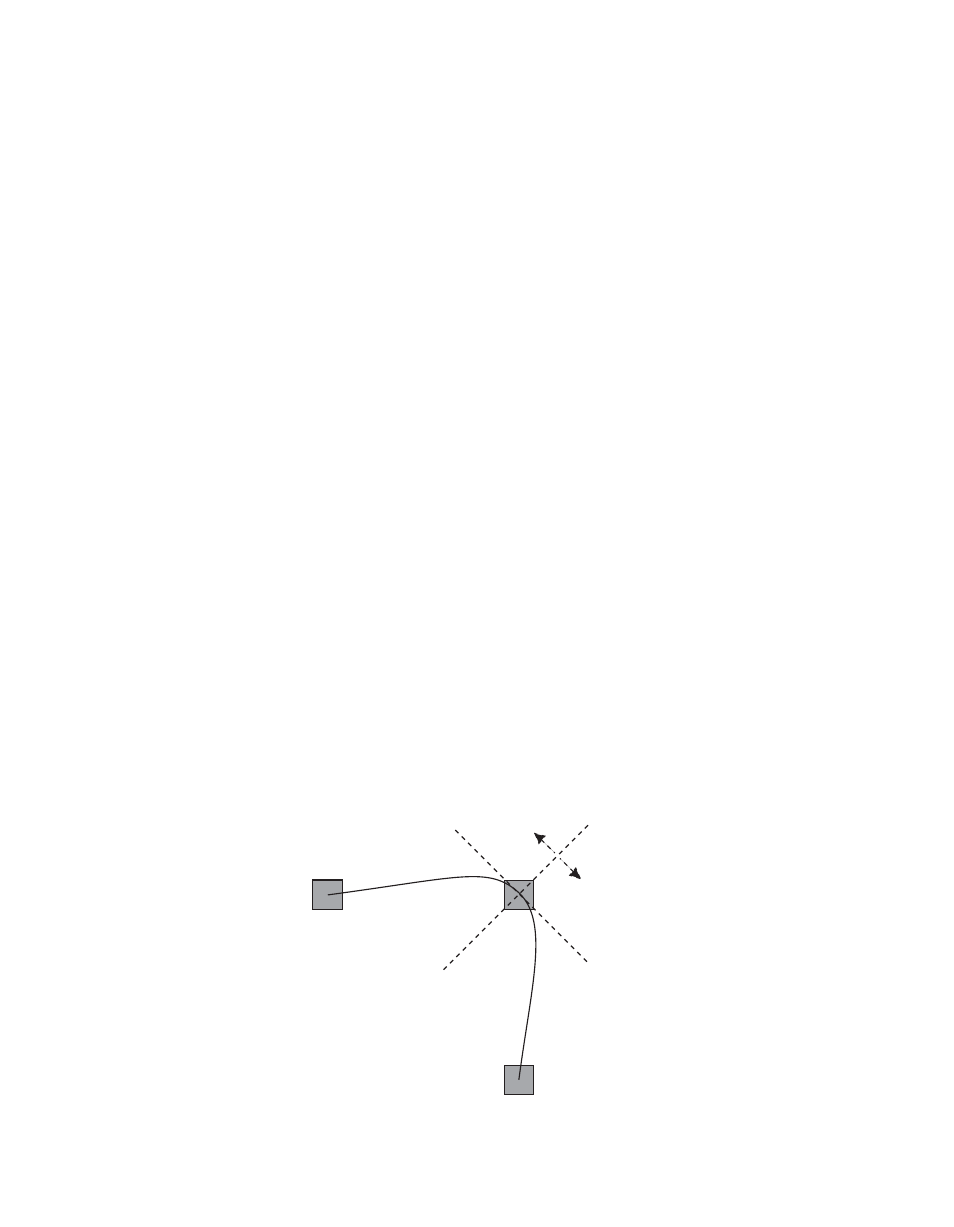
Path Vectors
With respect to the path between keyframes, each keyframe is made up of
three vector parameters as shown below. The soft knob controls act on these
vector parameters to adjust the path into (entry) and out of (exit) the key-
frame. The path through KF2 is parallel to an imaginary line drawn
between KF1 and KF3 (
Figure 98. Path Vectors
KF1
KF2
KF3
Tension
Vector
+
–
+
–
Bias
Vector
Continuity
Vector
0721_06_46_r1
- Kalypso User Manual V.12.0 Apr 10 2007 Kalypso Reference Manual V.11.0 Kalypso Reference Manual V.12.0 Mar 16 2006 Kalypso Reference Manual V.12.0 Apr 10 2007 Kalypso Classic Installation V.11.0 Kalypso Classic Installation V.12.0 Mar 13 2006 Kalypso Classic Installation V.12.0 Apr 10 2007 Kalypso User Manual V.11.0 Kalypso User Manual V.12.0 Mar 16 2006 Kalypso Reference Manual V.15.1 Kalypso User Manual V.15.1 HD/Duo Kalypso Installation V.15.0 HD/Duo Kalypso Installation V.11.0 HD/Duo Kalypso Installation V.15.1 Kalypso Reference Manual V.15.0 Video Switcher
