Section 38.1.2, Section 38.1.3 – Westermo RedFox Series User Manual
Page 884
Westermo OS Management Guide
Version 4.17.0-0
38.1.2
Hardware flow control using RTS/CTS
RS-232 serial ports can use the request to send (RTS) and clear to send (CTS) pins
to enforce flow control over the serial line. The DTE will assert the RTS to indicate
to the DCE that it has data to send, and the DCE will respond by asserting the
CTS when it is ready to receive data.
Similarly, the DCE asserts the CTS when it has data to send, and the DTE will
respond by asserting RTS to give the DCE permission to send. The extension to
allow the flow-control to work both ways is referred to as RTS/CTS handshaking
and was not included in the original RS-232 standard.
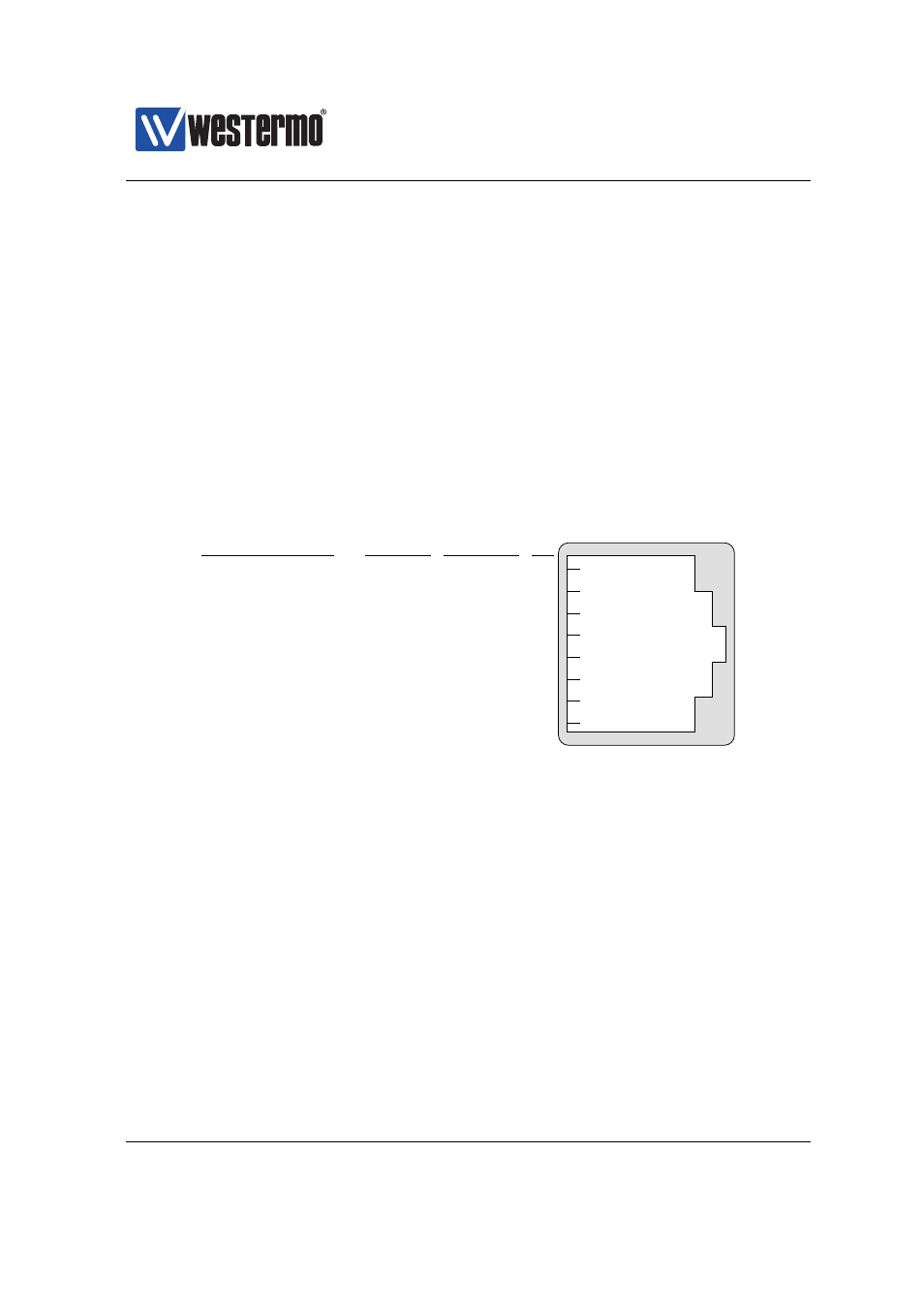
Serial ports on WeOS devices are typically RS-232 ports using RJ-45 sockets
(EIA/TIA-561) in DCE mode, as shown in
(for a definite description of
the serial port on your Westermo device, see the associated product User Guide).
In
Out
In
Out
In
Out
Out
8
6
3
2
1
4
5
7
RTS
TD
DTR
DCD
DSR
SG
RD
CTS
Data Carrier Detect
Data Terminal Ready
Signal Ground
Received Data
Transmitted Data
Clear To Send
Request To Send
Data Set Ready
Signal
Acronym Dir (DCE) Nb
Figure 38.1: Typical RS-232 serial port on WeOS devices – RJ-45 socket (EIA/TIA-
561) in DCE mode.
38.1.3
Software flow control using XON/XOFF
An alternative to hardware flow control is to use software flow control, which does
not require the presence of the RTS and CTS pins. With software flow control
(XON/XOFF) the receiver can stop the sender by transmitting a special character
(XOFF, ASCII 19) over the data line. Once the receiver is ready to receive more
data it transmits an XON character (ASCII 17).
884
➞ 2015 Westermo Teleindustri AB
